![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is Anatomy? |
Study of the body structure |
|
|
What is Physiology? |
Study of how the body functions |
|
|
What is Pathology? |
Study of the causes and effects of diseases |
|
|
What is the anatomical Position? |
-Body erect -Arms at sides with palms forward -it is the position of reference for anatomical nomenclature -feet shoulder width apart -eyes facing forward -feet on floor |
|
|
Where is the anterior? |
Front |
|
|
Where is everything measured towards? |
Midline of the body |
|
|
Where is the posterior? |
In the back |
|
|
Where is the ventral? |
On front of your body |
|
|
Where is the dorsal? |
On the back of your body |
|
|
What is superior? |
Above the transversal plane |
|
|
What is inferior? |
Below transversal plane |
|
|
What is mesial? |
Towards the midline |
|
|
What is distal? |
Away from the midline? |
|
|
What is lateral? |
Away from the midline if the body |
|
|
What is medial? |
Towards the midline of the body |
|
|
What is proximal? |
Refers to the part of body closest to the point of attachment |
|
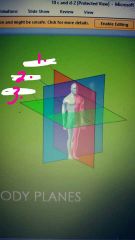
1. 2. 3. |
1. Sagittal plane 2. Coronal plane 3. Transverse plane |
|
|
What is the sagittal plane? |
-Divides body into left and right halves -Mid sagittal plane is 2 equal halves |
|
|
What is the Coronal plane? |
-Divides body into the front and back -also called frontal plane |
|
|
What is the transverse plane? |
-Divides body into upper and lower sections -also called horizontal plane |
|
|
What is the Dorsal body cavity? |
Posterior portion of the body (spinal canal and cranial cavity) |
|
|
What does the cranial cavity contain? |
Contains the brain |
|
|
What is the ventral body cavity? |
Anterior portion of the body (thoracic cavity, abdominal cavity, and pelvic cavity) |
|
|
What does the Thoracic Cavity contain? |
Chest cavity, lungs, heart, and all accessory parts needed for their functioning |
|
|
What does the abdominal cavity contain? |
Most of the digestive tract and all organs needed for the process needed for digestion |
|
|
What does the pelvic cavity contain? |
Urinary bladder, rectum, and reproductive system |
|
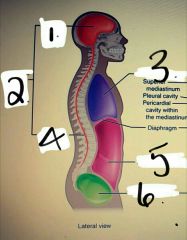
|
1. Cranial cavity 2. Dorsal body cavity 3. Thoracic cavity 4. Vertebral cavity 5. Abdominal cavity 6. Pelvic cavity |
|
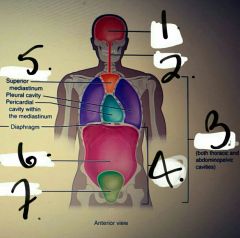
|
1. Cranial cavity 2. Vertebral cavity 3. Ventral body cavity 4. Abdominal pelvic cavity 5. Cranial cavity 6. Dorsal body cavity 7. Vertebral cavity |
|
|
What is the Axial Region? |
Bones of the cranium, face, spinal column, ribs, and sternum |
|
|
What is the Appendicular Region? |
Bones from the upper and lower extremities (arms, hands, legs, feet, shoulders, and hips) |
|
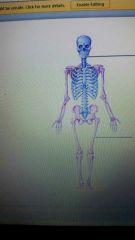
What are the 2 lines pointing to? |
Axial skeleton (in blue) Appendicular skeleton (pink) |
|
|
What are the two main body cavities? |
-Dorsal cavity -Ventral Cavity |
|
|
What makes up the Ventral Cavity? |
Thoracic cavity, abdominal cavity, and pelvic cavity |
|
|
Which cavity contains the brain? |
Cranial cavity |
|
|
Which region contains the upper and lower extremities? |
Appendicular Region |
|
|
What bones are in the Axial Region? |
Cranium, face, ribs, spinal column, sternum |
|
|
What are the 4 main groups of tissue in the human body? |
-Epithelial -Connective -Nervous -Muscle |
|
|
What is the function on of the Epithelial tissue? |
Protection, secretion, absorption, and filtration |
|
|
What is the function of connective tissue? |
Support and protection |
|
|
What is the function of nervous tissue? |
Sensing stimuli and transmitting signals to and from different parts of an organism |
|
|
What does the skeletal do? |
Functions in pairs to bring about the coordinated movements of limbs, trunk, jaw, etc. |
|
|
What's another name for skeletal? |
Striated |
|
|
What does smooth do? |
Controls slow involuntary movements |
|
|
What does cardiac do? |
Most important role, contraction of the atria and ventricles of the heart |
|
|
Where is the Epithelial tissue? |
Covers the body surface and forms the lining for most internal cavities |
|
|
What is connective tissue found? |
-Ordinary loose connective tissue -fat tissue -dense fibrous tissue -cartilage -bone -blood and lymph -skeletal, smooth, and cardiac |
|
|
Where is nerve tissue found? |
-Lines the body surface or divide organs into parts -Also found in brain, spinal cords and nerves |

