![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Central Nervous System vs. Peripheral Nervous System
|
-CNS=brain+spinal cord
-PNS: roots, spinal nerves, rami, peripheral nerves, ganglia |
|
|
Sensory vs. Motor information
|
-sensory: afferent info, periphery receptors --> CNS
-motor: efferent info, CNS --> skeletal, cardiac, smooth muscle |
|
|
Somatic vs. Visceral
|
-somatic=body surface or muscoloskeletal
-visceral=organs, glands, organs w/smooth or cardiac muscle |
|
|
Structure, Fxn, location of Lower Motor Neurons
|
-final common pathway from CNS-->skeletal muscle
-cell bodies located in spinal cord (ventral horn) -axons extend out to PNS and eventually signal muscles |
|
|
Structure, fxn, location of Primary Sensory Neurons
|
-convey sensory info from periphery to CNS
-part of the axon is located at receptor on periphery -cell body is in PNS -axon continues into white matter of spinal cord (ends in dorsal horn of grey matter) |
|
|
Fxn/location of astrocytes
|
-CNS
-helps maintain blood-brain barrier |
|
|
Fxn/location of oligodendrocyctes
|
-CNS
-myelin forming cells |
|
|
Fxn/location of microglia
|
-CNS
-scavenger cells |
|
|
Fxn/location of Schwann cells
|
-PNS myelin-forming cells
-myelin surrounds membranes of most axons -allows for increased speed in action potential propagation without increasing diameter of axon |
|
|
What layers surround the spinal cord and what are they collectively called?
|
-meninges:
-pia mater -arachnoid mater/subarachnoid space -dura mater |
|
|
Fxns/location of the spinal cord?
|
-vertebral canal
-motor innervation of neck, trunk, extremities -process/relay sensory info from neck, trunk, extremities to brain -integrate sensory and motor fxns of basic reflexes |
|
|
What are the two main regions of the cross section of the spinal cord?
|
-grey matter (cell bodies)
-white matter (axons) |
|
|
What are the different regions of white/gray matter in a cross section of the spinal cord?
|
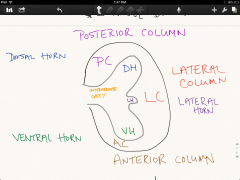
-White matter: posterior column, anterior column, lateral column
-grey matter: dorsal horn, lateral horn, ventral horn, intermediate grey |
|
|
What does it mean that the spinal cord/spinal nerves are segmentally organized?
|
-spinal cord can be divided into segments just like the vertebrae
-each segment is has its respective spinal nerves that innervate a specific section of the body -C1-C8 -T1-T12 -L1-L5 -S1-S5 -Coccygeal nerve |
|
|
What is the relationship between spinal segments and vertebrae?
|
-except in the cervical spine, the spinal segments are superior to the intevertebral foramen through which their spinal nerve passes
-b/c in early development, the spinal cord and vertebral grow at the same rate, but later the vertebral column grows faster, thus shifting the spinal cord in a relatively rostral direction -most of the vertebral growth occurs in the thoracic/lumbar region, thus leaving the cervical spine relatively even |
|
|
What are the main components of spinal nerves and their functions?
|
-dorsal root (axons of sensory neurons)
-dorsal root ganglion (cell body of sensory nerves; gathers ventral root within as well) -ventral root (axons of lower motor neurons) -spinal nerve (region where dorsal and ventral root neurons meet and cross) -ventral ramus (sensory and motor neurons responsible for ventral side) -dorsal ramus (sensory and motor neurons responsible for dorsal side) |
|
|
What is a dermatome? What dermatomes serve as reference locations?
|
-an area of skin innervated by the branches of a single spinal nerve
-T4=nipple line -T10=umbilicus |
|
|
What is a sensory cutaneous field?
|
-area of skin supplied by a specific cutaneous nerve
-crosses dermatomes |
|
|
What is a myotome?
|
-all the muscles innervated by a single spinal nerve
|
|
|
Why does herpres zoster have a dermatomal distribution?
|
-varicella virus (chicken pox) inserts DNA into neurons and remains dormant for a period of time
-later in life, often in times of stress, virus becomes reactivated and infects a spefic nerve and introducing lesions across the entire dermatome |
|
|
Somatic motor system vs. Visceral motor System
|
-somatic motor=skeletal muscles
-autonomic (visceral) motor=smooth or cardiac muscle |
|
|
Somatic sensory system vs. Visceral sensory system
|
-somatic sensations=well localized
-visceral sensations=poorly localized |
|
|
What/where is the pia mater?
|
-meningeal layer
-thin layer stuck directly to spinal cord |
|
|
What/where is the arachnoid mater/subarachnoid space and what does it contain?
|
-arachnoid mater=meningeal layer stuck to the dura mater
-subarachnoid space is maintained by tribechulae and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid |
|
|
What/where is the dura mater?
|
-outermost layer of the meninges
-toughest layer; attached to arachnoid mater |
|
|
What/where is the epidural space?
|
-between the dura mater and the vertebra
-contains fat & veins |
|
|
What are the main components of peripheral nerves and their functions?
|
-epineurium: surrounds the fascicles of a nerve; continuous with the dura mater
-perineurium: surrounds the axons of a fascicle; continuous with the arachnoid mater -fascicles: groups of budled myelinated and unmyelinated axons -fxn of the connective tissues is to provide tinsel strength to axons that are thin and would otherwise tear easily |
|
|
Where does the spinal cord end on the vertebral column, what is this point and inferior section of nerves called?
|
-L1/L2
-caudus midularis -cauda equinus |

