![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
324 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Anatomy |
The study of structures and relationship among structures |
|
|
|
Physiology |
Study of the functions of body parts |
|
|
|
Levels of biological organization |
Adom, molecule, cell tissue organ, organ system, organism |
|
|
|
Metabolisms |
Some total of all chemical reactions that occur within an organism |
|
|
|
Anabolism |
Building of complex molecules from simpler ones |
Ana is a architect |
|
|
Catabolism |
Breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones |
Cat tears things down |
|
|
Responsiveness |
Ability to respond to changes in the internal and external environment |
|
|
|
Stimuli |
Any physical or chemical change in the environment that elicits a response |
|
|
|
Movement |
Motion of organelles cells, Organ and body |
|
|
|
growth |
Increase in the number or size of cells and organisms |
|
|
|
Development |
Changes that take place during the life of organism |
|
|
|
Cell differentiation |
Change that a cell undergoes from and in unspecialize to specialized |
|
|
|
asexual |
Only one parent involved (mitosis) |
|
|
|
Sexual |
To parent cells are involved (Meosis) |
Egg and sperm |
|
|
Homeostasis |
And condition of equilibrium or balance in the body's internal environment |
When disrupted disses can occur |
|
|
What happens if you cannot maintain homeostasis? |
Disease this disorder and even death occurs |
|
|
|
Which is more common a negative or positive feedback loop? |
Negative |
|
|
|
What is an anatomical body position for humans. |
Standardized method of imaging the body that allows precise and constant anatomical reference. standing feet together Facing observer arms to the side Palms facing forward |
|
|
|
Cephalic |
Head |
|
|
|
Cervical |
Neck |
|
|
|
Trunk |
From chest to pelvis |
|
|
|
Thoracic |
Chest |
Tummy |
|
|
Abdominal |
Abdomin |
|
|
|
Pelvis |
Pelvis |
|
|
|
Upper limbs |
Arms |
|
|
|
Lower limbs |
Legs |
|
|
|
Pedal |
Foot |
|
|
|
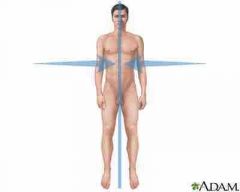
Medial |
|
|
|
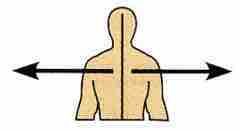
Lateral away from midline of body |
|
|
|
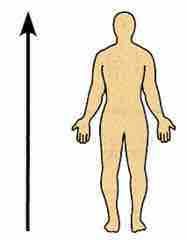
Superior |
|
|
|
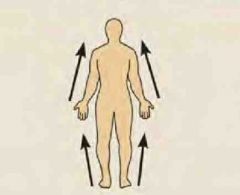
Proximal |
|
|
|
Distal |
|
|
|
Inferior |
|
|
|
Frontal plane |
|
|
|
Transverse plane |
|
|
|
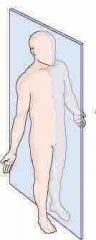
Midsagittal plane |
|
|
|
After the first shell how many electrons can be held on each shell |
8 |
|
|
|
Valence electrons |
an electron of an atom, located in the outermost shell (valence shell) of the atom, that can be transferred to or shared with another atom. |
|
|
|
Ion |
An atom that has lost or gained an electron |
|
|
|
Molecule |
Two or more atoms sharing electrons |
|
|
|
Compound |
A substance that can be broken down in to 2 or more elements |
|
|
|
Ionic bond |
Involves the transfer of electrons |
|
|
|
Cation |
Positively charged particles |
|
|
|
Anion |
Negatively charged particles |
|
|
|
Covalent bond |
Sharing of electrons between atoms in which valence shells of both Atoms our filled |
|
|
|
Hydrogen bond |
a weak bond between two molecules resulting from an electrostatic attraction between a proton in one molecule and an electronegative atom in the other. |
|
|
|
Synthesis - anabolism |
Combination of 2 or more atoms to form larger atoms (joining amino acid to make protein) |
|
|
|
Endergonic |
(of a biochemical reaction) requiring energy. |
|
|
|
Exchange reaction |
Part synthesis part decomposition maintenance of acid/base balance |
|
|
|
Decomposition reaction |
Catabolism Breaking down digestion Braking of protein in to amino acid. |
|
|
|
Exergonic |
(of a biochemical reaction) liberating energy. |
|
|
|
Reversible reaction |
Products may revert back to reactants |
|
|
|
Inorganic compound |
A compound that does not contain hydrocarbon groups. |
|
|
|
What is the most abundant substance in all living things |
Water |
|
|
|
What is the universal solvent |
Water |
|
|
|
Hydrophilic |
"Water loving" substance that readily interact with water |
|
|
|
Hydrophobic |
"Water fearing" substances that do not interact with water |
|
|
|
Hydrolysis |
chemical decomposition in which a compound is split into other compounds by reacting with water. |
|
|
|
Dehydration synthesis |
is the process of joining two molecules, or compounds, together following the removal of water. |
|
|
|
Specific heat |
The specific heat of water is 1 calorie/gram °C = 4.186 joule/gram °C which is higher than any other common substance. |
|
|
|
Heat of vaporation |
the amount of energy needed to change one gram of a liquid substance to a gas at constant temperature. (540 cal/g at 100 °C, water's boiling point.) |
|
|
|
what is an acid? and what is its pH level? |
A substance that dissociates in solution to yield hydrogen cation and anion.(they also really is a high concentration of h+) Greater than 7 |
|
|
|
Base |
A substance that dissociates in solution yielding hydroxide anions and cations (release a high concentration of OH-) Less than 7 |
|
|
|
Mass |
Anything that occupies space and has mass |
|
|
|
Weight |
Force of gravity acting on mass |
|
|
|
After the first shell how many electrons can be held on each shell |
8 |
|
|
|
Valence electrons |
an electron of an atom, located in the outermost shell (valence shell) of the atom, that can be transferred to or shared with another atom. |
|
|
|
Ion |
An atom that has lost or gained an electron |
|
|
|
Molecule |
Two or more atoms sharing electrons |
|
|
|
Compound |
A substance that can be broken down in to 2 or more elements |
|
|
|
Ionic bond |
Involves the transfer of electrons |
|
|
|
Cation |
Positively charged particles |
|
|
|
Anion |
Negatively charged particles |
|
|
|
Covalent bond |
Sharing of electrons between atoms in which valence shells of both Atoms our filled |
|
|
|
Hydrogen bond |
a weak bond between two molecules resulting from an electrostatic attraction between a proton in one molecule and an electronegative atom in the other. |
|
|
|
Synthesis - anabolism |
Combination of 2 or more atoms to form larger atoms (joining amino acid to make protein) |
|
|
|
Endergonic |
(of a biochemical reaction) requiring energy. |
|
|
|
Exchange reaction |
Part synthesis part decomposition maintenance of acid/base balance |
|
|
|
Decomposition reaction |
Catabolism Breaking down digestion Braking of protein in to amino acid. |
|
|
|
Exergonic |
(of a biochemical reaction) liberating energy. |
|
|
|
Reversible reaction |
Products may revert back to reactants |
|
|
|
Inorganic compound |
A compound that does not contain hydrocarbon groups. |
|
|
|
What is the most abundant substance in all living things |
Water |
|
|
|
What is the universal solvent |
Water |
|
|
|
Hydrophilic |
"Water loving" substance that readily interact with water |
|
|
|
Hydrophobic |
"Water fearing" substances that do not interact with water |
|
|
|
Hydrolysis |
chemical decomposition in which a compound is split into other compounds by reacting with water. |
|
|
|
Dehydration synthesis |
is the process of joining two molecules, or compounds, together following the removal of water. |
|
|
|
Specific heat |
The specific heat of water is 1 calorie/gram °C = 4.186 joule/gram °C which is higher than any other common substance. |
|
|
|
Heat of vaporation |
the amount of energy needed to change one gram of a liquid substance to a gas at constant temperature. (540 cal/g at 100 °C, water's boiling point.) |
|
|
|
what is an acid? and what is its pH level? |
A substance that dissociates in solution to yield hydrogen cation and anion.(they also really is a high concentration of h+) Greater than 7 |
|
|
|
Base |
A substance that dissociates in solution yielding hydroxide anions and cations (release a high concentration of OH-) Less than 7 |
|
|
|
What is the normal pH range for plants and animals |
7.2-7.4 |
|
|
|
Mass |
Anything that occupies space and has mass |
|
|
|
Weight |
Force of gravity acting on mass |
|
|
|
Buffer |
Help regulate pH by converting strong acids or bases into weak acid or base is. |
|
|
|
Salts |
Dissociates into anions and cations when dissolved in water |
|
|
|
Where in the body or salts important? |
Teeth and bones Lymph blood and interstitial fluid |
|
|
|
Where in the body or salts important? |
Teeth and bones Lymph blood and interstitial fluid |
|
|
|
What elements do all organic compounds contain? |
Carbon |
|
|
|
Do carbons dissolve easily in water? Are they a good source of energy? |
No they don't dissolve easily in water. Yes they are a good source of energy |
|
|
|
Carbohydrates contain carbon hydrogen and oxygen what is the function of carbohydrates? |
They provide energy.A bodies main source of fuel |
|
|
|
Monosaccharides are also know as ________, and are the basic building blocks of ______. |
Simple sugars. Complex carbs. |
|
|
|
Where would you find glucose, fructose, and galactose? |
Blood sugar Fruit sugar Component of milk sugar |
|
|
|
Do carbons dissolve easily in water? Are they a good source of energy? |
No they don't dissolve easily in water. Yes they are a good source of energy |
|
|
|
Monosaccharides are also know as ________, and are the basic building blocks of ______. |
Simple sugars. Complex carbs. |
|
|
|
Where would you find glucose, fructose, and galactose? |
Blood sugar Fruit sugar Component of milk sugar |
|
|
|
Disaccharides are composed of ______? |
2 monosaccharides |
|
|
|
Do carbons dissolve easily in water? Are they a good source of energy? |
No they don't dissolve easily in water. Yes they are a good source of energy |
|
|
|
Carbohydrates contain carbon hydrogen and oxygen what is the function of carbohydrates? |
They provide energy.A bodies main source of fuel |
|
|
|
Monosaccharides are also know as ________, and are the basic building blocks of ______. |
Simple sugars. Complex carbs. |
|
|
|
Where would you find glucose, fructose, and galactose? |
Blood sugar Fruit sugar Component of milk sugar |
|
|
|
Maltose is compose of what 2 monosaccharides? |
Glucose+glucose |
|
|
|
Sucrose is composed of what 2 disaccharides? |
Glucose and frutose |
|
|
|
Lactose is made of what 2 disaccharides? |
Glucose +galactose |
|
|
|
Starch: chief energy storage for___? Example? |
Plants Potatoes, rice and corn |
|
|
|
Glycogen: chief energy storage for ________? Examples? |
Animals. Stored mainly in liver and muscle tissue. |
|
|
|
Where do you find maltose, surprise and lactose? |
Malt sugar Table sugar Milk sugar |
|
|
|
Can animals digest cellulose easily? |
No |
|
|
|
Are non polar soluble in water |
No |
|
|
|
Can animals digest cellulose easily? |
No |
|
|
|
What is the function of lipids? |
Long term energy storage |
|
|
|
Starch: chief energy storage for___? Example? |
Plants Potatoes, rice and corn |
|
|
|
Glycogen: chief energy storage for ________? Examples? |
Animals. Stored mainly in liver and muscle tissue. |
|
|
|
Can animals digest cellulose easily? |
No |
|
|
|
Are non polar soluble in water |
No |
|
|
|
What is the function of lipids? |
Long term energy storage |
|
|
|
What contains Carbon , Hydrogen and few Oxygen |
Lipids |
|
|
|
Saturated fatty acids only contains single ______ _____? |
Covalent bonds |
|
|
|
Saturated fatty acid is saturated with____? |
Max number of hydrogen atom |
|
|
|
Where do you find phospholipids? |
Cell membranes |
|
|
|
Cholesterol |
Structural component of plasma membranes |
|
|
|
Bile salts |
Break large that's into smaller ones |
|
|
|
Steroid hormones |
Regulate metabolic and reproductive process |
|
|
|
Vitamin D |
Regulation of calcium levels bone growth and repair |
|
|
|
Carotenes |
Need for vision |
|
|
|
Vitamin E |
Promote healing and scarring |
|
|
|
Vitamin K |
Blood clotting |
|
|
|
What six functions to proteins have? |
Structural components growth and repair hormones and chemical Enzymes messengers defense transport movement |
|
|
|
What four elements are proteins composed of? |
Carbon hydrogen oxygen nitrogen |
|
|
|
Where are saturated fatty acid found? |
Animal products Lard, butter |
|
|
|
What are the building blocks of proteins? |
Amino acids |
|
|
|
What sort of bond binds together amino acids? |
Condensation |
|
|
|
What are the four shapes proteins can make? (Know what they all look like) |
Primary structure Secondary structure Tertiary structure Quaternary structure |
|
|
|
What two things can cause the 3D structure of a protein to change? |
Heat Change in pH level |
|
|
|
Denaturation |
Proteins unfolds due to breaking of hydrogen bonds and ionic interactions |
|
|
|
What bonds are broken during denaturation? |
Hydrogen |
|
|
|
what is a enzyme and what do they do? |
Catalyst in a living cell. Lower the amount of energy required for a reaction to take place |
|
|
|
What do nucleic acids do? |
Transmit hereditary information and determines what proteins the cell makes |
|
|
|
What are the names of the two types of nucleic acids. |
DNA RNA |
|
|
|
What is DNA? |
Comprises the genes and all information for synthesizing proteins |
|
|
|
What health complications can arise from overconsumption of saturated fatty acid? |
Clogged arteries and atherosclerosis |
|
|
|
What is RNA? |
Uses that information from DNA to synthesize the proteins |
|
|
|
what are the building blocks of nucleic acids? |
Nucleotides |
|
|
|
What does ATP stand for? |
Adenosine triposphate |
|
|
|
What is ATP primary function? |
Primary energy molecule in all cells |
|
|
|
Cytology |
the branch of biology concerned with the structure and function of plant and animal cells. |
|
|
|
What does the cell theory state? |
all living things are composed of one or more cells; the cell is the basic unit of life; and new cells arise from existing cells |
|
|
|
What are the three parts a cell can be subdivided into? |
Plasma Cytoplasm Nucleus |
|
|
|
Are plasma membrane's flexible or solid? |
Flexible |
|
|
|
Are Unsaturated fatty acid packed closely together? |
No |
|
|
|
What is the function of the plasma membrane? |
Serves as a barrier between the outside and inside of the cell |
|
|
|
Amaphipathic |
Molecules with both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions |
|
|
|
In a phospholipid bilayer how do the phospholipid arrange them selfs? are they stuck in one spot? |
The hydrophobic tails associate with one another, forming the interior of the membrane. The polar heads contact the fluid inside and outside of the cell. They move easily. |
|
|
|
5% of the plasma membrane are made of glycolipids what are they? |
are lipids with a carbohydrate attached by a glycosidic bond. |
|
|
|
What role does cholesteryl play in the plasma membrane? |
Stabilizes the membrane and produces membrane fluidity |
|
|
|
Integral protein |
(Also called transmembrane) permanently attached to the biological membrane. connected through both sides |
|
|
|
Peripheral protein |
Only attached to one side or another. proteins that adhere only temporarily to the biological membrane with which they are associated |
|
|
|
The lipid bilayer is always permanentable to what? |
Small, non-polar, uncharged molecules |
|
|
|
How do you macromolecules pass through the plasma membrane? |
Bulk transport |
|
|
|
Passive processes |
No energy required simple diffusion facilicated defusion Osmosis |
|
|
|
Monounsaturated fatty acids has ___ double bond? |
One |
|
|
|
Active processes |
Requires use of ATP to move molecules in and out of the cell. Active transport Vesicular transport |
|
|
|
Which direction does active processes send chemicals in regards to the concentration gradient? |
Low to high |
|
|
|
Which direction does passive processes send chemicals in regards to the concentration gradient? |
High to low |
|
|
|
Simple diffusion |
Random movement of molecules from the area of high concentration to areas of low concentration |
|
|
|
Facilitated diffusion |
process of spontaneous passive transport of molecules or ions across a cell's membrane via specific transmembrane integral proteins |
|
|
|
Channel mediate facilitated diffusion |
Protien goes through the gate opens lets the protein out and then the gate closes |
|
|
|
Carrier mediate facilitated diffusion |
The ion attaches the transporter opens and the ion comes out the other side |
|
|
|
What are some examples of molecules that pass through facilitated diffusion? |
K+ (potassium) Glucose Amino acid |
|
|
|
Osmosis |
Diffusion of water |
|
|
|
Isotonic solution |
The concentration of salutes is equal both inside and outside the cell |
|
|
|
Polyunsaturated fatty acid has _____ double |
Many |
|
|
|
Hypotonic solution |
The concentration of salutes inside the cell are higher than outside the cell |
|
|
|
Hypertonic solution |
The concentration of salutes ore higher outside the cell than inside the cell |
|
|
|
Lysis |
If a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution the cell will swell and burst |
|
|
|
Crenation |
If the cell is placed in a hypertonic solution it will shrivel up |
|
|
|
Active transport |
Requires the use of energy ATP to move molecules in and out of the cell |
|
|
|
Sodium - potassium pump |
The pump is the protein complex of the ions pass-through |
|
|
|
What powers a sodium potassium pump? |
ATP |
|
|
|
Exocytosis |
Removal of waste products or necessary secreted products from the cell |
|
|
|
Endocytosis |
Cell eating or cell drinking |
|
|
|
Are unsaturated fatty acids liquid or solid at room temp? |
Liquid |
|
|
|
Is monounsaturated fatty acid or polyunsaturated fatty acid better for your health? |
Polyunsaturated fatty acid |
|
|
|
What is TRIGLYCERIDES composition? |
Composed of glycerol molecule attached to 3 fatty acids |
|
|
|
What are PHOSPHOLIPIDS composed of? And are they hydrophobic or hydrophilic? |
Phosphate group -hydrophilic 2 fatty acid tails- hydrophobic 1 glycerol - hydrophilic
|
|
|
|
Organelles |
any of a number of organized or specialized structures within a living cell. |
|
|
|
Why do smokers and nicotine users cough so much? |
There cilia is paralyzed. |
|
|
|
What are some similarities between cilia flagella. |
They are structurally identical |
|
|
|
What's the difference between attached and free ribosomes? |
Attached synthesize proteins for export out the cell and free synthesize proteins for use inside the cells |
|
|
|
What organic material do ribosomes contain? |
nRNA and protiens |
|
|
|
What is a endoplasmic reticulum? (E.R) |
forms an interconnected network of flattened, membrane-enclosed sacs or tube-like structures |
|
|
|
Function of smooth E.R? |
Detoxifies chemicals including alcohol pesticides and carcinogens. Liver |
|
|
|
Function of rough E.R? |
Stores and modifies newly synthesized proteins and prepares proteins for export out of cell |
|
|
|
What is Golgi apparatus? |
a complex of vesicles and folded membranes within the cytoplasm of most eukaryotic cells, involved in secretion and intracellular transport. |
|
|
|
What's the function of the Golgi apparatus? |
It has been likened to the cell's post office. A major function is the modifying, sorting and packaging of proteins for secretion. |
|
|
|
Lysosomes |
Breaks down and recycles worn out cell parts |
|
|
|
What makes up the composition of cytosol? |
Water |
|
|
|
What do lysosomes contain? |
Hydrolytic enzymes. |
|
|
|
Peroxisomes |
Similar in structure and shape to lysosomes but smaller & contain enzymes that use oxygen to break down proteins and fatty acids |
|
|
|
Proteasomes |
Barrel shaped and destroy unneeded, damaged or faulty protiens by cutting in to smaller peptides |
|
|
|
What's the nick name of mitochondria? |
Power house of cells |
|
|
|
What's the functions of the folds and cristae of mitochondria? |
Increase surface area |
|
|
|
Function of mitochondria? |
to produce the energy currency of the cell |
|
|
|
Function of the nucleus? |
Contains the cells genes |
|
|
|
Nuclear envelope |
Lipid bilayer which surrounds the genetic material. |
|
|
|
What leaves the nucleus and doesn't leave the nucleus? |
DNA never leaves RNA leaves |
|
|
|
Nucleuolus |
a small dense spherical structure in the nucleus of a cell during interphase. |
|
|
|
Cytoskeleton |
a microscopic network of protein filaments and tubules in the cytoplasm of many living cells, giving them shape and coherence. |
|
|
|
Chromosomes |
a threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes. |
|
|
|
How are chromosomes wounded in to its X shape? |
DNA swirled up tightly |
|
|
|
Centrosome |
the region of a chromosome to which the microtubules of the spindle attach, via the kinetochore, during cell division. Middle piece in chromosomes |
|
|
|
Process of gene expression? |
Blue print for protien DNA to RNA RNA TO protein |
|
|
|
The order for mitosis? |
Prophase Metaphase Anaphase telophase |
|
|
|
Prophase |
Chromosomes appear |
|
|
|
Metaphase |
Chromosomes line up in the middle |
|
|
|
Anaphase |
Chromosomes split apart |
|
|
|
Telophase |
New nuclear membrane forms. |
|
|
|
Cytokinesis |
Fully splitting of cell |
|
|
|
What is the cytoskeleton made of? |
three kinds of protein filaments: Actin filaments (also called microfilaments) Intermediate filaments and. Microtubules. |
|
|
|
What is the cytoskeleton function? |
It forms a framework for the movement of organelles around the cytoplasm |
|
|
|
What are the centrosome / centrioles composed of? |
Protiens |
|
|
|
What is the role of centrosome and centrioles? |
organization and nucleation of microtubules in animal cells and also regulate the cell cycle during cellular division |
|
|
|
What are cilia? |
Extension of cytoplasma |
|
|
|
What are flagella? |
Extension of cytoskeleton |
|
|
|
Where do you find cilia? |
Humans respiratory tract. |
|
|
|
Tissue |
A group of similar cells that function together to carry out specialized activities |
|
|
|
Tissue |
A group of similar cells that function together to carry out specialized activities |
|
|
|
Histology |
The study of tissues |
|
|
|
Characteristics of epithelial tissue |
Adheres firmly to connective tissue via the basement cell |
|
|
|
Characteristics of epithelial tissue |
Adheres firmly to connective tissue via the basement cell |
|
|
|
Composition of epithelial tissue |
Closely packed cells Little matrix |
|
|
|
What is the function of epithelium tissue ? |
Covers the body surfaces The lion body cavities forms glands |
|
|
|
What's the classification of epithelial tissue? (Layers) |
Simple - single layer Stratified - stacked Pseudostratified |
|
|
|
What's the classification of epithelial tissue? (Layers) |
Simple - single layer Stratified - stacked Pseudostratified |
|
|
|
What's the classification of epithelial tissue? (Shapes)
|
Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Transitional |
|
|
|
What is the Characteristics of connective tissue? |
Lots of matrix Few cells do not occur on free surfaces High vascularized and has a nerve supply |
|
|
|
What is the Characteristics of connective tissue? |
Lots of matrix Few cells do not occur on free surfaces High vascularized and has a nerve supply |
|
|
|
What is the composition of connective tissue? |
Mostly fibroblasts |
|
|
|
What is the Characteristics of connective tissue? |
Lots of matrix Few cells do not occur on free surfaces High vascularized and has a nerve supply |
|
|
|
What is the composition of connective tissue? |
Mostly fibroblasts |
|
|
|
What is the function of connective tissue |
Binds and supports Separate structures Stores reserve energy |
|
|
|
What is the function of muscular tissue? |
Provides motion maintains posture generates heat |
|
|
|
What is the Characteristics of connective tissue? |
Lots of matrix Few cells do not occur on free surfaces High vascularized and has a nerve supply |
|
|
|
What is the composition of connective tissue? |
Mostly fibroblasts |
|
|
|
What is the function of connective tissue |
Binds and supports Separate structures Stores reserve energy |
|
|
|
What is the function of muscular tissue? |
Provides motion maintains posture generates heat |
|
|
|
What's the classification of cardiac muscle? |
Heart Strained involuntary Intercalated disc |
|
|
|
What is the Characteristics of connective tissue? |
Lots of matrix Few cells do not occur on free surfaces High vascularized and has a nerve supply |
|
|
|
What is the composition of connective tissue? |
Mostly fibroblasts |
|
|
|
What is the function of connective tissue |
Binds and supports Separate structures Stores reserve energy |
|
|
|
What is the function of muscular tissue? |
Provides motion maintains posture generates heat |
|
|
|
What's the classification of cardiac muscle? |
Heart Strained involuntary Intercalated disc |
|
|
|
What is the classification of smooth muscle |
Walls of hallow structured Nonstriated Involentary |
|
|
|
What is the Characteristics of connective tissue? |
Lots of matrix Few cells do not occur on free surfaces High vascularized and has a nerve supply |
|
|
|
What is the composition of connective tissue? |
Mostly fibroblasts |
|
|
|
What is the function of connective tissue |
Binds and supports Separate structures Stores reserve energy |
|
|
|
What is the function of muscular tissue? |
Provides motion maintains posture generates heat |
|
|
|
What's the classification of cardiac muscle? |
Heart Strained involuntary Intercalated disc |
|
|
|
What is the classification of smooth muscle |
Walls of hallow structured Nonstriated Involentary |
|
|
|
What is the classification of skeletal muscle |
Attached to bone Striated Long cylindrical Voluntary controlled |
|
|
|
What is the Characteristics of connective tissue? |
Lots of matrix Few cells do not occur on free surfaces High vascularized and has a nerve supply |
|
|
|
What is the composition of connective tissue? |
Mostly fibroblasts |
|
|
|
What is the function of connective tissue |
Binds and supports Separate structures Stores reserve energy |
|
|
|
What is the function of muscular tissue? |
Provides motion maintains posture generates heat |
|
|
|
What's the classification of cardiac muscle? |
Heart Strained involuntary Intercalated disc |
|
|
|
What is the classification of smooth muscle |
Walls of hallow structured Nonstriated Involentary |
|
|
|
What is the classification of skeletal muscle |
Attached to bone Striated Long cylindrical Voluntary controlled |
|
|
|
Neurons |
structural and functional units of the nervous system |
|
|
|
What is the Characteristics of connective tissue? |
Lots of matrix Few cells do not occur on free surfaces High vascularized and has a nerve supply |
|
|
|
What is the composition of connective tissue? |
Mostly fibroblasts |
|
|
|
What is the function of connective tissue |
Binds and supports Separate structures Stores reserve energy |
|
|
|
What is the function of muscular tissue? |
Provides motion maintains posture generates heat |
|
|
|
What's the classification of cardiac muscle? |
Heart Strained involuntary Intercalated disc |
|
|
|
What is the classification of smooth muscle |
Walls of hallow structured Nonstriated Involentary |
|
|
|
What is the classification of skeletal muscle |
Attached to bone Striated Long cylindrical Voluntary controlled |
|
|
|
Neurons |
structural and functional units of the nervous system |
|
|
|
Neuroglia |
Protects and supports neurons |
|
|
|
What is the Characteristics of connective tissue? |
Lots of matrix Few cells do not occur on free surfaces High vascularized and has a nerve supply |
|
|
|
What is the composition of connective tissue? |
Mostly fibroblasts |
|
|
|
What is the function of connective tissue |
Binds and supports Separate structures Stores reserve energy |
|
|
|
What is the function of muscular tissue? |
Provides motion maintains posture generates heat |
|
|
|
What's the classification of cardiac muscle? |
Heart Strained involuntary Intercalated disc |
|
|
|
What is the classification of smooth muscle |
Walls of hallow structured Nonstriated Involentary |
|
|
|
What is the classification of skeletal muscle |
Attached to bone Striated Long cylindrical Voluntary controlled |
|
|
|
Neurons |
structural and functional units of the nervous system |
|
|
|
Neuroglia |
Protects and supports neurons |
|
|
|
When does Mitosis of nervous tissue occurred? |
In embryos |
|
|
|
Mucous membranes |
Line digestive respiratory and urinary system and reproductive |
|
|
|
Mucous membranes |
Line digestive respiratory and urinary system and reproductive |
|
|
|
What is the function of mucous membrane |
Barrier to keep microbes out Lubricate food Traps particles in respiratory track secretes digestive enzymes |
|
|
|
Mucous membranes |
Line digestive respiratory and urinary system and reproductive |
|
|
|
What is the function of mucous membrane |
Barrier to keep microbes out Lubricate food Traps particles in respiratory track secretes digestive enzymes |
|
|
|
What sort of tissue does mucous membrane contain |
Epithelial and connective |
|
|
|
Mucous membranes |
Line digestive respiratory and urinary system and reproductive |
|
|
|
What is the function of mucous membrane |
Barrier to keep microbes out Lubricate food Traps particles in respiratory track secretes digestive enzymes |
|
|
|
What sort of tissue does mucous membrane contain |
Epithelial and connective |
|
|
|
What are serous membrane? |
Line cavities that do not open to the exterior and covers organs that lie in those cavities |
|
|
|
Mucous membranes |
Line digestive respiratory and urinary system and reproductive |
|
|
|
What is the function of mucous membrane |
Barrier to keep microbes out Lubricate food Traps particles in respiratory track secretes digestive enzymes |
|
|
|
What sort of tissue does mucous membrane contain |
Epithelial and connective |
|
|
|
What are serous membrane? |
Line cavities that do not open to the exterior and covers organs that lie in those cavities |
|
|
|
What is the composition of serous membrane? |
Parietal layer Visceral layer |
|
|
|
What is the Serous membrane function? |
Secretes a lubricating fluid called serous fluid allows organs to Glide past one another |
|
|
|
What are some examples of serous membrane? |
Pleura- lines thoroughly cavity and lungs Pericardium- surrounds heart Peritoneum -Lines the abdominal cavity and organs |
|
|
|
What are some examples of serous membrane? |
Pleura- lines thoroughly cavity and lungs Pericardium- surrounds heart Peritoneum -Lines the abdominal cavity and organs |
|
|
|
what makes up the composition of synovial membrane? |
Areolar connective tissue Elastic fibers Fats |
|
|
|
What are some examples of serous membrane? |
Pleura- lines thoroughly cavity and lungs Pericardium- surrounds heart Peritoneum -Lines the abdominal cavity and organs |
|
|
|
what makes up the composition of synovial membrane? |
Areolar connective tissue Elastic fibers Fats |
|
|
|
Function of synovial membrane? |
Lubricates and nourishes cartilages. |
|
|
|
What are some examples of serous membrane? |
Pleura- lines thoroughly cavity and lungs Pericardium- surrounds heart Peritoneum -Lines the abdominal cavity and organs |
|
|
|
what makes up the composition of synovial membrane? |
Areolar connective tissue Elastic fibers Fats |
|
|
|
Function of synovial membrane? |
Lubricates and nourishes cartilages. |
|
|
|
Bursae |
Cushioning sacs between tendons |
|

