![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Regional terms, identify what is within them |
Axial and appendicular skeleton Axial- cranium, spine, rib cage Appendicular - appendages |
|
|
|
Identify the 3 body planes |
Sagittal- left and right Frontal- coronal, front and back Transverse- upper and lower |
|
|
|
Identify the 2 internal body cavities and what they contain |
Dorsal- cranial and vertebral cavity Ventral- thoracic and adminopelvic cavities |
|
|
|
Examples of necessary life functions |
Maintaining boundaries, movement, responsiveness, digestion, metabolism, excretion, reproduction, and growth |
|
|
|
Survival needs |
Nutrients- energy, and cell building Oxygen- essential for energy release Water- major body solvent Normal body temp Appropriate atmospheric pressure- gas exchange |
|
|
|
Explain homeostasis and feedback loops |
Homeostasis is the maintenance of relatively stable internal conditions, all organ systems contribute to this dynamic state of equilibrium. Negative loop: dcreased initial stimulus Positive: increases initial stimulus |
|
|
|
Mixtures: Colloids, suspensions, and solutions |
Colloids- heterogeneous, do not settle out, sometime gel like Solutions- homogeneous, true solutions, usually clear Suspensions- heterogeneous, large particles settle out/ separate |
|
|
|
Compounds vs. mixtures |
Compounds contain bonding btwn. Chemical components, are all homogeneous. Mixtures: physically intermixed, can be separated |
|
|
|
Chemically inert vs. reactive elements |
Invert- stable and unreactive, valence shell full Reactive- valence shell not full, able to loose or gain electrons |
|
|
|
Ionic bonds |
The transfer of electrons from one atom to another. Usually salts Cation- looses an electron and is positively charged Anion- gains electron, and is negatively charged. Attraction of the negative charges results in the Ionic bond |
|
|
|
Covenant bonds |
Nonpolar- equal sharing of electrons, electrically balanced. Polar- unequal sharing of electrons, produces polar (dipole) molecule. |
|
|
|
Redox rxns |
Decomposition/ exchange rxns Electron donor is oxidized Electron acceptor is reduced. |
|
|
|
Acids and bases |
Both are electrolytes. Acids- proton donor (release H+) Bases- proton acceptor (take up H+) pH: 7 is neutral Below 7 is acidic, above is basic Buffers resist abrupt changes swings in pH |
|
|
|
Carbohydrates |
Simple sugars, source of cellular fuel. 3 classes: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides |
|
|
|
Lipids |
Insoluble in water 4 main types: Triglycerides - neutral fat Phosophlipids - modified triglycerides Steroids- cholesterol Eicosanoids- prostaglandins |
|
|
|
Proteins |
Are polymers, amino acids are monomers, act as acid or base. 4 levels of structure- primary secondary, tertiary and quaternary. Fibrous proteins (keratin) and globular proteins (enzymes) |
|
|
|
DNA and RNA |
DNA: double stranded helix, penthouse sugar, thymine , directs protein synthesis and replicates self. RNA: uracile, ribose sugar, 3 variations, genetic instructions for protein synthesis |
|
|
|
Intergral protein s vs. peripheral proteins |
Integral: firmly asserted into membrane, hydrophillic and phobic regions, function as transport proteins. Peripheral: loosely attached to integral proteins, function as enzymes |
|
|
|
Cell junctions: |
Tight junction: adjacent intergral proteins fuse together to form impermeable membrane encircled cell. Desmosomes: spot welds that anchor cells together. Linker proteins connect plaques, keratin filaments gives stability. Reduces tearing possibilities Gap junctions: transmembrane proteins form pors/ connexon, allowing small molecules pass |
|
|
|
Active transport vs. passive |
Active: ATP, larger solutes, against [] gradient Passive: substances move with [] gradient |
|
|
|
The cell cycle |
Interphase : G1(growth), S(growth and DNA synthesis), and G2 (final preparations for division (mitotic phase) Mitotic phase: prophase, metaphase, anaphase (cytokinesis begins), telophase, cytokinesis ends |

|
|
|
Protein synthesis- transcripton |
Transcription: DNA info is coded in mRNA thru 3 steps. Initiation- RNA polymerase separates DNA strands Elongation- RNA polymerase add complimentary nucleotides Termination- stop signal |

|
|
|
Cytosolic protein degradation |
Autophagy: bits put into autophagosomes and degraded by lysosomes. Ubiquitins: tag damaged/ unneeded materials and is digested by enzymes or proteasomes |
|
|
|
Types of tissue: epithelial |
Forms boundaries, have polarity, apical or basal, specialized contacts, regeneration, avascular, innervated 2 main types: covering/ lining, and glandular epithelia Simple or stratified, squamous/ custodial or columnar |
|
|
|
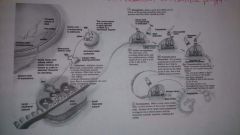
Protein synthesis- translation |
Translation: genetic info (base sequence of nucleic acid) is decoded by ribosome to form polypeptide (proteins). Initiation- tRNA and mRNA scan for start codon, Functional ribosome is formedElongation- tRNA binds complimentary codons in A site, peptide bond forms and translocatesTermination- stop codon enters: A site, peptide is released and pressed into 3D form |
|
|
|
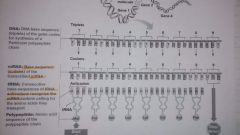
Summary: DNA to proteins. |
DNA gene triplets > mRNA codons > tRNA anticodons > amino acid polypeptide |
|
|
|
Resting membrane potential |
Diffusion causes Ionic imbalances that polarize membrane, due to potassium Active transport process maintains membrane potential |
|

