![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
1. What are the boundaries of the anterior portion of the hypothalamus and the posterior portion of the hypothalamus?
2. What structures are located in : a. Anterior Portion of the Hypothalamus b. Middle Portion of the Hypothalamus c. Posterior Portion of the Hypothalamus |
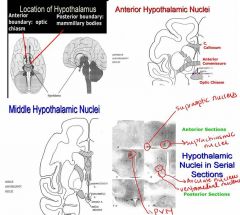
1. Anterior boundary: optic chiasm
Posterior boundary: mammillary bodies 2. a. I. Anterior Portion of the Hypothalamus A. Suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) B. Sexually dimorphic nucleus (SDN) C. The Organum Vasculosum Lamina Terminalis (OVLT) b. II. Middle Portion of the Hypothalamus A. Paraventricular nucleus (PVN) B. Supraoptic nucleus (SON) C. Arcuate nucleus D. Ventromedial nucleus (VMN) c. III. Posterior Portion of the Hypothalamus A. Mammillary nuclei |
1. ASShOle
2. MAPS Visit 3. PM |
|
|
What is the role of the hippocampus?
|
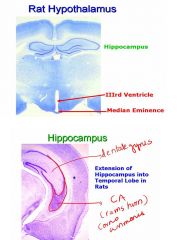
-This is important for memory formation.
-It also functions in spatial learning. -In Humans, Hippocampus is Restricted to Temporal Lobe. -CREB Protein is a Marker of Synaptic Plasticity and Learning. CREB appears in the postsynaptic cell. -It will detach from the activated synapses. The CREB will go to the nucleus and permanently change the function of a nerve cell in response to stimuli. This is an important component in memory. -The dentate nucleus and the CA have lots of CREB protein. AD damages the hippocampus and areas attached to the hippocampus. The hippocampus is for memory formation. |
|
|
|
1. Describe the role of the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus?
2. Describe the role of Sexually Dimorphic Nucleus (Near Suprachiasmatic Nucleus)? |
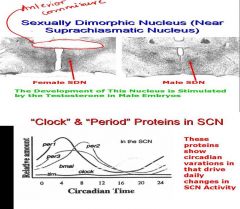
1. Suprachiasmatic Nucleus
FUNCTION: Generation of Circadian Rhythms in Sleep, Eating, Body Temperature, Hormones, etc NOTES: SCN act like little clocks which may establish circadian rhythm in sleep, eating, body, temp, hormones, etc. These cells are involved when you get jet lag. These cells generate these autonomous cells all throughout the day. It does this with the aid of clock and period proteins in SCN. These clock and period proteins show circadian varations in that drive daily changes in SCN Activity. 2. The Development of This Nucleus (SDN) is Stimulated by the Testosterone in Male Embryos. In Rats, SDN lesions diminish male sexual behavior and the preference of males for females; may mediate influence of olfactory cues upon sexual behavior In Humans, a homologue of the SDN has been found (1.5 times larger in Males). Possible role in human sexual behavior and homosexuality is controversial. |
|
|
|
A. What are Circumventricular Organs?
B. Describe the functions of these Circumventricular Organs? 1. The Organum Vasculosum Lamina Terminalis (OVLT) 2. Median Eminence 3. Area Postrema of Medulla |
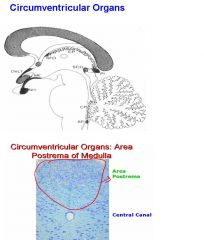
A. They are Located Around the Margins of the IIIrd Ventricle and they are Unusually Permeable Capillaries that Allow Entry of Molecules into Brain.
B. NOTES: Circumventricular Organs are located around the margins of the IIIrd ventricle Above the hypoglossal nucleus is the area postalis. Medial eminence is another Circumventricular Organ. They contain unusually permeable capillaries allowing entry of molecules into brain and this allows these organs to act as chemoreceptors. They can have an effect on the physiological functions of the hypothalamus. B. 1. OVLT, in Preoptic area of Hypothalamus, responds to IL-2 during infections to generate FEVER. It also responds to Na+ and angiotensin to regulate drinking. 2. Median Eminence has Permeable capillaries allow entry of glucose, insulin, etc. into feeding regulating region of middle hypothalamus. 3. Area Postrema of Medulla has Capillaries of AP Lack a Blood-Brain Barrier Protein (GLUT1) Found in Other Capillaries. Activation of AP Neurons by Toxic Chemicals Causes VOMITING by acting on the hypoglossal and vagal nerve. These cells basically act as chemoreceptors. |
|
|
|
Describe the role of the 2 neurons in the Paraventricular nucleus (PVN)in the middle portion of the hypothalamus and mention 3 hormones located in this region.
|
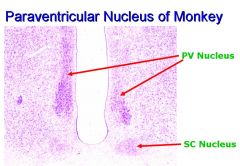
Paraventricular nucleus (PVN)has two types of neurons:
1. Large, Magnocellular Neurons Make Vasopressin and it is stored in the posterior pituitary gland. Vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone) causes the production of a concentrated urine; secreted to conserve body fluids during water lack or blood loss. -Other Magnocellular Neurons Make Oxytocin and Also Project to Posterior Pituitary (Pituitary Oxytocin is Most Important for Lactation; Uterine Oxytocin Probably Plays Major Role in Labor). 2. Smaller, Parvocellular Neurons: -Make Releasing Hormones and Project to Median Eminence -Make Other Neurotransmitters and Project to INTERMEDIO- LATERAL HORN (Sympathetic Neurons). Therefore, it Contains releasing hormones (CRH and TRH) that activate the anterior pituitary during stress. Project directly onto neurons in the intermediolateral horn of the spinal cord that control the sympathetic nervous system (also activated during stress). |
|
|
|
1. What is the role of Supraoptic Nucleus?
2. What is the role of Ventromedial Hypothalamic Nucleus? |
1. Supraoptic Nucleus Secretes Vasopressin in Response to Dehydration and Also Oxytocin and transport it to posterior pituitary; seems particularly sensitive to changes in blood osmolarity.
2. Ventromedial Hypothalamic Nucleus: Abundant Estrogen Receptors. There is Steroidogenic Factor 1 (SF-1) in VMN and this is also Highly Expressed in the Developing Reproductive System! damage or lesions that are confined to the VMN itself have little effect upon body weight or obesity; instead, they impair female reproductive behavior and fertility in rats. |
|
|
|
What are the 2 types of neurons located in the Arcuate nucleus and where do they project to?
|
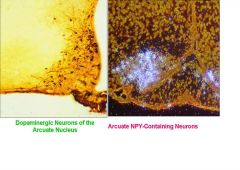
Arcuate Nucleus is above the median eminence and the most ventral.
1. Dopaminergic Neurons of the Arcuate Nucleus Project to Median Eminence to Inhibit Pituitary Release of Prolactin and they Project to Other Hypothalamic Areas 2. Arcuate Neuropeptide Y (NPY) - Containing Neurons Project to PVN and Stimulate Feeding Behavior. Obesity Results When Feeding-stimulating Neurons of the Arcuate Nucleus Become Overactive. |
|
|
|
What is the role of these cirulating substances in modulating Arcuate NPY+ Neurons in the hypothalamus?
1. Leptin 2. Insulin 3. Glucose |
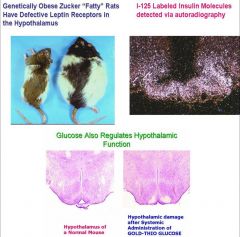
1. Genetically Obese Zucker “Fatty” Rats Have Defective Leptin Receptors in the Hypothalamus. Therefore, the leptin cannot control Arcuate NPY+ Neurons so Arcuate NPY+ Neurons are Overactive and the rats are Sterile, Due to Defective Release of LH-RH.
2. I-125 Labeled Insulin Molecules Readily Escape from Permeable Capillaries of the Median Eminence to Affect Hypothalamic Function (detected via autoradiography). 3. Glucose Also Regulates Hypothalamic Function A poison form of glucose (GOLD-THIO GLUCOSE) can damage cells in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus because they are sensitive to glucose. |
|
|
|
1. What is the effect of Medial Hypothalamic Damage or lesions?
2. What is the effect of Lateral hypothalamic lesions? 3. What is the function of Orexin and relate this to narcolepsy? 4. What are Tanycytes? |
1.Medial Hypothalamic Damage Causes Hyperphagia (Overeating). Mediobasal hypothalamic lesions cause massive obesity and infertility.
2. Lateral hypothalamic lesions can cause severe and sustained body weight loss in rats. Effects may be related to feeding-regulating neurons in the lateral hypothalamus that contain peptide neurotransmitters: melanin concentrating hormone and orexin. 3. Lateral Hypothalamic Neurons Contain Orexin. Orexin is involved in Mild Stimulation of Feeding Strong Stimulation of AROUSAL. In Rats, Damage to Orexin+ cells Produced by Electrolytic Lesions Causes Weight Loss & Impaired Arousal. IN HUMANS, Impaired Orexin Function causes NARCOLEPSY. 4. Tanycytes: specialized ependymal elements that course through the arcuate nucleus. Ependymal Cells are simple columnar cells of the IIIrd Ventricle. |
|

