![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
sternocleidomastoid m.
|
|

Nerve crosses the surface of the superior part of the sternocleidomastoid muscle and lies adjacent to the external jugular vein.http://www.flashcardexchange.com/editcard?rec=%20yui-rec1&id=51919214#tab2
|
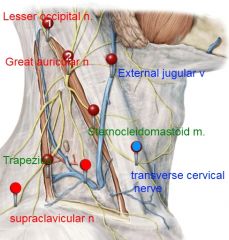
great auricular nerve (C2,C3)
|
|

|
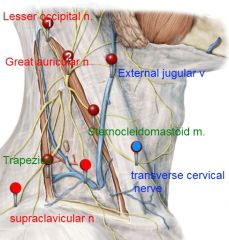
transverse cervical nerve (C2, C3).
it courses transversely across the sternocleidomastoid muscle to provide cutaneous sensory innervation over the anterior region of the neck. |
|
|
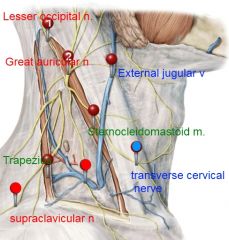
medial supraclavicular nerve
br of supraclavicular nerve (C3, C4). |
|
|
accessory nerve (CN XI)
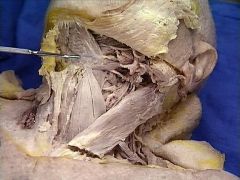
in the fascia of the posterolateral triangle. It passes on the deep surface of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. It then emerges from a point slightly superior to the middle of the posterior edge of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. It crosses the posterolateral triangle, passing inferiorly and posteriorly in the fascia between the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles. About 2 cm above the clavicle, it passes to the deep surface of the trapezius muscle. It innervates the sternocleidomastoid muscle and the trapezius muscle. |
|
|
omohyoid m.
|
|
|
external jugular vein
|
|
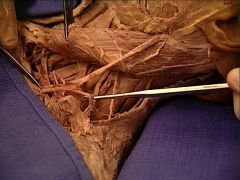
|
transverse cervical v.
|
|

|
subclavian v.
|
|
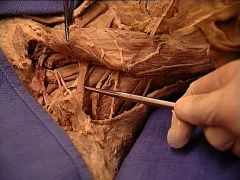
|
transverse cervical a.
|
|
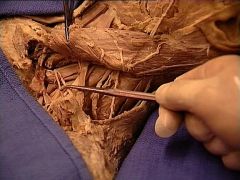
|
suprascapular a.
|
|

|
scalenus anterior m.
transverse cervical artery [tip of probe] and suprascapular artery as they arise from the thyrocervical trunk and pass anterior to the ______ |
|
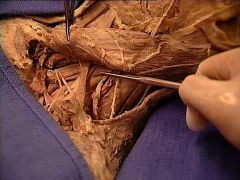
|
scalenus medius and posterior muscles
|
|
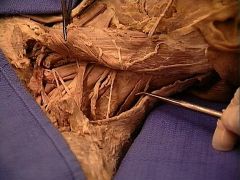
|
splenius capitis muscle
|
|

|
brachial plexus trunks
(upper, middle, and lower) |
|
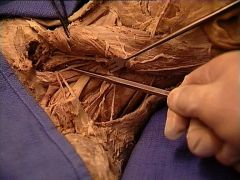
|
phrenic nerve (C3, C4, C5)
as it crosses vertically, along with the ascending cervical artery, on the anterior surface of the scalenus anterior muscle |
|
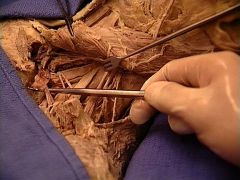
|
subclavian vein
Anterior to the scalenus anterior muscle |
|

|
thyrocervical trunk
The transverse cervical,suprascapular, inferior thyroid, and ascending cervical arteries arise from the thyrocervical trunk [to be dissected in another exercise], which, in turn, is a branch of the subclavian artery. |
|
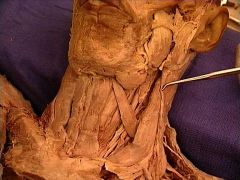
|
external jugular vein
|
|

|
common facial vein
|
|

|
internal jugular vein
|
|
|
hyoid bone
|
|
|
omohyoid muscle.
|
|
|
sternohyoid muscle
|
|
|
sternothyroid muscle
|
|

|
thyrohyoid muscle
|
|
|
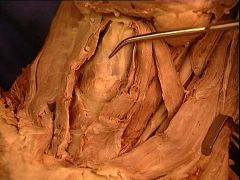
thyroid cartilage
with its laryngeal prominence |
|
|
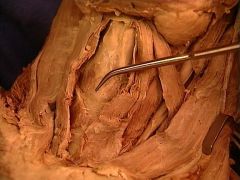
cricoid cartilage
|
|
|
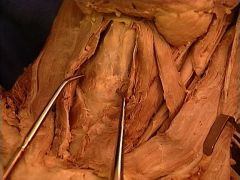
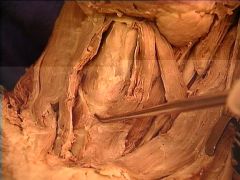
cricothyroid muscles
|
|
|
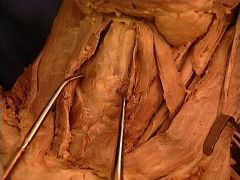
cricothyroid muscles
|
|
|
1st tracheal ring
|
|

|
thyroid gland
|
|

|
digastric muscle,
posterior belly |
|

|
accessory nerve (CN XI)
|
|

|
hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
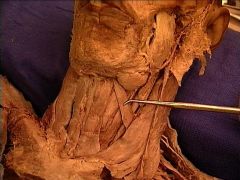
superior to the greater horn of the hyoid bone.it lies medial to the posterior belly of the digastric muscle, and passes lateral to the internal and external carotid arteries |
|

|
ansa cervicalis,
superior root |
|

|
ansa cervicalis
both roots and its branches |
|
|
|
internal jugular vein
|
|
|
|
internal jugular vein
|
|
|
|
internal jugular vein
|
|

|
internal jugular vein
|
|
|
|
internal jugular vein
|
|

|
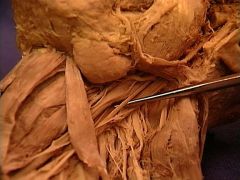
common carotid artery
|
|
|
vagus nerve (CN X)
|
|
|
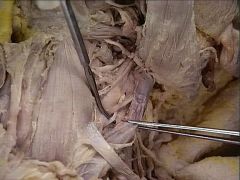
vagus nerve (CN X)
|
|

|
sternothyroid muscle
|
|
|
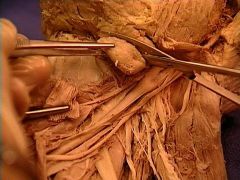
submandibular gland
|
|
|
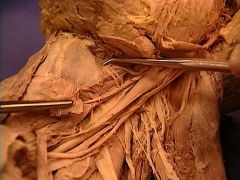
thyrohyoid membrane
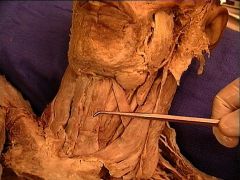
extending between the thyroid cartilage and the hyoid bone. |
|
|
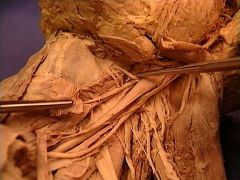
internal laryngeal nerve
a branch of the superior laryngeal nerve, as it pierces the thyrohyoid membrane to supply sensory innervation to the superior portion of the larynx. |
|
|
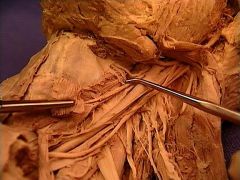
superior laryngeal artery,
a branch of the superior thyroid artery, (由上到下) internal laryngeal nerve, superior laryngeal artery, superior laryngeal vein |
|
|
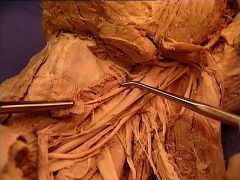
superior laryngeal vein
同行(由上到下) internal laryngeal nerve, superior laryngeal artery, superior laryngeal vein |
|
|
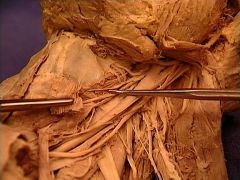
external laryngeal nerve
|
|

|
external carotid artery
|
|

|
internal carotid artery
|
|

|
superior thyroid artery
|
|

|
lingual artery
|
|

|
occipital artery
|
|

|
ascending pharyngeal artery
|
|

|
superior thyroid artery
arises from the anterior border of the external carotid artery and passes inferiorly to the thyroid gland |
|

|
superior laryngeal artery
|
|

|
hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
|
|

|
facial artery
facial artery and facial vein pass in a groove on the deep surface of the submandibular gland. |
|

|
digastric muscle, posterior belly
|
|

|
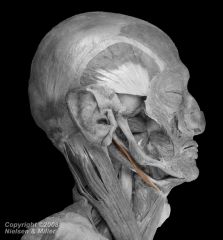
stylohyoid muscle
spanning from the styloid process to the hyoid bone. |
|
|
stylohyoid muscle
spanning from the styloid process to the hyoid bone. |
|

|
hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
|
|

|
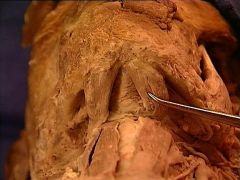
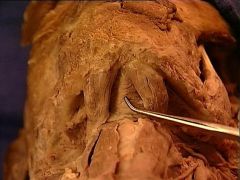
mylohyoid muscle
|
|
|
digastric muscle, anterior belly
|
|
|
mylohyoid muscle
|
|

|
recurrent laryngeal nerve
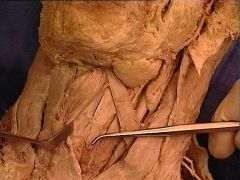
which is located in the tracheo-esophageal groove. The inferior laryngeal nerve may be injured when the inferior thyroid artery is ligated during surgical removal of the thyroid gland |
|

|
inferior thyroid artery
The inferior part of the thyroid gland is supplied by the inferior thyroid artery, a branch of the thyrocervical trunk. The course of the inferior thyroid artery. it crosses the recurrent laryngeal nerve which is located in the tracheo-esophageal groove. |
|
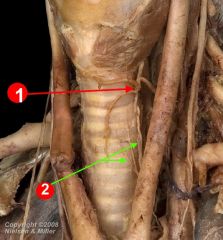
|
1. inferior thyroid artery
2. recurrent laryngeal nerve |

