![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
6 Functions of the respiratory system
|
1. Gas exchange
2. Communication (vocal) 3. Sensory (olfaction/smell) 4. Filtration/clearing of pathogens 5. Humidification of air + equation (making equal) of temperature 6. 2 divisions: Conduction and respiratory |
|
|
Differentiate between the functions and anatomical area of the conducting division and respiratory division.
|
CONDUCTING DIVISION
1. Low resistance pathway for airflow 2. Defense 3. Warms and moistens air 4. Articulation and resonance (Nostrils to bronchioles) RESPIRATORY DIVISION Sites of O2 and CO2 exchange with the blood. (Respiratory bronchioles and the alveolar ducts) = 10% gas exchange (Alveoli) = 90% |
|
|
What are pneumatic bones?
What are they for? |
Hollow, air-filled bones.
Functions: - Lightening skull - Vocal resonance - Warming & humidification |
|
|
Name 5 pneumatic bones on the skull.
|
Frontal
Maxillary Ethmoid Sphenoid Mastoid air cells in temporal bone |
|
|
What do nasal turbinates/conchae do?
|
Help create turbulence, which raises contact between air and mucosa, to warm and humidify air.
|
|
|
What arteries supply the nasal cavity?
|
Ophthalmic (eye-related), maxillary, and facil arteries.
|
|
|
Name the 3 divisions of the pharynx, from top to bottom.
|
Nasopharynx (nose level)
Oropharynx (month level) Laryngopharynx (larynx level) |
|
|
Define the boundaries of the Nasopharynx, Oropharynx, and Laryngopharynx.
|
N: Base of skull to soft palate.
O: Uvula to hyoid bone. L: Hyoid to esophagus. |
|
|
What does the epiglottis do?
|
Covers the windpipe (trachea) when swallowing.
|
|
|
Clinically defined, what structures do the upper respiratory system consist of?
|
Nose
Nasal cavity Paranasal air sinuses (frontal, maxillary, etc) Pharynx Larynx |
|
|
Clinically defined, what structures do the lower respiratory system consist of?
|
Trachea
Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli |
|
|
What does the nasal mucosa do?
|
Warms and humidifies, and filters the air.
|
|
|
What is a choanae?
|
Internal nare (nostril) - a posterior nasal aperture (opening)
|
|
|
Where does the olfactory mucosae lie?
|
On the roof of the nasal cavity.
|
|
|
Where does the pharynx extend from and to?
|
Base of skull to C6.
|
|
|
List 4 functions of the respiratory epithelia.
|
Physical protection
Control permeability Provide sensation (neuroepithelium) Sites of specialised secretions (glandular epithelium) |
|
|
What are the apical (exposed) surface and basal surface exposed to, respectively?
|
Air, and a thin basement membrane.
|
|
|
What are parts of the pharynx and
epiglottis are lined by? What do these cells offer? |
Stratified columnar
epithelium. Offers specialised protection. |
|
|
What are the surface of mouth and
throat lined by? What do these cells offer? |
Stratified squamous epithelium.
Offers protection from physical and chemical attack. |
|
|
What are the ear's 6 hearing functions, and 2 balance/equilibrium functions?
|
Hearing:
• collects • conducts • modifies • amplifies • analyses • converts Equilibrium • “static” • “dynamic” |
|
|
What are 3 functions of the external ear?
|
• Collection of sound waves.
• Location of sound (the auricle "casts a sound shadow" that aids in location of the source of the sound). • Slight amplification of the sound waves due to the size and shape of the external acoustic meatus. |
|
|
What are 3 functions of the middle ear?
|
•Conductionof vibrations of the tympanic membrane to the membrane of the oval window.
•Modificationof the vibrations of membrane to movements of bones. •Amplificationof the vibrations mainly because of the size difference between the tympanic membrane and oval window. |
|
|
Bony labyrinth:
What are the fluid-filling structures, used to determine the , Y, and Z-axes, called? |
Semi-lunar canals.
|
|
|
Membraneous labyrinth:
What are the 2 types of ducts called? |
Semi-lunar ducts and cochlear duct.
|
|
|
Bony labyrinth:
Names the 4 structures. |
Semi-lunar canals.
Vestibule (entrance). Cochlea (snail thing) Fenestra Vestibuli Fenestra Cochleae |
|
|
What's the Fenestra Vestibuli for?
|
Place where sound waves enter the cochlea, via vibrations from the tympanic membrane -> Malleus -> Incus -> Stapes.
|
|
|
What's the Fenestra Cochleae for?
|
Place where sound waves leave the cochlea.
|
|
|
Which nerve innervates in internal auditory meatus?
What are its roles? |
Cranial Nerve 8 (Vestibulocochlear nerve)
Sensory nerve. Equilibrium (vestibular nerve) and hearing (cochlear nerve). |
|
|
What are 4 functions of the external ear?
|
•Conduction of the vibrations.
•Analysis of the vibrations because different parts of the spiral organ are related to different frequencies of vibration. •Conversion of mechanical vibrations to electrical impulses. •Equilibrium; both "static" and "dynamic". |
|
|
What are the 3 names of the tube connecting the upper pharynx to the middle ear?
Which one matters? |
•Auditory tube***
•Pharyngotympanic tube •Eustachian tube |
|
|
What is the core component of the cochlea?
Why is it important? |
Organ of Corti - sensory organ for hearing.
|
|
|
What do the oval window and round window correspond to, respectively?
|
Fenestra Vestibuli, and Fenestra Cochleae.
|
|
|
What structures contain perilymph, and what contain endolymph?
|
Perilymph: Fenestra Vestibuli, and Fenestra Cochleae.
Endolymph: Organ of Corti |
|
|
Semicircular Canals (osseous) contain Semicircular Cucts (membraneous), which contain Cupla Ampullae, which contain Crista Ampullaris, which detects what?
|
Dynamic equilibrium: Rotational/angular motion.
|
|
|
Vestibule (osseous) containing Utricle and Saccule (membraneous), which contain Maculae, which detects what?
|
Static equilibrium: Gravity and linear acceleration.
|
|
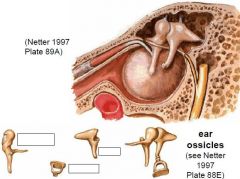
Name the structures.
|
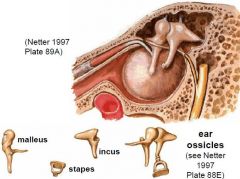
|
|
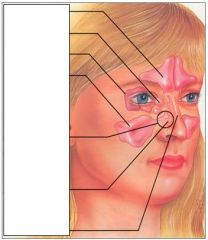
Name the sinuses.
|
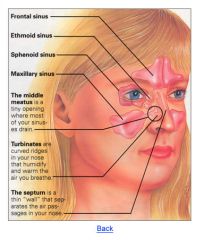
|

