![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
191 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Which of the following is not one of the three major components of a typical eukaryotic cell?
a. plasma membrane b. ribosome c. cytoplasm d. nucleus |
B. Ribosome
|
|
|
|
Which of the following acts as the digestive system of the cell, breaking down material?
a. endoplasmic reticulum b. ribosome c. nucleus d. lysosome |
D. Lysosome
|
|
|
|
Where in a typical eukaryotic cell would you expect to find genes?
a. In the nucleolus within the nucleus b. In the chromatin c. In chromosomes within the cytosol d. In the DNA within the cells nucleus |
D. In the DNA within the cells nucleus
|
|
|
|
Which of the following statements about cells is false?
|
A. cells are the most basic unit of life
B. Although human cells are diverse in size, shape, and function, they have essentially the same organelles and general structure. C. cells join together to form organelles which then form our organs and organ systems. D. The cells in our bodies collectively carry out all of the functions necessary for us to stay alive |
C. cells join together to form organelles which then form our organs and organ systems
|
|
|
The plasma membrane is made primarily of.........?
|
phospholipids
|
|
|
|
What is the main component of cell membrane?
|
phospholipids
|
|
|
|
Which of the following is a characteristic of the cell membrane?
a. not permeable b. semipermeable c. fully permeable d. impermeable |
b. semipermeable
|
|
|
|
Which of the following is not a major function of protein on the cell membrane?
a. forming channels b. acting as receptor c. anchoring cells to other structure d. forming the entire glycocalyx |
D. forming the entire glycocalyx
|
|
|
|
What part of a cell membrane is usually in contact with interstitial fluid?
|
phosphate heads of phospholipids
|
|
|
|
Some types of cells move freely through the body, while others are bound into tightly knit communities.
|
true
|
|
|
|
What organelle is responsible for synthesizing proteins?
|
ribosome
|
|
|
|
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of peroxisomes?
|
They contain powerful enzymes called acid hydrolases
|
|
|
|
What is a characteristic of cilia?
|
They are whiplike, motile cellular extensions that occur in large numbers on the exposed surface of certain cells.
|
|
|
|
Lysosome perform digestive functions within a cell
|
true
|
|
|
|
The nucleolus
|
Is the site of ribosome assembly in a cell
|
|
|
|
osmosis
|
water movement across the membrane
|
|
|
|
Which nucleic acid molecules are involved in the synthesis of a particular polypeptide
|
DNA
|
|
|
|
phagocytosis
|
endocytosis of large items, such as bacteria or cellular debris
|
|
|
|
ribosome
|
site of protein synthesis
|
|
|
|
What is a fluid mosaic model of the plasma membrane?
|
a lipid bilayer with protein molecules dispersed within it
|
|
|
|
glycolipid
|
a plasma - membrane lipid possessing a sugar chain that functions in cell recognition
|
|
|
|
a cell will likely swell and likely burst if it is placed in a.............. solution.
|
hypotonic
|
|
|
|
The mRNA start codon, AUG, matches up with a tRNA anticodon, .............
|
UAC
|
|
|
|
by what method does the following move into the cell: movement of large particles, bacteria, or cellular debris by endocytotic vesicle?
|
phagocytosis
|
|
|
|
rough endoplasmic reticulum
|
produces protein transport vesicles
|
|
|
|
golgi apparatus
|
possesses a cis and tran side; composed of cisternae
|
|
|
|
mitochondrion
|
cristae; matrix
|
|
|
|
cells of the body mainly use..........for the selective endocytosis of most macromolecules.
|
receptor - mediated endocytosis
|
|
|
|
cells may be said to be "sugar coated" due to the presence of?
|
glycocalyx
|
|
|
|
centrioles
|
composed of microtubules arranged in nine groups of three
|
|
|
|
ribosome
|
protein synthesis
|
|
|
|
strands of DNA and associated histones in the nucleus of a nondividing cell
|
chromatin
|
|
|
|
intermediate filaments
|
These cytoskeleton members are tough, insoluble protein fibers that possess a high tensile strength.
|
|
|
|
microtubules
|
These members of the cytoskeleton are composed of spherical protein subunits that can quickly assembled and disassembled by the cell.
|
|
|
|
histones
|
spherical protein molecules around which DNA wraps.
|
|
|
|
microfilaments
|
The thinnest members of the cytoskeleton are composed of strands of actin protein.
|
|
|
|
nucleoplasm
|
jelly like fluid found within the nucleus of a cell.
|
|
|
|
nuclear envelope or nuclear membrane
|
membrane that surrounds the nucleus of a cell.
|
|
|
|
nucleus
|
control center of the cell.
|
|
|
|
chromosomes
|
dark - staining, rod - shaped structures composed of highly coiled chromatin, found in cells undergoing cell division.
|
|
|
|
nucleolus
|
dark - staining body found in the nucleus of a cell that functions in producing ribosomes.
|
|
|
|
nuclear pore
|
tiny passageway that allows large molecules to freely pass in and out of the nucleus.
|
|
|
|
The primary site of cellular production in most cells is the??
|
mitochondrion
|
|
|
|
What is the correct sequence of mitosis?
|
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
|
|
|
|
phospholipids
|
The most abundant molecule found within the lipid bilayer of the plasma membrane.
|
|
|
|
cilia
|
propel substances across cell surfaces
|
|
|
|
extended chromatin
|
fine, uncoiled strands of DNA in the nucleus of a non - dividing cell.
|
|
|
|
nucleolus function is
|
RNA synthesis
|
|
|
|
ribosomes are found
|
In the cytosol and on the rough endoplasmic reticulum
|
|
|
|
osmosis
|
type of transport mechanism involving the movement of water.
|
|
|
|
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
|
lipid synthesis
|
|
|
|
All of the following are considered "footloose" except.
A. phagocytosis B. blood cells C. sperm cells D. epithelial cells |
D. epithelial cells
|
|
|
|
Which item is NOT a function performed by proteins found in the plasma membrane?
|
A. receptor for chemical messenger
B. attachment site for cytoskeleton C. joining of adjacent cells D. transport of solutes E. synthesis of proteins |
E. synthesis of proteins
|
|
|
prophase
|
chromatin condenses into chromosomes; centrioles move toward opposite poles of the cell
|
|
|
|
anaphase
|
sets of chromosomes are moved to opposite sides of the cell.
|
|
|
|
match the stage of interphase with the events that occur: G1
|
The cell is metabolically active, synthesizing proteins, and growing rapidly.
|
|
|
|
condensed chromatin
|
dark - staining regions in the nucleus of non - dividing cell composed of tightly coiled strands of DNA
|
|
|
|
golgi apparatus
|
protein packaging and modification
|
|
|
|
metaphase
|
chromosomes line up along the cell equator.
|
|
|
|
definite changes in the .......... of the cell membrane can be seen in a cell that is becoming cancerous.
|
glycocalyx
|
|
|
|
desmosomes
|
anchoring junctions
|
|
|
|
function of a Lysosome
|
intracellular digestion
|
|
|
|
The outer boundary of a human cell is the?
|
plasma membrane
|
|
|
|
proteins in the cell membrane that bind hormones and relay messages into the interior of the cell........
|
perform a function known as transduction
|
|
|
|
nucleosome
|
a section of DNA and its eight associated histone proteins
|
|
|
|
cholesterol
|
a plasma membrane lipid that stabilizes the plasma membrane
|
|
|
|
What is the function of peroxisomes?
|
neutralize dangerous free radicals
|
|
|
|
match the stage of interphase with the event that occurs: G2
|
Cell division enzymes are synthesized, and the centrioles complete replication.
|
|
|
|
match the stage of interphase with the events that occur: S
|
DNA replicates
|
|
|
|
telophase
|
chromosomes uncoil and revert to chromatin: nuclear membranes from around the sets of chromosomes
|
|
|
|
prophase
|
chromatin condenses into chromosomes; centrioles move toward opposite poles of the cell.
|
|
|
|
function of cytoskeleton
|
support cellular structures
|
|
|
|
cytokinesis
|
Division of the parent cell cytoskeleton into two daughter cells.
|
|
|
|
gene
|
a segment of DNA that carries instructions for the production of one polypeptide chain
|
|
|
|
simple diffusion
|
moving passively down a concentration gradient.
|
|
|
|
function of microtubules
|
support the cell and give it shape; involved in cell movement
|
|
|
|
mitosis
|
separation of two identical sets of chromosomes to opposite sides of the parent cell
|
|
|
|
golgi apparatus produces what product
|
Lysosome and secretory vesicles
|
|
|
|
centrioles produce what product?
|
cilia and flagella (microtubules)
|
|
|
|
crenation takes place when a cell is placed in a.............?
|
hypertonic solution
|
|
|
|
DNA is replicated during the....... phase of the cell cycle.
|
S
|
|
|
|
During transcription, .............
|
DNA is used as a template to make RNA.
|
|
|
|
nucleolus produces
|
ribosomes
|
|
|
|
integral protein
|
The component of the plasma membrane that can act as a doorway for charged particles.
|
|
|
|
product produce by rough endoplasmic reticulum
|
transport vesicles
|
|
|
|
function of centrioles
|
organize the spindle during mitosis
|
|
|
|
interphase
|
non-dividing stage involving rapid growth, DNA replication, and preparation for division.
|
|
|
|
vesicular transport is involved in all of the following transport process, EXCEPT.........
|
solute pumps
|
|
|
|
product of mitochondrion
|
ATP
|
|
|
|
All of the following are functions of membrane receptors EXCEPT
A. cell adhesion B. G - protein linking C. contact signaling D. chemical signaling |
A. cell adhesion
|
|
|
|
During transcription. .........
|
DNA is used as a template to make RNA
|
|
|
|
The resting membrane potential is mainly determined by
|
The differential permeability of the plasma membrane to K+ and other ions.
|
|
|
|
Lysosome contain
|
digestive enzymes
|
|
|
|
tight junction
|
adjacent cells joined by a line of membrane proteins that form an impermeable junction
|
|
|
|
What is not found in the plasma membrane of a human cell?
|
RNA
|
|
|
|
In which stage of mitosis do the chromosomes align along the cell equator?
|
metaphase
|
|
|
|
desmosome
|
button like junctions that use linker proteins to hold adjacent cells together.
|
|
|
|
gap junctions
|
adjacent cells held together by connexon proteins that form cylinders allowing ion flow between the cells cytoplasm
|
|
|
|
form of RNA with its function:rRNA
|
combines in a complex with proteins to make the large and small subunits of a ribosome
|
|
|
|
flagella
|
long, cellular projections that are tail-like and aid in propulsion
|
|
|
|
primary active transport
|
movement of a substance that utilizes a carrier; energy comes directly from hydrolysis of ATP
|
|
|
|
The underlying cause of Tay-Sachs disease is
|
The lack of the enzymes needed to break down a glycolipid abundant in nerve cell membranes
|
|
|
|
RNA with its function:mRNA
|
carries genetic instructions from the nucleus to the site of protein synthesis
|
|
|
|
What type of RNA contain regions that act as a switch to turn protein synthesis on and off for the protein it codes for?
|
riboswitches
|
|
|
|
RNA with its function:tRNA
|
uses an anticodon to guide it's attached amino acids to the complementary codon on the mRNA at the ribosome
|
|
|
|
microvilli
|
tiny fingerlike projections of the plasma membrane; increase surface area for absorption
|
|
|
|
Lysosome perform what function?
|
intracellular digestion
|
|
|
|
membrane transport of:SECONDARY ACTIVE TRANSPORT
|
movement of a substance that utilizes a carrier, and has a concentration gradient as the source of energy
|
|
|
|
desmosomes function
|
anchoring junctions found in areas subjected to pulling forces
|
|
|
|
cilia
|
motile cellular extensions found in large numbers in some epithelial cells
|
|
|
|
endocytosis
|
The method by which larger particles and macromolecules enter the cell by an in folding of the plasma membrane
|
|
|
|
function of tight junction
|
prevent molecules from passing through the extracellular space between adjacent cells
|
|
|
|
RNA with its function: microRNA
|
Can control, or inhibit, certain genes
|
|
|
|
cristae are found in which cell organelle?
|
mitochondria
|
|
|
|
Which of the following cell organelle produce secretory vesicles?
|
golgi apparatus
|
|
|
|
exocytosis
|
The fusion of vesicle with the plasma membrane to move substance out of the cell
|
|
|
|
hypertonic solution
|
a solution containing more solutes than the cell
|
|
|
|
hypotonic solution
|
a solution containing fewer solutes than the cell
|
|
|
|
peroxisome
|
posesses oxidase enzymes that function in neutralizing harmful free radicals
|
|
|
|
primary active transport
|
uses ATP as a source of energy
|
|
|
|
osmosis
|
The movement across a selectively permeable membrane
|
|
|
|
osmosis is.........
|
The diffusion of water across a membrane
|
|
|
|
integral protein
|
a protein that is firmly inserted into the lipid bilayer
|
|
|
|
hydrostatic pressure
|
The force of a liquid pushing against something
|
|
|
|
isotonic solution
|
a solution containing the same solutes as the cell
|
|
|
|
osmotic pressure
|
The force that solutes have to attract water
|
|
|
|
hydrophobic
|
water-fearing
|
|
|
|
peripheral protein
|
a protein that is not embedded in the lipid bilayer
|
|
|
|
C
|
A. endocytosis: passive membrane transport process
B. osmosis: active membrane transport process I know I should but.....you shouldn't be in bad shape too much longer it's tax season. C. exocytosis: active membrane transport process |
|
|
|
cytoskeleton
|
support cellular structure and generates cell movement
|
|
|
|
isotonic solution
|
solution containing the same solutes as the cell
|
|
|
|
diffusion
|
The tendency of solutes to move along their concentration gradient from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration
|
|
|
|
active transport mechanisms
|
methods depending on carrier proteins and energy derived from ATP
|
|
|
|
mitochondrion
|
responsible for generating most of the energy the cell uses to perform work
|
|
|
|
gap junctions
|
important for cell communication
|
|
|
|
solutions with a higher concentration of solutes inside the cell are
|
hypertonic
|
|
|
|
diffusion is a form of active transport. true or false
|
false
|
|
|
|
transcription is
|
The synthesis of RNA using DNA as a template
|
|
|
|
What is not in RNA?
|
Thyamine
|
|
|
|
During DNA replication, the covalent bonding of nucleotides into a strand of DNA is performed by
|
DNA polymerase
|
|
|
|
............... is a molecular "ferry" that brings amino acids to the ribosome to build a protein.
|
t-RNA
|
|
|
|
During interphase of the cell life cycle, the parent cell divides into two daughter cells
true or false |
false, mitosis is the phase of the cell cycle in which cell division occurs. interphase is the phase of the cell life cycle in which the cell grows and carries on its usual activities.
|
|
|
|
What is the correct order of mitosis?
|
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
|
|
|
|
Which of the phase does DNA replication occur?
|
synthesis or interphase
|
|
|
|
During which phase does chromatin condense and become chromosomes?
|
prophase
|
|
|
|
interphase can be broken down in 3 phases...
|
G1, S, and G2
|
|
|
|
Which of the following processes allows cells to concentrate material that is present only in small amounts in the extracellular fluid?
|
receptor - mediated endocytosis
|
|
|
|
cells of the body mainly use .......for the selective endocytosis of most macromolecules.
|
receptor - mediated endocytosis
|
|
|
|
G protein
|
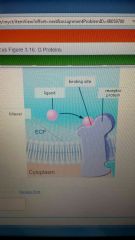
|
|
|
|
G protein activation
|
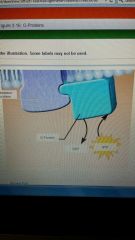
|
|
|
|
effector binding
|
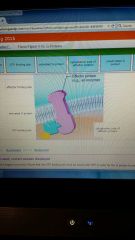
|
|
|
|
formation of 2nd mesenger
|
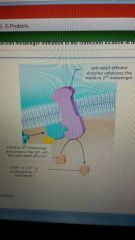
|
|
|
|
G protein step sequence
|
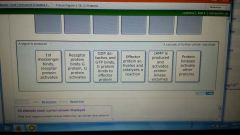
|
|
|
|
Which item below is NOT a function performed by proteins found in the plasma membrane?
A joining of adjacent cells B transport of solutes C attachment site for cytoskeleton D receptor for chemical messenger molecules E synthesis of proteins |
E. synthesis of proteins
|
|
|
|
All of the following are functions of membrane receptors, EXCEPT...
A. G protein linking B. cell adhesion C. contact signaling D. chemical signaling |
B. cell adhesion
|
|
|
|
Which of the following would not diffuse through the plasma membrane by means of simple diffusion?
A. steroid hormone B. oxygen C. glucose D. A lipid soluble vitamin |
C. glucose
|
|
|
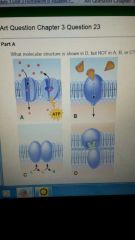
What molecular structure is shown in D but not in the others?
|
a carbohydrate molecular group
|
|
|
|
Which nucleic acid molecules are involved in transcription but not translation in the synthesis of a particular polypeptide?
|
DNA
|
|
|
|
Which of these would a steroid molecule diffuse into a cell?
|
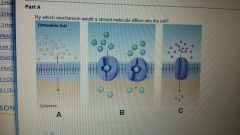
|
A
|
|
|
proteins in the cell membrane that bind hormones and relay messages into the interior of the cell.....
|
perform a function known as signal transduction
|
|
|
|
simple diffusion is best described as substances....
|
moving passively down a concentration gradient
|
|
|
|
a gene is best defined as
|
a segment of DNA that carries instructions for the production of one polypeptide chain
|
|
|
|
Which set of membrane proteins in the figure depicts the transport of solute molecules?
|
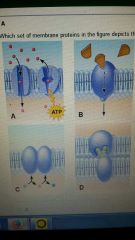
A shows passive and active transport processes
|
|
|
|
label the parts inside the interphase
|
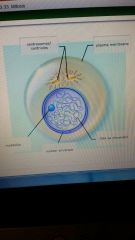
|
|
|
|
subphase of G1
|
1. centrioles begin to replicate
2. cellular growth and biosynthesis of organelles and proteins for various functions |
|
|
|
subphase of S
|
DNA replication
|
|
|
|
subphase of interphase G2
|
1. centrioles finish replicating
2. growth and biosynthesis of products to be used in mitosis |
|
|
|
structures containing DNA only visible during mitosis and first seen in prophase...
|
chromosomes
|
|
|
|
DNA containing structures which condense during prophase..
|
chromatin
|
|
|
|
microtubules array around centrosomes.
|
asters
|
|
|
|
These structures act as focal points for the appearance of the mitotic spindle.
|
centrosomes
|
|
|
|
These RNA structures disappear when chromosomes appear.
|
nucleoli
|
|
|
|
Which is representative of early prophase?
|
chromosomes condense as sister chromatid pairs.
|
|
|
|
Which is representative of late prophase?
|
attachment of chromatid pairs to spindle microtubules
|
|
|
|
Which phrase describes metaphase?
|
sister chromatids are aligned at the metaphase plate
|
|
|
|
Select the correct activity occurring during anaphase.
|
chromosomes move toward opposite poles of the cell
|
|
|
|
Which is true regarding cytokinesis?
|
cytokinesis usually begins in anaphase
|
|
|
|
mitosis
|
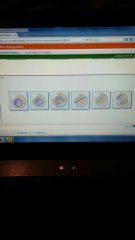
|
|
|
|
Which of the following is a function of a plasma membrane protein?
|
molecular transport through the membrane |
|
|
|
Which of the following is the most correct statement regarding transcription/translation?
|
The nucleotide sequence in a tRNA anticodon is an exact copy of the DNA triplet that coded for it except that uracil is substituted for thymine. |
|
|
|
After DNA replication is completed, each DNA double helix strand consists of _____
|
One old parent strand and one new daughter strand. This mechanism is called semiconservative replication and is based on the ability of each strand of the DNA double helix to function as a template for the synthesis of the opposite strand. |
|
|
|
What is the function of mRNA during translation?
|
mRNA carries the code for a polypeptide's sequence of amino acids. The code for each amino acid is a 3-base sequence called a codon. |
|
|
|
Messenger RNA
|
Produced in the nucleus, this molecule specifies the exact sequence of amino acids of the protein to be made |
|
|
|
The RNA responsible for bringing the amino acids to the ribosome for protein formation is ________.
|
tRNA
|
|
|
|
By which mechanism would a steroid molecule diffuse into the cell?
|
Diffusion Steroid molecules are nonpolar fat-soluble molecules, which would be expected to diffuse directly across the phospholipid bilayer. Such solutes do not require a membrane protein to facilitate transport. |
|
|
|
Some transport processes use transport proteins in the plasma membrane, but do not require ATP. This type of transport is known as ____.
|
Facilitated diffusion Facilitated diffusion is a passive transport during which molecules move down their concentration gradient through transport proteins. |
|
|
|
Which of the following solutions contains the most solute?
a. hypertonic b. hypotonic c. isotonic d. equilibrium |
Hypertonic
"Hyper" means "high," so a hypertonic solution has a higher solute concentration than the solution to which it is being compared. |
|
|
|
What part of a cell membrane is usually in contact with the interstitial fluid?
|
phosphate heads of phospholipids The phosphate heads of the phospholipids are polar, so they are attracted to the polar water molecules. |
|
|
|
Passive membrane transport processes include
a. movement of a substance down its concentration gradient b. movement of water from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration c. consumption of ATP d. the use of transport proteins when moving substances from areas of low to high concentrations |
A. movement of a substance down its concentration gradient
|
|
|
|
Chemical reactions that release energy are called ________.
|
exergonic |
|
|
|
Chemical reactions that absorb energy are called ________.
|
endergonic
|
|

