![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
81 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
anatomical position
|
-position of reference for all anatomical discussions
-standing straight -facing forward/looking forward -palms forward, arms near sides -feet together |
|
|
median plane
|
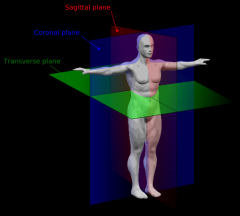
-plane that runs from from ventral-->dorsal, thus dissecting the body into right and left sides
-helps determine medial/lateral |
|
|
coronal plane
|
plane running from finger tip to finger tip that divides body into anterior and posterior sections (front and back)
|
|
|
sagittal planes
|
any plane parallel to medial plane
|
|
|
transverse plane
|
-aka horizontal or axial
-runs anterior to posterior and divides the body into superior and inferior sections (top/bottom) |
|
|
superior vs. inferior
|
-aka cranial vs. caudal
-higher (superior) or lower (inferior) |
|
|
anterior vs. posterior
|
-aka ventral vs. dorsal
-closer to front (anterior) or closer to back (posterior) |
|
|
medial vs. lateral
|
-medial=closer to midline
-lateral=father from midline |
|
|
proximal vs. distal
|
-proximal=closer to body/reference point
-distal=farther from body/reference point |
|
|
superficial vs. deep
|
-superficial=closer to surface
-deep=farther from surface |
|
|
ipsilateral
|
same side as structure
|
|
|
contralateral
|
opposite side as structure
|
|
|
basic bony landmarks (3)
|
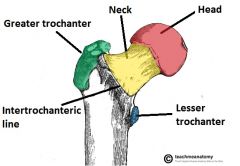
-head
-neck -shaft |
|
|
fovea
|
-L. pit
-indentation of bone |
|
|
trochanter
|
-G. runner
-greater and lesser trochanter near neck of femur |
|
|
fossa
|
-L. trench or ditch
-trochanteric fossa |
|
|
tubercule
|
-L. swelling
-quadrate tubercule -ischial tuberosity |
|
|
crest
|
-L. crista=ridge
-intertrochanteric crest |
|
|
foramen
|
-L. aperature
-obturator formane of hip bone |
|
|
condyle
|
-G. knuckle
-medial and lateral condyle on inferior end of femur |
|
|
sustentaculum tali
|
-healbone of foot
-L. to support |
|
|
caracoid process
|
-G. like a crow's beak
-L. projection/outgrowth -small hook on lateral edge of superior anterior portion of scapula |
|
|
pterygoid plate
|
-portion of bone at skull base
-pterygoid=wing -plate=flate, broad |
|
|
tissue
|
collection of similar cells and the intercellular substances surrounding them
|
|
|
types of skin
|
-thin hairy skin (most of body)
-glabrous skin (palms of hands, soles of feet) |
|
|
layers of skin
|
-epidermis=superficial
-dermis=deepest layer of skin |
|
|
superficial fascia qualities
|
-connective tissue
-contains veins, cutaneous nerves -aka fatty layer -irregular, loose arrangement of connective tissue |
|
|
deep fascia qualities
|
-forms tough barrier covering muscles
-dense, irregular arrangement of connective tissue -helps compartmentalize body |
|
|
types of cartilage
|
-hyaline
-fibrocartilage -elastic |
|
|
hyaline cartilage
|
-covers surfaces of most bones
-protection for bones rubbing against each other |
|
|
fibrocartilage
|
-tougher, subject to more wear and tear
-e.g. menisci of knee; head of mandible |
|
|
elastic cartilage
|
-flexible cartilage
-e.g. external ear |
|
|
compact bone
|
-aka cortical bone
-hard, white shell of bones |
|
|
spongy bone
|
-orange/yellow/reddish color of bones
-marrow of bones -red=blood-producing -yellow=fat-storing |
|
|
composition of bone matrix
|
-collagen-->resists tinsel (side) forces
-minerals (calcium, phosphate)--> resists compression forces |
|
|
flexion
|
movement that decreases the angle between two body parts
|
|
|
extension
|
movement that increases the angle between two body parts
|
|
|
abduction
|
movement away from the midline
|
|
|
adduction
|
movement towards the midline
|
|
|
medial rotation
|
rotating movement towards the midline
|
|
|
lateral rotation
|
rotating movement away from the midline
|
|
|
elevation vs. depression
|
-elevation=movement in a superior direction
-depression=movement in an inferior direction |
|
|
pronation
|
-moves palm of hand so that it is facing posteriorly
-forearms are pronated when typing on a keyboard |
|
|
supination
|
-moves palm of hand so it's facing anteriorly
-hands are supinated when holding a bowl of soup |
|
|
dorsiflexion vs. plantarflexion
|
-dorsi=extension at ankle so foot points superiorly
-plantar=flexion at ankle so foot point inferiorly |
|
|
opposition vs. reposition
|
-opposition=thumb and little finger together
-reposition=thumb and little finger apart |
|
|
Bony landmarks
|
-aka "bone markings"
-appear wherever tendons, ligaments and fascias are attached or where arteries lie next to/enter bones |
|
|
capitulum
|
-small, round articular head
-e.g. capitulum of humerus |
|
|
epicondyle
|
-eminence superior to a condyle
-e.g. lateral epicondyle of the humerus |
|
|
facet
|
-smooth, flat area covered with cartilage
-where bone articulates with another bone -e.g. superior costal facet on body of vertebra for articulation with rib |
|
|
groove
|
-elongated depression or furrow
-e.g. radial groove of the humerus |
|
|
line
|
-linear elevation
-e.g. soleal line of the tibia |
|
|
malleolus
|
-rounded process
-e.g. lateral malleolus of the fibula |
|
|
notch
|
-indentaion at the edge of a bone
-e.g. the greater sciatic notch |
|
|
protuberance
|
-projection of bone
-e.g. external occipital protuberance |
|
|
spine
|
-thorn-like process
-e.g. spine of the scapula |
|
|
spinous process
|
-projecting spine-like part
-e.g. spinous process of a vertebra |
|
|
trochlea
|
-spool-like articular process or process that acts as a pulley
-e.g. trochlea of humerus |
|
|
tuberosity
|
-large, rounded elevation
-e.g. ischial tuberosity |
|
|
Types of solid joints
|
-fibrous (interosseus)
-cartilaginous (growth plates, intevertebral discs) |
|
|
Fibrous joints
|
-transfers weight/forces between bones
-allow little to no movement -e.g. between bones of skull |
|
|
Cartilaginous joints
|
-synchondroses=growth plates, hyaline only, aka "primary cartilaginous joints"
-symphses=intevertebral discs, hyaline or fibrocartilage, aka "secondary cartilaginous joints" |
|
|
Synovial joints
|
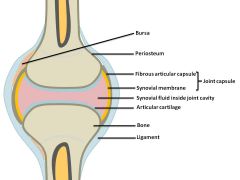
-allow for increased movement
-produce synovial fluid that acts as a lubricant |
|
|
Types of synovial joints
|
-plane
-hinge -saddle -condyloid -ball and socket -pivot |
|
|
Plane joint
|
-synovial joint
-sliding/gliding movement limited by tight joint capsules |
|
|
Hinge joint
|
-synovial joint
-flex/ext movement only -loose capsule in movement direction but tight lateral to movement -e.g. elbow joint |
|
|
Saddle joint
|
-synovial joint
-allows flex/ext, abduction/adduction, circumduction -articular surfaces look like a saddle -e.g. carpometacarpal joint (thumb base) |
|
|
Condyloid joint
|
-synovial joint
-allows same biaxial movement but movement in one plane is greater than the other -e.g. metacarpophalangeal (knuckles) |
|
|
Ball and Socket joint
|
-synovial joint
-movement in multiple planes/axes -flex/ext, abduct/adduct, circumduction, medial/lateral rotation -e.g. hip joint |
|
|
Pivot joint
|
-synovial joint
-rotation around a central axis -e.g. atlantoaxial joint: atlas (C1 vertebrae) rotates around axis (C2 vertebrae) |
|
|
diaphysis
|
-midsection of long bones
-"between growth" -primary center of ossification -ossification begins after a vascular invasion of necrotic cartilage |
|
|
ephiphysis
|
-rounded ends of long bones
-secondary ossification center |
|
|
traction epiphysis
|
-bony landmarks/growths cause by stress/force of muscle attachments and actions
-e.g. greater and lesser trochanter of the femur |
|
|
epiphyseal plate
|
-"growth plate"
-cartilage separations of the two centers of ossification (diaphysis and epiphysis) -present in pubescent or pre-pubescent bones |
|
|
epiphyseal line
|
-seam formed by fusion of diaphysis and epiphysis
-present in adult bones |
|
|
Types of muscle
|
-skeletal
-cardiac -smooth |
|
|
Skeletal Muscle Qualities
|
-found in skeletal muscles
-striated -strong, quick, discontinuous contraction -voluntary -multi-nucleated w/nuclei near fiber edges |
|
|
Cardiac muscle qualities
|
-found only in the heart
-striated -strong, quick, continuous contraction -involuntary -multi-nucleated w/nuclei within fibers |
|
|
Smooth muscle qualities
|
-found in vessels, organs, glands
-spindle-shaped -longer, slower contractions -involuntary |
|
|
Functions of skeletal muscles
|
-movement/move joints
-support/stabilize joints -body heat generation |
|
|
Skeletal Muscle Nomenclature
|
-Attachments (flexor carpi ulnaria)
-Function (extensor digitorum) -Shape (deltoid) -Location (biceps brachii) -Appearance (lumbrical) |

