![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
115 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Anatomy |
Study of structure |
|
|
|
Physiology |
Study of function |
|
|
|
Function influences.... |
The size, shape, action, and reaction of the structure |
|
|
|
_________ designs the specific function |
Structure |
|
|
|
Structure determines ________ possibilities |
Functional |
|
|
|
Embryology |
First 8 weeks of development |
|
|
|
Developmental Biology |
All stages of development |
|
|
|
Cell Biology |
Cell structure and function |
|
|
|
Histology |
Microscopic structure of tissues |
|
|
|
Surface Anatomy |
Surface markings of the body. Observed through visualization and palpatation. |
|
|
|
Gross Anatomy |
Structures viewed without a microscope |
|
|
|
Systemic Anatomy |
Structure of specific systems |
|
|
|
Regional Anatomy |
Specific regions of the body |
|
|
|
Radiographic Anatomy |
Body structures visualized with X-ray, CT, or MRI |
|
|
|
Pathological Anatomy |
Structural changes with disease |
|
|
|
Neurophysiology |
Functional properties of nerve cells |
|
|
|
Endocrinology |
Hormones and how they control body functions |
|
|
|
Cardiovascular physiology |
Function of the heart and blood vessels |
|
|
|
Immunology |
How the body defends itself against disease causing agents |
|
|
|
Respiratory physiology |
Functions of the air passageways and lungs |
|
|
|
Renal physiology |
Functions of the kidneys |
|
|
|
Exercise physiology |
Changes in cell and organ functions as a result of muscular activity |
|
|
|
Pathophysiology |
Functional changes associated with disease and aging |
|
|
|
Levels of organization: |
Chemical Cellular Tissue Organ System Organism |
|
|
|
Chemicals that carry out essential functions at a microscopic level. |
DNA and RNA |
|
|
|
3 things all cells are made of |
1) fatty layer called PLASMA MEMBRANE 2) lipid bilayer that holds a chemical soup called the CYTOPLASM 3) control center where instructions encoded in RNA and DNA are stored is the NUCLEUS |
|
|
|
Cells gathered in a group make up |
Tissue |
|
|
|
Collection of tissues which perform a function |
Organ |
|
|
|
Number of body systems that form the Organism |
Eleven |
|
|
|
Group of organs which carry out a more complete set of functions |
System |
|
|
|
Examples of atoms |
Hydrogen Carbon Nitrogen Oxygen Sodium Magnesium Phosphorus |
|
|
|
Examples of molecules |
Carbohydrates Lipids (fats) Proteins Nucleic Acids Vitamins |
|
|
|
Examples of cells |
Plasma membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus |
|
|
|
Tissues |
Epithelial tissue Connective tissue Muscular tissue Nervous tissue |
|
|
|
Example of organs |
Brain Heart Lungs Small and large intestine Ovaries Stomach |
|
|
|
Examples of organ systems |
Integumentary Skeletal Muscular Nervous Endocrine Lymphatic and Immune Cardiovascular Respiratory Digestive Urinary Reproductive |
|
|
|
Protects the body, helps regulate body temperature, detects sensation like touch |
Integumentary System |
Body system |
|
|
Supports and protects the body, provides surface area for muscle attachments, aids body movement |
Skeletal System |
Body system |
|
|
Produces body movements, such as walking, stabilizes body position, generates heat. |
Muscular System |
Body system |
|
|
Generates action potentials (nerve impulses) to regulate body activities, detects change in the body's internal and external enviorments, interprets the change, and responds by causing muscular contractions or grandular secretions. |
Nervous System |
Body system |
|
|
Regulates body activities by releasing hormones, which are chemical messengers transported in blood |
Endocrine System |
Body system |
|
|
Heart pumps blood through blood vessels, blood carries oxygen and nutrients to cells and carbon dioxide and waste away from cells |
Cardiovascular System |
Body system |
|
|
Returns proteins and fluids to blood, carries lipids from gastrointestinal tract to blood |
Lymphatic System |
Body System |
|
|
Transfers oxygen from inhaled air to blood and carbon dioxide from blood to exhaled air |
Respiratory System |
Body system |
|
|
Acheives physical and chemical breakdown of food, absorbs nutrients and water, eliminates solid waste |
Digestive System |
Body system |
|
|
Produces, stores, and eliminates urine |
Urinary System |
Body system |
|
|
Gonads produce gametes (sperm or oocytes) that unite to form a new organism |
Reproductive System |
Organ system |
|
|
Balance in all body systems |
Homeostasis |
|
|
|
Small changes in any of the levels in the Organism can cause major problems called a |
Disease |
|
|
|
Standing erect with palms forward, head level, eyes facing forward, feet flat, feet directed forward, arms at side |
Anatomical position |
|
|
|
The head (cephalic) region contains |
Skull (cranial) Base of skull (occiptal) Face (facial) Forehead (frontal) Temple (temporal) Eye (orbital, ocular) Ear (otic) Cheek (buccal) Nose (nasal) Mouth (oral) Chin (mental) |
2 |
|
|
Major regions of the human body |
Head (cephalic) Neck (cervical) Spinal Column (vertebral) Trunk Upper extremity Lower extremity |
5 |
|
|
Trunk region contains |
Chest (thoracic) Breastbones (sternal) Breast (mamary) Shoulder blade (scalpular) Back (dorsal) Abdomen (abdominal) Naval (umbilical) Hip (coxal) Loin (lumbar) Between hips (sacral) Pelvis (pelvic) Groin (inguinal) Pubis (pubic) Buttock (gluteal) Perineal |
|
|
|
The upper extremity region includes |
Armpit (axillary) Arm (brachial) Front of elbow (antecubital) Back of elbow (olecranial, cubital) Forearm (antebrachial) Wrist (carpal) Hand (manual) Thumb (pollux) Palm (palmar, volar) Back of hand (dorsum) Fingers (digital, phalangeal) |
|
|
|
The Lower extremity region contains |
Thigh (femoral) Knee Anterior surface (patellar) Posterior surface (popliteal) Leg (crural) Calf (sural) Foot (pedal) Ankle (tarsal) Sole (plantar) Top of foot (dorsum) Heel (calcaneal) Toes (digital, phalangeal) Great toe (hallux) |
|
|
|
Above |
Superior |
|
|
|
Below |
Inferior |
|
|
|
Toward the middle/ cented |
Medial |
|
|
|
Toward the outside |
Lateral |
|
|
|
Closer to point of orgin/ attachment |
Proximal |
|
|
|
Further away from point of origin or attachment |
Distal |
|
|
|
Toward the front |
Anterior (ventral) |
|
|
|
Toward the back |
Posterior (dorsal) |
|
|
|
Same side of midline |
Ipsilateral |
|
|
|
Opposite side of midline |
Contralateral |
|
|
|
Towards the surface |
Superficial |
|
|
|
Toward the core |
Deep |
|
|
|
Membrane closest to the cavity wall |
Parietal |
|
|
|
Membrane closest to the organ inside the cavity |
Visceral |
|
|
|
Dividing medial from lateral, |
Sagittal |
|
|
|
Dividing superior from inferior |
Transverse (horizontal) |
|
|
|
Dividing anterior from posterior |
Frontal |
|
|
|
Dividing the body into two mirror image halves |
Midsagittal |
|
|
|
All other sagittal planes |
Parasagittal |
|
|
|
Two main body cavities |
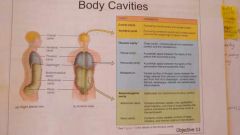
Dorsal Ventral |
|
|
|
Cranial and vertebral cavities make up |
Dorsal Cavity |
|
|
|
Thoracic and abdominopelvic region make up |
The ventral cavity |
|
|
|
This divides the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities |
Diaphragm |
|
|
|
The thoracic cavity contains |
Pleural cavities and mediastinum. Mediastinum contains the pericardial cavity. |
|
|
|
Ventral cavities are an adult derivative of the embryonic cavity called |
Coelom |
|
|
|
Four abdominopelvic quadrants |
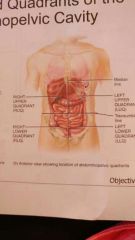
Righ Upper Quadrant Right Lower Quadrant Left Upper Quadrant Left Lower Quadrant
|
|
|
|
Two lines that separate the 4 abdominopelvic quadrants |
Median and transumbilical lines |
|
|
|
The 9 abdominopelvic regions |
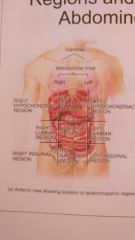
Right: hypochondriac region Lumbar region Inguinal region Left: hypochondriac region Lumbar region Inguinal region Epigastric (top middle) Umbilical region (center) Hypogastric region (bottom middle) |
|
|
|
Organs in RUQ |
Liver and gallbladder |
|
|
|
Organs in LUQ |
Stomach, spleen, left kidney |
|
|
|
Organs in RLQ |
Cecum and appendix |
|
|
|
Organ in LLQ |
Left ovary |
|
|
|
Technique used to visualize structures |
Modality |
|
|
|
Monitors controlled condition |
Receptors |
|
|
|
Receives input and provides output |
Control center |
|
|
|
Bring about change in controlled condition |
Effectors |
|
|
|
Homeostasis feedback loop |
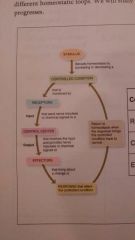
Stimulus Controlled condition Receptors Control center Effectors Response that alters the controlled condition Returns to homeostasis |
|
|
|
A disruption of homeostasis |
Disease |
|
|
|
Determined by observation of a patient |
Signs of disease |
|
|
|
Determined by asking the patient |
Symptoms of disease |
|
|
|
A group of signs and/ or symptoms that commonly occur together |
Syndrome |
|
|
|
Modes of disease transmission |
Contact Common vehicle Airborne Vector |
|
|
|
Causes abnormal homeostasis |
Autoimmune disease |
|
|
|
Positive homeostasis feedback characteristics |
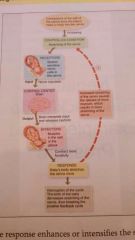
STRENGTHEN or REINFORCE change. Action continues until it is interrupted. Reinforces conditions that do not happen very often |
|
|
|
Negative homeostasis feedback characteristics |
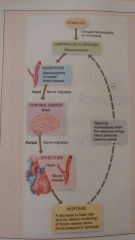
REVERSES a change in a controlled condition. Action stops automatically when set point is reached. Regulate conditions that remain fairly stable over long periods of time. |
|
|
|
Disease transmitted within 1 meter of a person |
Contact transmission |
|
|
|
Infection carried through food, water, or bodily fluids |
Common Vehicle Transmission |
|
|
|
Infectious agents carried on droplets that travel more than 1 meter |
Airborne Transmission |
|
|
|
Disease transmitted by a "third party" |
Vector Transmission |
|
|
|
If the vector is a person who does not appear to be ill they are called a |
Carrier |
|
|
|
Infections that occur in individuals here and there, no evidence it is widespread |
Sporadic Infection |
|
|
|
Infections that are more common in one geographic area than elsewhere |
Endemic Infections |
|
|
|
Infections that occur at a higher than normal level in a population |
Epidemic Infections |
|
|
|
Infections that occur worldwide |
Pandemic Infections |
|
|
|
Hospital acquired infections |
Nosocomial Infections |
|
|
|
Nosocomial Infections that are transmitted from an external environment |
Exogenous |
|
|
|
Nosocomial Infections that arise from organisms already present in or on the patient |
Endogenous |
|
|
|
Us system to metric |

|
|
|
|
Metric system prefixes |
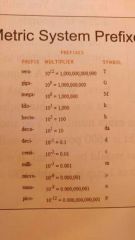
|
|
|
|
Converting US to metric |

|
|

