![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
113 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Who am I?
I divide the body into equal right and left halves |
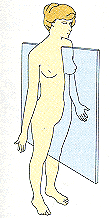
Median/Midsagittal Plane
|
|
|
Who am I?
I am a very "well-developed" supraspinous ligament |
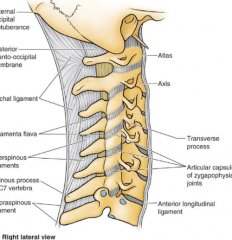
Ligamentum Nuchae
|
|
|
Who am I?
I am the motor nerve supply to the trapezius muscle. |
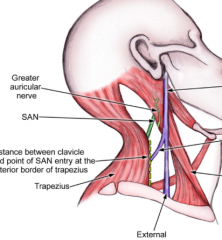
Spinal Accessory Nerve
(Cranial Nerve 11) |
|
|
Who am I?
I attach to the superior angle of the scapula |
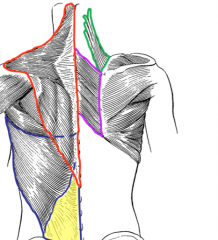
Levator Scapulae
|
|
|
Who am I?
I supply motor innervation to the deep back muscles |
Dorsal Primary Rami
|
|
|
Who am I?
I am located immediately posterior to an IV disc and immediately anterior to a facet joint. |
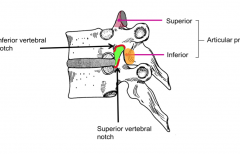
IV foremen
|
|
|
Who am I?
The vertebral arteries pass through me before they reach the skull |
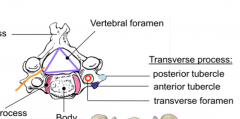
Transverse Foramina
From C6 through atlas then they wrap around and enter the skull through the Foremen magna |
|
|
Who am I?
I am glistening white. I have "teeth" and I stabilize the spinal cord. |
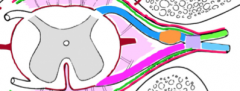
Denticulate ligament
|
|
|
Who am I?
I cover the end of long bones in synovial joints. |
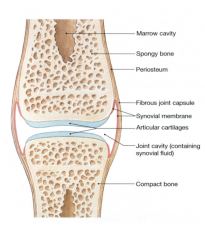
Articular (hyaline) cartilage
|
|
|
Who am I?
I may become stretched or torn in a whiplash injury. |
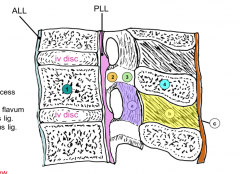
Anterior Longitudinal Ligament (ALL)
|
|
|
Who am I?
A cancer cell within me can "ride" all the way to the cranial cavity. |
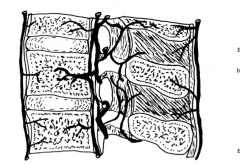
Vertebral Venous Plexus
|
|
|
Who am I?
I am not a nerve root, but I am found within the cauda equina |
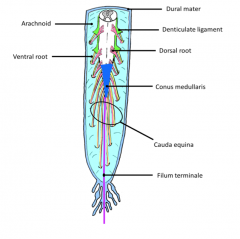
Filum Terminale
|
|
|
Who am I?
I come to an end at the S2 vertebral level |
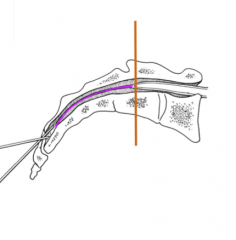
Dural Sac (aka Fecal sac)
|
|
|
What is the embryonic period?
|
The period of organogenesis that takes place from the 3-8th week of fertilization.
|
|
|
When is the bilaminar disc formed in a zygote?
|
The second week
|
|
|
What is significant of the 18th day after fertilization (early in the third week)?
|
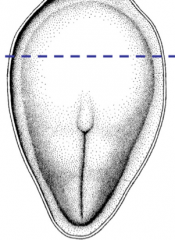
Formation of the trilaminar disc
|
|
|
What are the three germ layers of the trilaminar disc?
|
Ectoderm
Mesoderm Endoderm |
|
|
What is the period from week 9 to week 38 of pregnancy?
|
The fetal period
|
|
|
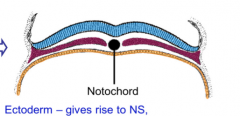
What does the ectoderm give rise to?
|
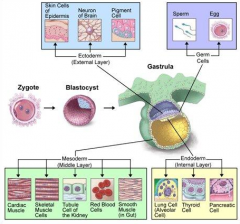
Nervous System
Epidermis Hair Nails Sweat Glands |
|
|
What does the mesoderm give rise to?
|
Muscle
Bone Connective tissue blood Gonads Kidneys |
|
|
What does the endoderm give rise to?
|
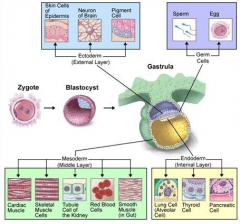
Epithelial lining of respiratory
Genitourinary System Gastrointestinal System |
|
|
From what germ layer do the kidneys arise?
|
Mesoderm
|
|
|
From what germ layer do the sweat glands arise?
|
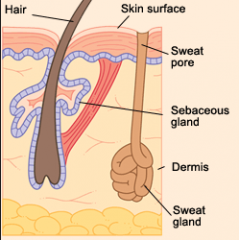
Ectoderm
|
|
|
From what germ layer does connective tissue arise?
|
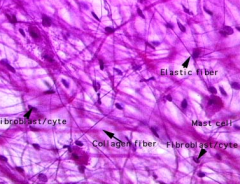
Mesoderm
|
|
|
From what germ layer does the epithelial lining of the respiratory system arise?
|
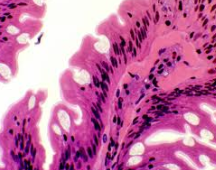
Ectoderm
|
|
|
What is the notochord?
|
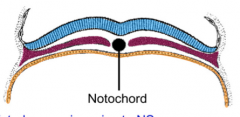
The organizing device in the midline of the embryo that aids the ectoderm to form the neural tube.
|
|
|
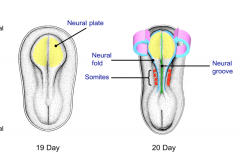
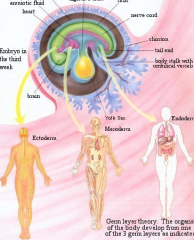
What is neurulation?
|
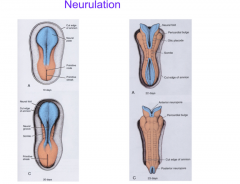
The formation of the neural tube-between days 19 and 28 the ectoderm folds in on itself to form the primordial central nervous system.
|
|
|
What is the difference between the neural plate, groove, and fold?
|
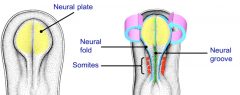
The plate is the ectoderm cells that bend at the neural grove. The neural fold is the piece that folds to form the tube.
|
|
|
What are somites?
|
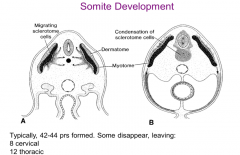
Block like elevations on the dorsal side of the embryo. There are 42-44 pairs of somites of which some are lost leaving 35 pairs:
4 Occipital 8 Cervical 12 Thoracic 5 Lumbar 5 Sacral 8-10 Coccygeal |
|
|
At what days to the superior and inferior sides of the neural tube close?
|
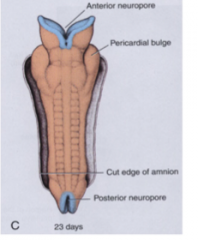
Days 25 and 28 respectively
|
|
|
What does the CNS include?
|
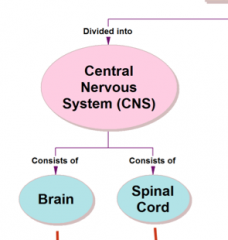
The brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
From where do the neural crest cells originate?
|
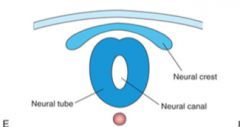
The margins of the neural groove which separate from the surrounding ectoderm to give rise to many other tissues.
|
|
|
Describe neural crest cells.
|
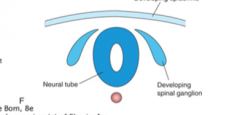
-Derive from a dorsal portion of neural tube
-Migrate into the body and enter multiple organs and tissues -Differentiate into numberous cellular and tissue structures |
|
|
What is the fourth germ layer?
|
This term is commonly applied to neural crest cells due to the number of tissues they give rise to.
|
|
|
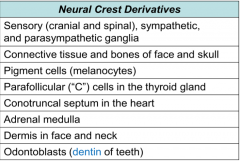
What tissues are derived from neural crest cells?
|
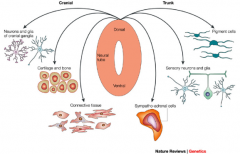
-Sensory, sympathetic, and parasympathetic ganglia
-Connective tissue and bones of the face and skull -Pigment cells (melanocytes) -Parafollicular (C) cells in the thyroid gland -Conotruncal septum in the heart -Adrenal medulla -Dermis in the face and neck -Odontoblasts (dentin [not enamel] of teeth) |
|
|
What tissues to somites give rise to?
|
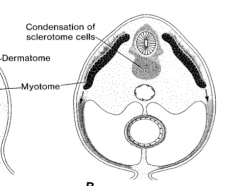
-Dermatome (dermis of skin)
-Myotome (skeletal muscle) -Sclerotome (bone and hard tissues) |
|
|
What type of somite surrounds the neural tube?
|
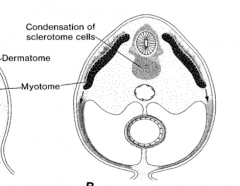
Sclerotomes because they give rise to the bone that will surround the spinal cord.
|
|
|
What will notochord tissue eventually give rise to?
|
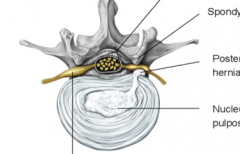
The nucleus pulposus of intervertebral discs.
|
|
|
If myotome cells migrate posterior to the notochord what nerves will they be innervated by?
|
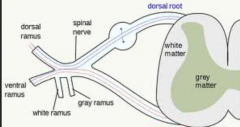
Dorsal primary rami (DPR)
|
|
|
Why are muscles innervated by multiple spinal nerves?
|
Because most muscles are formed from portions of several myotomes and the spinal nerve supplying each somitic segment of muscle remains with that muscle wherever it migrates.
|
|
|
Describe the formation of the upper limb during the embryonic period.
|
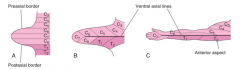
-Buds appear at week 4 as small projections in the coronal plane
-At week 6 upper limb moves horizontally in sagittal plane; by week 8 it rotates laterally 90 degrees |
|
|
Which somites compose the upper limb?
|
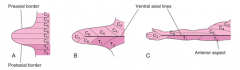
C4-8 and T1 and T2
|
|
|
Somites of the anterior and posterior surface of the limb bud form which muscles respectively?
|
Flexor and Extensors
|
|
|
What is a dermatome?
|
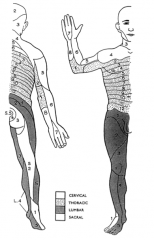
An area of skin supplied by a single spinal nerve
|
|
|
What is a myotome?
|
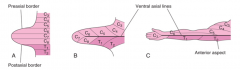
The mass of skeletal muscle innervated by a single spinal nerve.
|
|
|
How would abnormalities in the third or fourth week of development affect the nervous system?
|
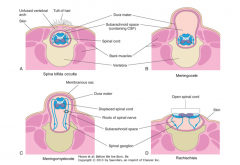
During the neural tube folding this may involve meninges, vertebrae, overlying muscles and skin. This occurs in 1/1000 births
|
|
|
What are neural tube defects in the spinal cord region called?
|
Spina bifida-all NTDs involving the spinal region
|
|
|
Why do pregnant women take folic acid?
|

To prevent around 70% of neural tube defects (NTDs)
|
|
|
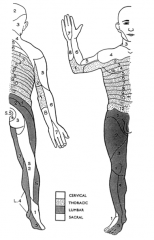
What is spina bifida occulta?
|
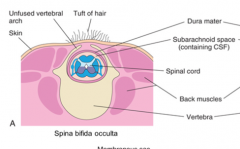
10% of the population has this asymptomatic type of spina bifida where the vertebral arch is not completely formed sometimes recognized by a tuft of hair or dimple in the lower back?
Occulta = hidden |
|
|
What is a meningocele?
|
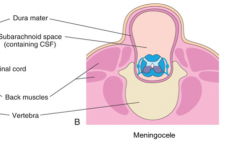
This is a herniation of the dural sac through an incompletely formed vertebral arch during embryonic development. This is termed spina bifida cystica
|
|
|
What is a meningomyelocele?
|
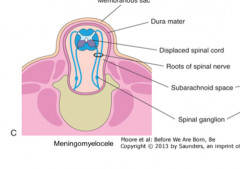
A herniation of the dural sac and the spinal cord through an incompletely formed vertebral arch during embryonic development. This is called spina bifida cystica with meningomyelocele.
|
|
|
What is rachischisis?
|
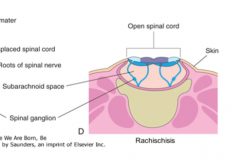
This is the most severe form of spina bifida where the spinal cord opens to the dorsal side of the body exposed to the outside world and not covered by skin.
|
|
|
Why does neural tube closure affect vertebral arch development?
|
Due to the migration of somites, if the neural tube does not close the vertebral arch development and overlying soft tissue will not be induced.
|
|
|
Name the disorder of the child in the picture.
|
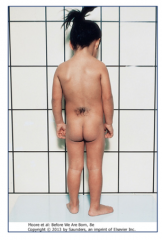
Spina bifida occulta
|
|
|
Name the disorder of the child in the picture.
|
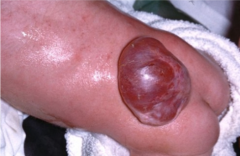
Spina bifida cystica
|
|
|
What are the two divisions of the nervous system?
|
The central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS)
|
|
|
How is the PNS divided anatomically?
|
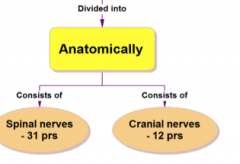
Into 31 spinal nerves and 12 cranial nerves
|
|
|
What muscle is innervated by the eleventh cranial nerve?
|
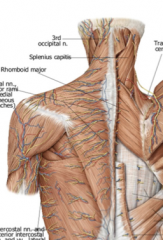
Trapezius muscle
|
|
|
What is the difference between the somatic and the autonomic nervous system?
|
The SNS controls the body's external environment (soma = body) and the ANS controls the body's internal environment.
|
|
|
What are the three parts of the functional neuron?
|
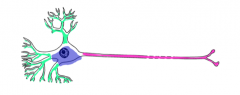
-Cell body containing a nucleus
-Single axon -Several dendrites |
|
|
What is the functional and anatomic unit of the nervous system?
|
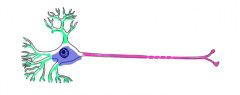
The neuron
|
|
|
What are the functional classifications of PNS neurons
|
-Motor/Efferent neurons
-Sensory/Afferent neurons |
|
|
What are efferent neurons?
|
Transmit impulses away from the CNS to various parts of the body such as skeletal muscle and viscera.
Somatic motor neurons travel toward skeletal muscle Visceral motor neurons travel toward visceral organs |
|
|
What are Afferent neurons?
|
Transmit impulses from the body (internal and external stimuli) toward the CNS
|
|
|
Where are the cell bodies of motor neurons located?
|
The central nervous system
|
|
|
What has a single axon and conducts impulses away from the cell to effector tissue?
|
Motor neurons
|
|
|
What is the difference from damaging a few motor axon to dissection of the entire nerve?
|
The consequences range from weakening the contraction of the muscle to paralyzing the effector muscle completely
|
|
|
What is the difference between multipolar neurons and pseudo-unipolar neurons?
|
Multipolar are motor neurons and pseudo-unipolar neurons are sensory neurons histologically
|
|
|
What is a ganglion?
|
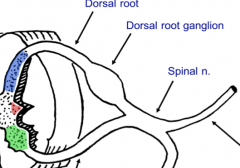
A collection of cell bodies outside of the central nervous system. The ganglion does not indicate the neurons existing within.
|
|
|
Which is longer in the sensory neuron-the peripheral or the central process?
|

The peripheral process that serves as a dendrite or specialized receptor ending.
|
|
|
What are the types of functions of specialized receptor processes?
|

Exteroceptors
Proprioceptors Interoceptors |
|
|
What are exteroceptors?
|
Sensory neuron peripheral process that mediates general sensations of pain, touch, temperature, and pressure
|
|
|
What are proprioceptors?
|
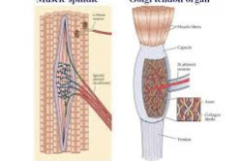
Sensory neuron peripheral process that in muscles, ligaments, joint capsules provides body its sense of position
|
|
|
What are Interoceptors?
|
Sensory neuron peripheral process within internal organs and convey sensory information such as ischemia, constriction, and dilation.
|
|
|
What is paresthesia?
|

The pins and needles feeling from cutting off the blood supply to sensory nerves
|
|
|
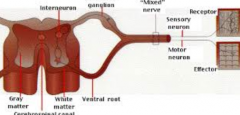
Which portions in the image above are white matter and gray matter?
|
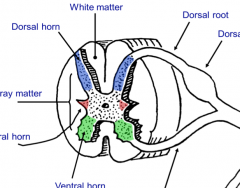
White matter are myelinated tracts of axons that are carrying sensory and motor information in the peripheral part of the spinal cord
Gray matter is the butterfly structure that represents nerve cell bodies in the spinal cord |
|
|
What are the dorsal horns of the gray matter in the spinal cord?
|
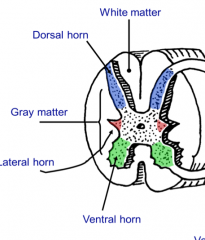
The entry zone of the central processes of sensory neurons.
|
|
|
What are the ventral horns of the gray matter in the spinal cord?
|
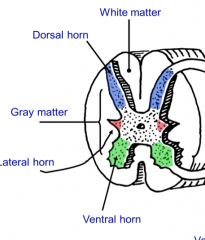
The location of the cell bodies for our somatic motor neurons also the exit zone of the axons of somatic motor neurons and preganglionic autonomic neurons
|
|
|
What are lateral horns in the spinal cord?
|
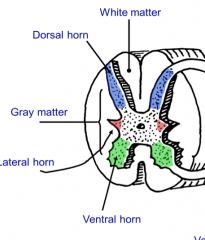
T1-L2 and S2,3, and 4 levels have these present and contains cell bodies of preganglionic autonomic neurons. These axons exit through the ventral horn and enter the ventral root.
|
|
|
Where are the cell bodies of sensory neurons?
|
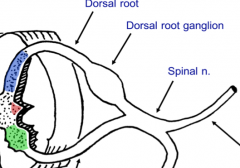
Dorsal root ganglion
|
|
|
What is a spinal nerve?
|
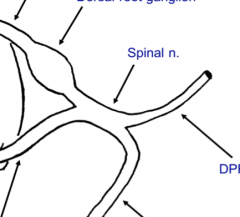
The mixed nerve (contains motor and sensory axons) where the dorsal and ventral root combines.
|
|
|
What nerves are contained in the DPR and VPR?
|
Both motor and sensory in both therefore these are "mixed" nerves
|
|
|
What do DPRs innervate?
|
These supply segments of deep back muscles and a small strip of dermis on the posterior of the body.
|
|
|
What do VPRs innervate?
|
The lateral an anterior dermis through the lateral and anterior cutaneous branches.
|
|
|
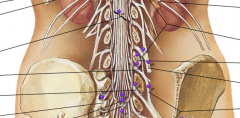
Why are the nerves on the superficial side of trapezius not associated with the muscle?
|
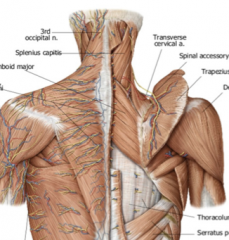
They are innervating a small medial to lateral strip of skin on the back.
|
|
|
True or False: The spinal nerves on the superficial side of trapezius innervate the muscle.
|
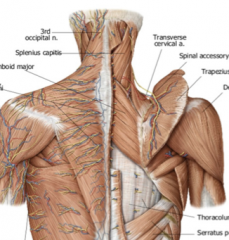
FALSE the segmented nerves and blood vessels are the cutaneous muscles coming out to the skin.
|
|
|
True or False: The spinal cord and the vertebral column are the same length.
|
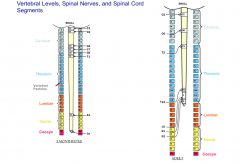
BOTH. In adults the spinal cord is shorter than the VC, but in infancy they are the same length.
|
|
|
How many pairs of spinal nerves exist?
|
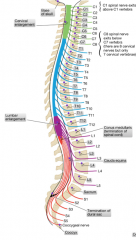
31
-Cervical 8 -Thoracic 12 -Lumbar 5 -Sacral 5 -Coccygeal 1 |
|
|
The 5th cervical nerve exits the IV foramen between which two vertebrae?
|
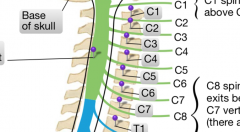
C4 and C5
|
|
|
The second thoracic vertebrae exits the IV foramen between which two vertebrae?
|
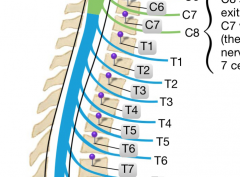
T2 and T3
|
|
|
Where are the enlargements of the spinal cord in adults?
|
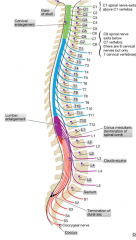
The C4-T1 segment that goes out to the upper limb
The L1-S3 segment that goes out to the lower limb |
|
|
At what vertebral level does the spinal cord and the dural sac end?
|
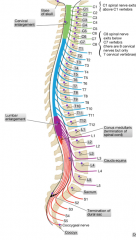
The spinal cord ends at L1/L2 (L3 in children) and the dural sac ends at the S2 level.
|
|
|
What vertebral level is parallel with the Iliac Crest?
|
L4
|
|
|
Describe from superficial to deep the layers that a lumbar puncture passes through
|
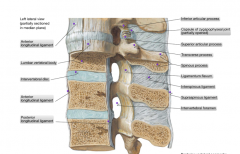
Skin-Superficial facia-lumbar facia-supraspinous ligament-interspinous ligament-ligamentum flavum (pop)-dura mater-arachnoid mater-SUBARACHNOID SPACE WINNER
|
|
|
What is meningitis?
|
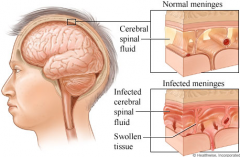
An inflammation of the meninges which can lead to a severe headache, stiff neck "nuchal rigidity", and photophobia
|
|
|
What is photophobia?
|
A fear or sensitivity to bright light. This is a possible symptom of meningitis.
|
|
|
What is spondylolysis?
|
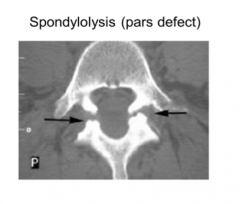
The pars defect is a defect in the lumbar spine in which the pars interarticularis (the segment between the superior and inferior articular processes is incomplete
|
|
|
What is spondylolisthesis?
|
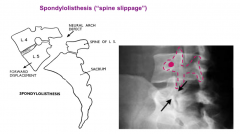
A slippage of a vertebra due to the pars defect or spondylolysis. This is a common injury in young athletes
|
|
|
What is the scottie dog fracture?
|
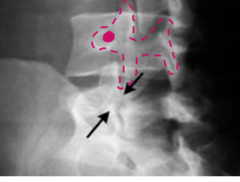
A fracture of the pars interarticularis as seen from an oblique x-ray in which the "dog" drawn from the superior to the inferior facet and transverse process (eye) has a fracture around its neck.
|
|
|
Describe the intervertebral disc
|
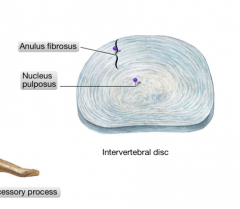
It is a fibrocartilaginous tissue to make a symphysis type joint. They resist compression and are the body's shock absorbers.
|
|
|
What are the two components of the IV disc?
|
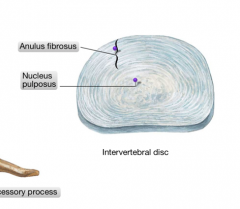
The anulus fibrosus (firmly bound to the bodies) and the nucleus pulposus (which is a highly hydrated colloid that derives from the neural tube of the embryo)
|
|
|
What is caused by a breakage in the anulus fibrosus?
|
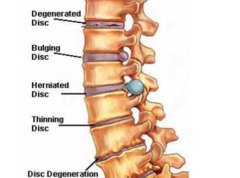
A IV disc herniation that causes some of the nucleus pulposus to leak out and impinge on descending nerve roots.
|
|
|
Why do IV herniations commonly occur posterior to the vertebral body?
|
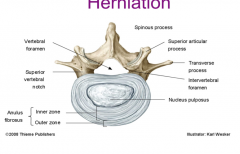
The nucleus pulposus is located posterior causing the anulus fibrosus to be thinner to the posterior more likely to tear.
|
|
|
Which nerve would be affected by a herniation of the IV disc between L2 and L3?
|
The L3 nerve
|
|
|
What is TOS?
|
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome caused by the existence of a cervical rib at C7 which can cause numbness in the upper limb
|
|
|
What spinal nerves innervate the diaphragm?
|
C3,4, and 5
|
|
|
What muscles form the suboccipital triangle?
|
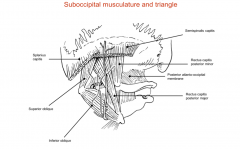
Rectus capitis posterior major
Superior oblique Inferior oblique |
|
|
Where are the attachments of the rectus capitis posterior major?
|
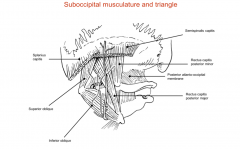
From the base of the skull to the spinous process of C2
|
|
|
What are the attachments of the inferior oblique muscle?
|
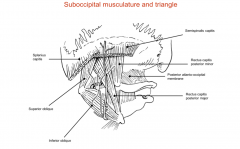
The spinous process of the C2 to the lateral mass of C1
|
|
|
What are the attachments of the superior oblique?
|
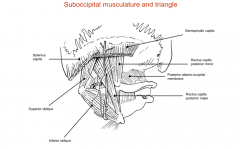
The lateral mass of C1/atlas to the base of the skull
|
|
|
What are the attachments of the rectus capitis posterior minor?
|
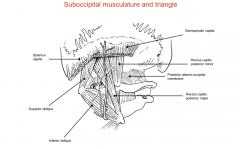
The posterior tubercle of atlas to the base of the skull
|
|
|
What is the greater occipital nerve?
|
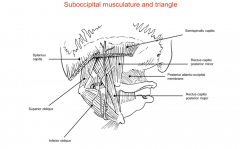
A part of the DPR of C2 that is the big sensory nerve that supplies the posterior part of the scalp and wraps around the inferior oblique muscle then passes through spinalis capitis and trapezius
|
|
|
What is the suboccipital nerve?
|
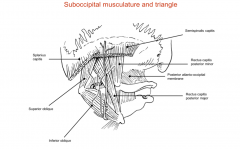
It is a motor nerve that comes from the DPR of C1
|

