![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
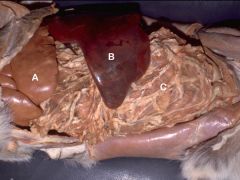
|
A) Liver-Left Lateral Lobe
B)Spleen C)Greater Omentum |
|
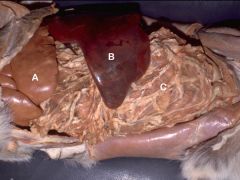
|
A) Liver-Left Lateral Lobe
B)Spleen C)Greater Omentum |
|
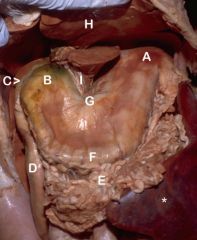
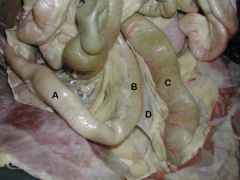
#What is the area between A&B Called?
|
#Body of the Stomach
A) Fundus B) Pylorus C) Cranial Flexure-Duodenum D) Descending Duodenum E) Greater Omentum (tucked) F) Greater Curvature of the Stomach G) Lesser Curvature of the Stomach H) Liver-Left Lateral Lobe I) Lesser Omentum *Spleen |
|
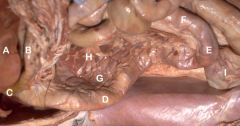
*Which branch of the Aorta is encircled by the root of the mesentery?
**What is the name of the mesentary in which the pancreas lies in (suspends Duodenum from body wall)? |
*Cranial mesenteric a.
**Mesoduodenum A) Liver B) Stomach C) Duodenum-Cranial Flexure D) Descending Duodenum E) Caudal Flexure F) Ascending Duodenum G) Pancreas H) Body Wall I) Urinary Bladder |
|
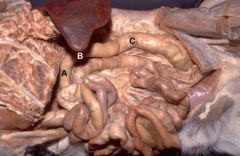
Caudal View of Abdomen
|
A) Descending Duodenum
B) Ascending Duodenum C) Descending Colon D) Duodenocolic Fold |
|
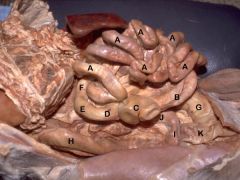
*Attachment between B&C?
** What is the mesenteric ligament between the ascending duodenum and the descending colon? |
*Ileocecal Fold
**Duodenocolic Ligament A) Jejunum B) Ileum C) Cecum D) Ascending Colon E) Right Colic Flexure F) Transverse Colon G) Descending Colon H) Descending Duodenum I) Caudal Duodenal Flexure J) Ascending Duodenum K) Urinary Bladder |
|
*As Descending Colon Enters Pelvic Cavity, what does it's name change to?
|
*Rectum
A) Transverse Colon B) Left Colic Flexure C) Descending Colon |
|
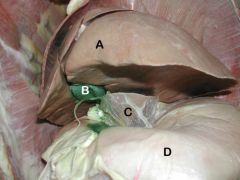
Left Side, Ventrolateral View
|
A) Liver - Left Lateral Lobe
B) Gall Bladder C) Lesser Omentum D) Stomach |
|
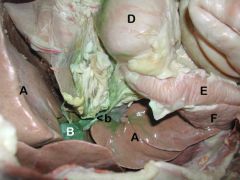
Lateral View, Right Side
|
A) Liver
B) Gall Bladder <b) Bile Duct D) Stomach E) Descending Duodenum F) Pancreas |
|
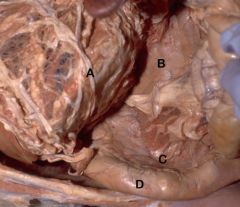
|
A) Stomach & Greater Omentum (reflected)
B) Pancreas - Left Lobe C) Pancreas - Right Lobe D) Descending Duodenum |
|
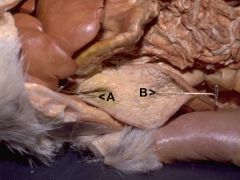
*What organ has been opened?
**What duct(s) empty upon A? ***What duct(s) empty upon B? |
*Descending Duodenum
**Pancreatic Duct & Common Bile Duct ***Accessory Pancreatic Duct A) Major Duodenal Papilla B) Minor Duodenal Papilla |
|

Right Side, Duodenum Reflected Medially
*Name of space between Caudal Vena Cava & Portal v.? |
*Epiploic Foramen
A) Liver- Caudate Process of Caudate Lobe B) Pancreas-Left Lobe C) Right Kidney D) Caudal Vena Cava E) Portal v. |
|
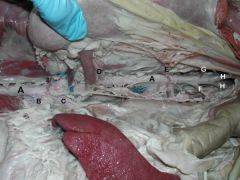
*Which organs does B Supply blood to?
**What organs are supplied by C? |
*Liver, Spleen, Stomach, Pancreas, Proximal Duodenum
**lies within the root of the mesentary and sends branches to supply the small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum) and large intestine (cecum, ascending colon, transverse colon, proximal descending colon). A) Aorta B) Celiac a. (1st unpaired branch in abdomen) C) Cranial mesenteric a.(2nd Unpaired vessel) D) Renal a. E) Testicular/Ovarian a. F) Caudal mesenteric a. (unpaired) G) Deep circumflex iliac a. H) External iliac aa. |
|
|
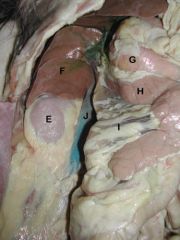
E) Right Kidney
F) Caudate Process of Caudate Lobe of Liver G) Descending Duodenum H) Body of Pancreas I) Mesoduodenum J) Caudal Vena Cava |
|
|
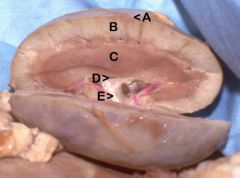
A) Capsule
B) Cortex C) Medulla D) Renal Pelvis E) Ureter |
|
|
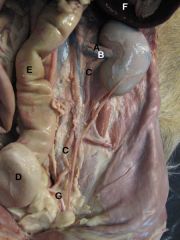
A) Renal a.
B) Renal v. C) Ureter (in Genital Fold/Broad Lig. in Female) D) Urinary Bladder E) Descending Colon F) Spleen G) Ductus Deferens |
|
|
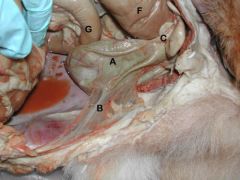
A) Urinary Bladder
B) Median Lig. of Bladder C) Lateral Ligs. of Bladder D) Ureters E) Ductus Deferens F) Descending Colon G) Caudal Duodenal Flexure |
|
|
A) Urinary Bladder
B) Median Lig. of Bladder C) Lateral Ligs. of Bladder D) Ureters E) Ductus Deferens F) Descending Colon |
|

|
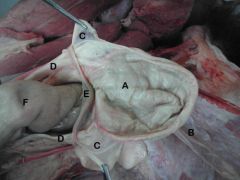
A) Testis
B1) Head B2) Body B3) Tail of Epididymis C) Proper Lig. of Testis D) Ductus Deferens E) Pampiniform Plexus F) Spermatic Cord H) Mesorchium |
|
|
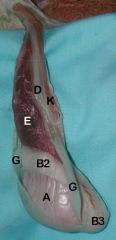
A) Testis
B2) Body B3) Tail of Epididymis D) Ductus Deferens E) Pampiniform Plexus G) Parietal Vaginal Tunic K) Cremaster m. |
|
|
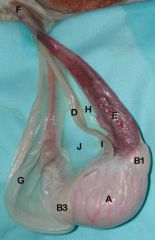
A) Testis
B1) Head B3) Tail of Epididymis D) Ductus Deferens E) Pampiniform Plexus F) Spermatic Cord G) Parietal Vaginal Tunic H) Mesorchium I) Mesoductus Deferens K) Cremaster m. |
|
|
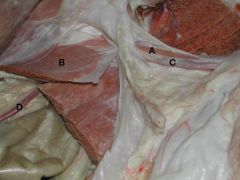
A) Cremaster m.
B) Internal Abdominal Oblique C) Spermatic Cord D) Testicular a./v. |
|
|
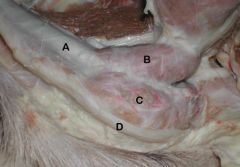
A) Penis
B) Ischiocavernosus m. (arises from the ischium and surrounds the crus and corpus cavernosum) C) Bulbospongiosus m. (surrounds the bulbs of the penis and corpus spongiosum) D) Retractor Penis m. |
|
|
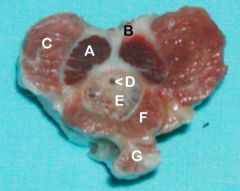
A. Left Crus of the Penis (joining to become the corpus cavernosum (right))
B. Tunica albuginea C. Ischiocavernosus D. Urethra E. Corpus spongiosum F. Bulbospongiosus m. G. Retractor penis m. |
|
|
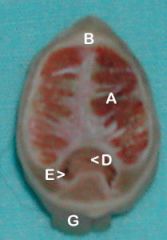
A. Left Crus of the Penis (joining to become the corpus cavernosum (right))
B. Tunica albuginea D. Urethra E. Corpus spongiosum G. Retractor penis m. |
|
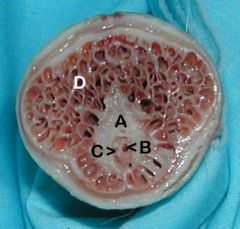
Cross-section at level of Glans Penis
|
A. Os penis
B. Urethra C. Corpus spongiosum (notice how it is continuous with bulbus glandis) D. Bulbus glandis |
|
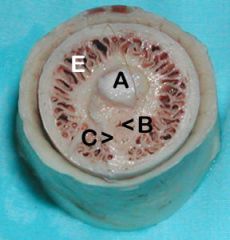
|
A. Os penis
B. Urethra C. Corpus spongiosum (notice how it is continuous with bulbus glandis) E. Pars longa glandis |
|
|
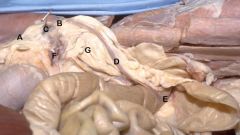
A. Suspensory Lig.of Ovary
(is the cranial free edge of the broad ligament) B. Proper Lig. of the Ovary (the caudal extension of A, which attaches the ovary to the cranial end of the uterine horn..The proper ligament of the ovary is continuous with the round ligament of the uterus) The pin is located within the ovarian bursa C. Ovary The uterine tube will primarily be on the lateral aspect of the ovary (ie, other side) D. Uterine horn E. Uterine body F. Ovarian a. (ruputured) G. Mesometrium |
|
|
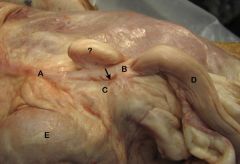
A. Suspensory Lig.of Ovary
B. Proper Lig.of the Ovary (attaches the ovary to the cranial end of the uterine horn) C. Ovary D. Uterine Horn The arrow shows the entrance of the ovarian bursa ?. Clump of fat within the Mesosalpinx. E. Kidney |
|
|
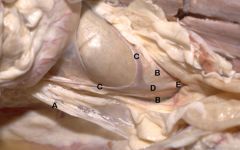
A. Round Lig. of Uterus
B. Mesometrium C. Uterine horns D. Uterine body E. Cervix |
|
|
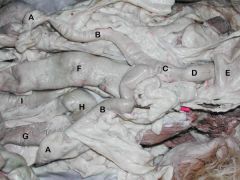
A. Ovaries
B. Uterine horns C. Body of the Uterus D. Cervix E. Urinary bladder F. Descending colon G. Descending duodenum H. Caudal duodenal flexure I. Ascending duodenum |
|
|
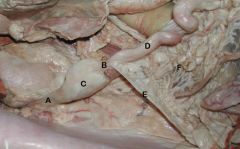
A. Suspensory Lig. of Ovary
B. Proper Lig.of Ovary C. Ovary D. Right uterine horn E. Round Lig. of Uterus (Comes off the lateral aspect of the broad ligament) F. Broad Lig. (extending from the caudal edge of the proper ligament of the ovary to the vaginal process in the body wall) |
|
|
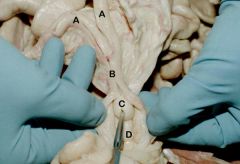
A. Uterine Horns
B. Uterine body C. Cervix D. Vagina |
|
|
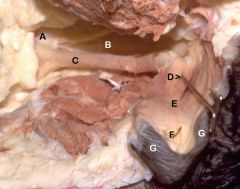
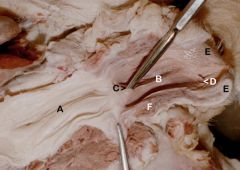
A. Cervix
B. Vagina C. Urethra D. Urethral tubercle The pin is within the external urethral orifice; At this point, the reproductive tract becomes the E. Vestibule F. Clitoris (Contains cavernous tissue) G. Labia |
|
|
A. Vagina
B. Vestibule C. Urethral tubercle The probe is entering the external urethral orifice D. Clitoris E. Labia F. Vestibular Bulbs (cavernous tissue) |
|
|
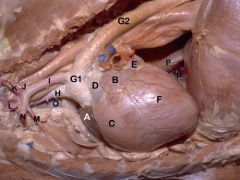
A. Right auricle
B. Left auricle C. Right ventricle D. Pulmonary trunk (gives rise to the two pulmonary aa.) E. Left atrium F. Left ventricle G1. Aortic arch G2 Descending aorta H. Brachiocephalic trunk (gives rise to the carotid a. and right subclavian a.) I. Left subclavian a. J. Vertebral a. K. Costocervical trunk L. Superficial cervical a. M. Internal thoracic a. N. Axillary a. O. Cranial vena cava P. Caudal vena cava p. Plica vena cava |
|
|
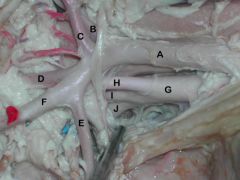
A. Left subclavian a.
B. Vertebral a. C. Costocervical trunk D. Superficial cervical a. E. Internal thoracic a. F. Axillary a. G. Brachiocephalic trunk H. Left common carotid a. I. Right common carotid a. J. Right subclavian a. |
|
|
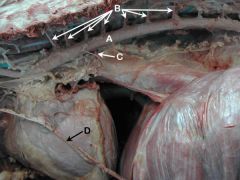
A. Aorta
B. Intercostal aa. (The costocervical trunk gives off intercostal aa. to the first three intercostal spaces, and the aorta supplies the rest of them) C. Bronchoesophageal a. D. Phrenic n. |
|

|
A. Aorta
B. Celiac a. C. Cranial mesenteric a. D. Renal a. E. Testicular/Ovarian a. F. Caudal mesenteric a. G. Deep circumflex iliac a. H. External iliac aa. |
|
|
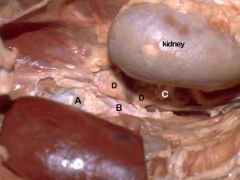
A. Celiac a.
B. Cranial mesenteric a. C. Phrenico-abdominal a./v. D. Adrenal Gland |
|
|
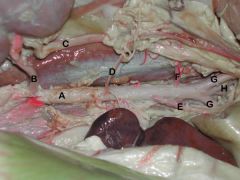
A. Aorta
B. Renal a. C. Ureter D. Testicular or ovarian a. E. Caudal mesenteric a. F. Deep circumflex iliac a. G. External iliac aa. H. Internal iliac aa. |
|
|
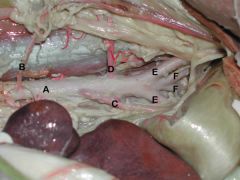
A. Aorta
B. Testicular a. C. Caudal mesenteric a. D. Deep circumflex iliac a. E. External iliac aa. F. Internal iliac aa. (The last unpaired artery to come off the aorta is the Median Sacral a. (not seen), which dives deep dorsally as it comes off the aorta to supply the tail) |
|
|
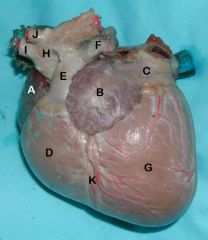
A. Right auricle
B. Left auricle C. Left atrium D. Right ventricle E. Pulmonary trunk F. Pulmonary a. G. Left ventricle H. Aorta (aortic arch) I. Brachiocephalic trunk J. Left subclavian a. K. Interventricular groove |
|
|
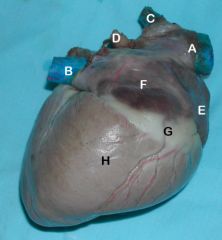
A. Cranial vena cava
B. Caudal vena cava C. Azygous v. D. Pulmonary v. (coursing to empty into the left atrium) E. Right auricle F. Right atrium G. Coronary groove containing fat and Right coronary a. H. Right ventricle |
|
|
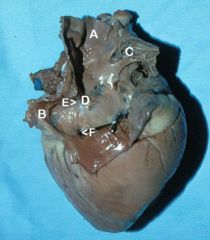
A. Cranial vena cava
B. Caudal vena cava C. Pectinate mm. of the auricle D. Intravenous tubercle E. Fossa ovale F. Coronary sinus |
|
|
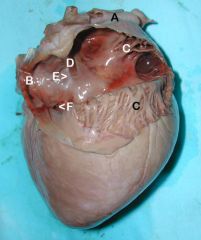
A. Cranial vena cava
B. Caudal vena cava C. Pectinate mm. of the auricle D. Intravenous tubercle E. Fossa ovale F. Coronary sinus |
|

|
A. Right atrioventricular valve B. Chordae tendonae
C. Papillary muscles D. Trabeculae carnae E. Trabeculae septomarginalis (Purkinje Fibers) |
|
|
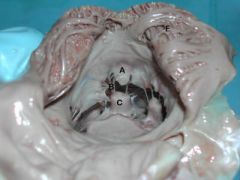
A. Right atrioventricular valve B. Chordae tendonae
C. Papillary muscles |
|
|
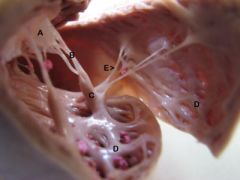
A. Right atrioventricular valve
B. Chordae tendonae C. Papillary muscles D. Trabeculae carnae E. Trabeculae septomarginalis (Purkinje Fibers) |
|
|
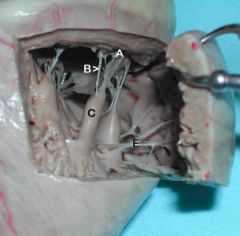
A. Right atrioventricular valve
B. Chordae tendonae C. Papillary muscles E. Trabeculae septomarginalis (Purkinje Fibers) |
|

|
A. Right atrioventricular valve
B. Chordae tendonae C. Papillary muscles E. Trabeculae septomarginalis (Purkinje Fibers) |
|
|
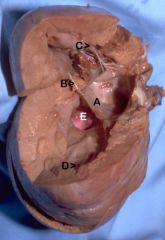
A. Left atrioventricular valve
B. Cordae tendonae C. Papillary muscle D. Trabeculae carnae E. Aortic valve |
|
|
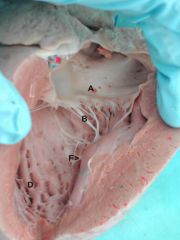
A. Left atrioventricular valve
B. Cordae tendonae D. Trabeculae carnae F. Trabeculae septomarginalis (Purkinje Fibers) |
|
|
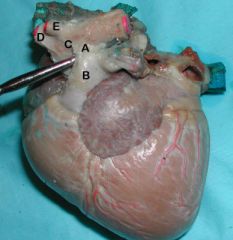
A. Ligamentum Arteriosum (remnant of fetal ductus arteriosus)
B. Pulmonary a. C. Aorta D. Brachiocephalic trunk E. Left subclavian a. |
|
|
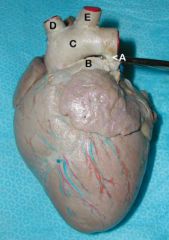
A. Ligamentum Arteriosum (remnant of fetal ductus arteriosus)
B. Pulmonary a. C. Aorta D. Brachiocephalic trunk E. Left subclavian a. |
|

|
A. Ligamentum Arteriosum (remnant of fetal ductus arteriosus)
B. Pulmonary a. C. Aorta D. Brachiocephalic trunk E. Left subclavian a. |
|

|
Femoral n.
|
|
|
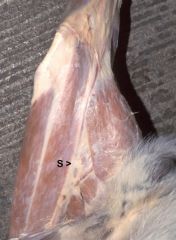
Saphenous n.
|
|
|
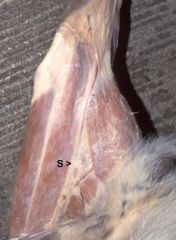
Saphenous n.
|
|
|
Common Peroneal n.
|
|

|
Tibial n.
|
|
|
A. Femoral a.
B. Femoral v. C. Saphenous a. & Medial Saphenous v. |
|
|
Cranial Tibial a.
|
|
|
Rostrolateral view of the pons and cerebellum.
|
The green pick is in the middle cerebellar peduncle, which is formed by transverse pontine fibers (asterisk), which are axons of contralateral pontine nuclei. The trigeminal nerve (V) exits the brainstem by passing through the middle peduncle. The arrow points to the primary fissure that divides the cerebellum into rostral and caudal lobes.
|
|
|
Transverse section through the
|
cerebellum and medulla oblongata of a dog.From medial to lateral, cerebellar nuclei are: fastigial (F), interpositus (I), and dentate (D). Fibers of the caudal cerebellar peduncle (red arrow) are evident before they turn dorsally into the cerebellum. (The term "restiform body" is a synonym for caudal cerebellar peduncle.).
|

