![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
State the functions of the skeletal system. |
Supports the body Stores minerals and fats Protects soft body parts Produces red blood cells Permits flexible body movement with muscles |
SSPPP |
|
|
What are the 5 types of bones? |
Long- more longer than wide Short- cube shaped; lengths and widths are about equal Flat- plate like broad surfaces Irregular- vary in shapes with many places for connections with other bones Round- circular shape |
|
|
|
What is the periosteum? |
A tough, fibrous connective tissue covering the bone. |
|
|
|
The epiphysis contains? |
Spongy bone! |
|
|
|
A thin, fibrous membrane, that lines the medullary cavity and the spaces of spongy bone. |
Endosteum |
|
|
|
The medullary cavity contains? |
Yellow marrow- contains large amounts of fat. |
|
|
|
A layer of hyaline cartilage on the bone. |
Articular cartilage |
|
|
|
Compact bone or dense bone, contains cylinder-shaped units called? |
Osteons |
|
|
|
Osteons are formed by concentric layers of matrix called? |
Lamellae |
|
|
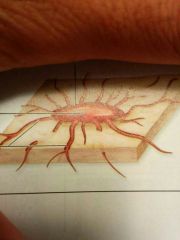
Canaliculi are small canals that connect to________. |
Lacunae |
|
|
|
The matrix of compact bone contains? |
Collagenous protein fibers and mineral deposits (calcium & phosphorus salts) |
|
|
|
In each osteon, the lamellae and lacunae surround a single? |
Central canal |
|
|
|
Blood vessels and nerves can travel from one central canal to another by? |
Perforating canals |
|
|
|
Spongy bone, or cancellous bone, contains numerous bony bars and plates called? |
Trabeculae |
|
|
|
What are the four types of cells involved in bone growth and repair? And what are their functions? |
Osteoprogenitor- unspecialized cells in the inner portion of the periosteum, endosteum, and central canal.
Osteoblasts- bone forming cells formed from osteoprogenitor cells. Secretes the matrix characteristics of bone.
Osteocytes- are mature bone cells derived from osteoblasts. Once the osteoblasts are surrounded by matrix, they become osteocytes in bone.
Osteoclasts- perform bone resorption; that is, they break down bone and assist in depositing calcium and phosphate in the blood. Important for growth and repair. |
|
|
|
What is ossification? |
The formation of bone |
|
|
|
Explain endochondral ossification. |
Hyaline cartilage models, which appear during fetal development, are replaced by bone as development continues. |
|
|
|
What are the two systems for classifying joints? |
1. According to the amount of movement they allow 2. According to their structure |
ANAT & PHYSIO |
|
|
Synarthrosis |
Immovable |
|
|
|
Amphiarthrosis |
Allows slight movement |
|
|
|
Diarthrosis |
Freely moveable |
|
|
|
What are fibrous joints? Give examples |
Sutured together by a thin layer of fibrous connective tissue. Examples: coronal, lambdoidal, squamosal, and saggital |
|
|
|
What are synovial joints? And explain their structure |
Freely movable joints. The two bones are separated by a joint cavity. The joint cavity is lined by the synovial membrane, which produces synovial fluid to lubricate the joint. |
|
|
|
Explain the saddle joint with an example. |
Each bone is saddle-shaped and fits into the complimentary region of the other. Example the joint between the carpal and metacarpal joints of the thumb. |
|
|
|
Explain the ball-and-socket joint and give an example. |
The ball-shaped head of one bone fits into the cup shaped socket of another. Example the shoulder and hip joint; movement in all planes as well as rotation. |
|
|
|
Explain the pivot joint and give an example. |
A small, cylindrical projection of one bone pivots within the ring formed bone and ligament of another bone. Example the join between the ulna and radius, and the joint between the atlas and axis. |
|
|
|
Explain the hinge joint and give an example. |
The convex surface of one bone articulates with the concave surface of another. Examples: the elbow and knee joints. |
|
|
|
Explain the gliding joint and give an example. |
Flat or slight curved shaped joints articulating. Examples: the joints between the bones or the wrist and between the bones of the ankle. |
|
|
|
Explain the condyloid joint and give an example. |
The oval shaped condyle of one bone fits into the elliptical cavity of another. Example the joints between the metacarpal and phalanges. |
|
|
|
What is osteoarthritis? |
Deterioration of the articular cartilage of a joint. |
|
|
|
What is rheumatoid arthritis (RA)? |
When the synovial membrane becomes inflamed and grows thicker cartilage. RA is caused by an autoimmune reaction when the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the synovial membrane. |
|
|
|
What is gout? |
Gout is an arthritis resulting from an excessive buildup of uretic acid in the blood. Crystals of uretic acid are deposited in the joints causing inflammation. |
|

