![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
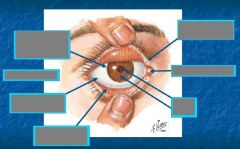
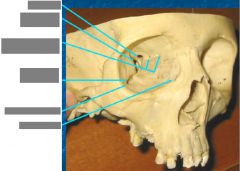
Between orbit & eyeball |
Periorbita - loose periosteum Membrane on surface |
|
|
|
|
|
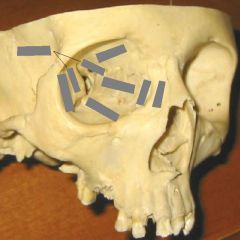
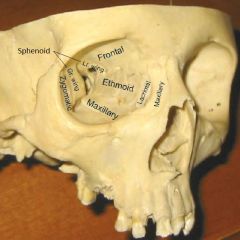
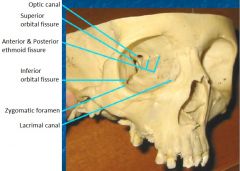
Openings to orbit & where they lead |
Superior orbital fissure -> middle cranial fossa A & P Ethmoid canal -> upper nasal cavity Inferior orbital fissure -> pteryhopalatine fossa Zygomatic foramen -> face Lacrimal canal -> inferior meatus of nose |
|
|
|
|
|
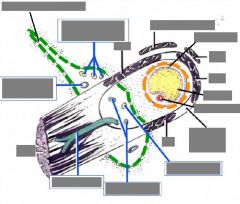
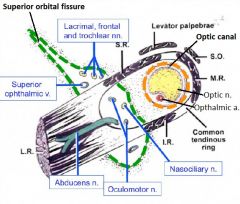
Openings in the apex of the orbit & structures through them |
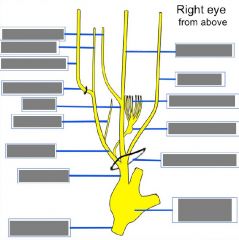
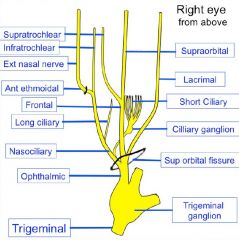
Superior orbital fissure: Opthalmic n. (V1): lacrimal, frontal, nasociliary n. CN III, CN IV, CN VI Opthalmic vv.'s Optic canal: CN II, opthalmic a. |
|
|
Other openings to the orbit & structures through them |
A & P Ethmoid canal-> A & P ethmoid nn. (of V1) Inferior orbital fissure -> Zygomatic n. (of V2) Zygomatic foramen -> Zygomatic n. (of V2) Lacrimal canal -> Nasolacrimal duct |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
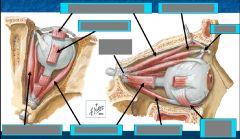
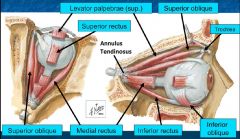
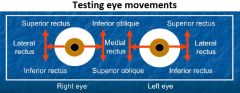
Muscles of the orbit: actions & innervation |
CN III: Medial rectus - adducts Superior rectus - elevates, adducts, intorts Inferior rectus - depresses, adducts, extorts Inferior oblique m. - elevates, abducts, extorts |
|
|
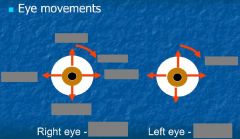
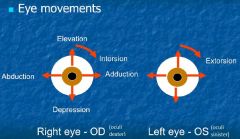
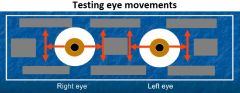
Eye movements: upgaze, downgaze, adduction - depression, abduction - elevation |
Upgaze: superior rectus + inferior oblique Downgaze: inferior rectus + superior oblique Adduction - depression: medial rectus + superior oblique Abduction - elevation: lateral rectus + superior rectus |
|
|
|
|
|
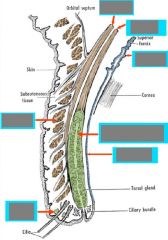
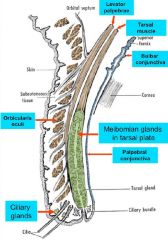
Eyelid mm. |
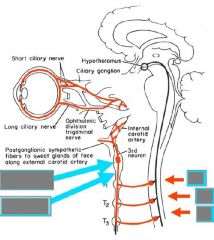
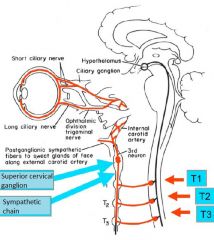
Upper eyelid Levator palpebrae -> tarsal plate (ptosis) Superior tarsal m. (sympathetic; < ptosis) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
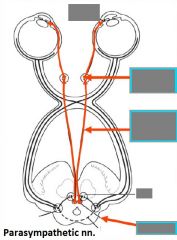
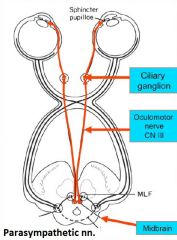
Ciliary m. contraction |
<- parasympathetic innervation Lens rounds (contracts) Suspensory ligaments relax Eye is squeezed -> short distance vision |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
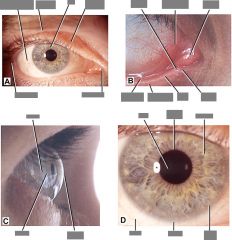
Pathology of eye socket |
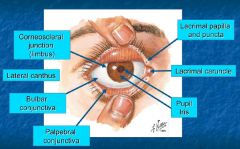
Pinguecula = yellow-white deposit (thickened CT) adjacent to limbus (cornea/sclera jxn) - degenerative (age) Pterygium = vascular inflammatory tissue growing from (usually) medial side of eye - both result from chronic irritation, don't vision |
|
|
Lacrimation |
Lacrimal gland - compound tubuloalveolar gland w/ serous acini - in superolateral orbit -> ducts -> conjunctival sac -> distribution across the eye -> lacrimal puncta & canaliculi -> lacrimal sac -> nasal cavity - tears contain enzymes & H2O + other secretions |
|
|
Optic n. |
Optic canal -> posteromedial eyeball = extension of brain: surrounded by dura mater (attaches to sclera), arachnoid, CSF |
|
|
|
|
|
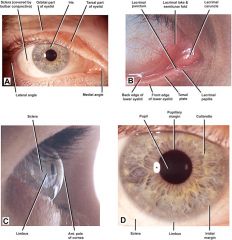
Abnormal pupil size |
Miosis = excessively small Mydriasis = excessively large |
|
|
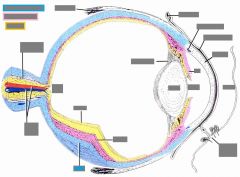
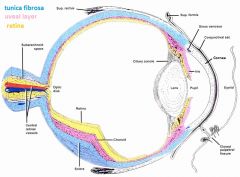
Layers of they eye |
Outer layer - fibrous tunic - sclera: dense layered CT (maintains eye shape) - cornea: clear anterior part Middle / uveal layer - vascular, loose CT, pigment, vorticose v.'s - choroid (anterior: most of ciliary body & iris) Retina (nourished from choroid) - outer pigmented layer - inner retina proper (neural) - 3 layers |
|
|
|
|
|
Chambers of the eye |
Aqueous humor Anterior: cornea - iris Posterior: iris - lens, zonular fibers, ciliary body Vitreous humor Vitreous space: posterior to lens, majority of the eye orbit |
|
|
Vitreous chamber |
- filled w/ gelatinous material (vitreous humor), not renewed! - embryology: hyaloid a. goes to lens directly (via middle of the eyeball) from optic n. - degenerates, can leave "floaters" |
|
|
Cornea - layers |
- Stratified squamous epithelium (5-6 l.), w/ basal cells -> mitosis - Bowman's membrane: thin layer of collagenous CT w/o cells - strength - Stroma (thick): ordered collagen l.'s, fibroblasts - Descemet's membrane: fine/thin collagen - Simple squamous endothelium - pumps ions -> maintains clarity, does not regenerate well |
|
|
Cornea - properties |
- avascular, only pain n.'s (opthalmic n.) - Limbus: stem cells -- constant replacement of corneal cells --| vascular ingrowth (endostatin, restin) -- inflammation -> neovascularization (VEGF) - Dmg to Bowman's layer --| abrasion repair - aqueous humor -> nutrition; tears -> moisture - strongest refracting layer ( -> Lasik surgery) |
|
|
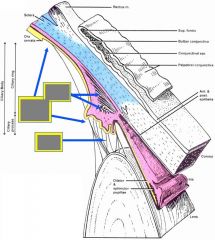
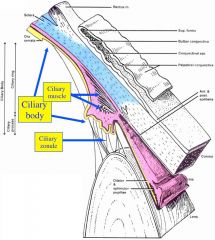
Ciliary body |
- mostly uveal - covered by cuboid epithelium der. from retina -> inner side of iris: produces aqueous humor -- pigment (outer) & nonpigment (inner) layers - attached to lens via suspensory lgt's: zonular fibers = oxytalan (elastic) fibers + collagen - ciliary m. contraction -> lens rounds, lgt's relax |
|
|
|
|
|
Lens |
- attached to zonular fibers
- becomes less elastic w/ age (presbyopia) - ciliary m. relaxes (pS CN III inhibited) -> suspensory lgt's & lens stretched by eye shape - avascular, 3 components -- capsule: refractile, thick BM (type IV collagen) -- subcapsular simple cuboidal epithelium (ant.) -- lens fibers: epit. -> renew, no nuclei, crystallin |
|
|
Diseases of the lense |
Abnormal refraction Focus behind retina: hyperopia (farsighted) Focus in front of retina: myopia (nearsighted) Irregular focus opint: astigmatism Dense cataract - lens fibers opacification |
|
|
Iris |
Mostly from uveal layer + epithelium backing: - epithelium layer (from retina): myoepithelium (dilator pupillae) - sphincter (S) & dilator (pS) pupillae mm. - layer of CT: blood vv., pigment (macrophages) - vascular l., loose CT, melanocytes (pigment) - irregular outer layer: pigment cells, fibroblast |
|
|
Corneal reflex |
Corneal epithelium nn. stimulation -> Opthalmic n. -> spinal root & nucleus of CN V -> IN's -> facial motor nuclei (bilateral) -> CN VII -> orbicularis oculi mm. -> protective blink response |
|
|
Pupillary light reflex |
Light -> CN II -> brainstem -> CN III (bilateral) -> pupillary constriction |
|
|
Aqueous humor |
- created in epithelial cells on ciliary body processes -> posterior chamber -> angle b/w iris & cornea -> canals of Schlemm (scleral venous sinus) -> veins (inadequate absorption -> glaucoma) |
|
|
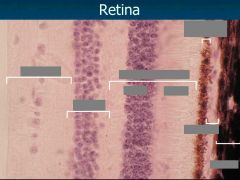
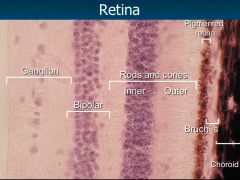
Retina |
Inner neural & outer pigmented layers - not firmly attached -> retinal detachment |
|
|
|
|
|
Ora serrata |
= point where neural retina disappears & becomes pars plana (all the way to ciliary body) |
|
|
Fundus |
= part of the eyeball opposite the pupil, contains: - optic disc - pt of CN II & central retinal vv. entry (optic cup in posteromedial eyeball) -> blind spot - macula lutea - greatest concentration of cones (fovea centralis in the middle) - can be viewed w/ opthalmoscope |

