![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
98 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is liposuction?
|
Surgically removing fatty tissue by using a needle
|
|
|
What is the basic chemical structure of a fat/lipid molecule?
|
Backbone of glycerol attached to three or more fatty acid chains
|
|
|
What is the normal stimulus for depositing of fat in our bodies?
|
Taking in more calories than you lose
|
|
|
Define the term peristalsis.
|
Waves of muscular contractions that force food down the digestive tract
|
|
|
Where does the digestion of protein begin in the human body?
|
Stomach
|
|
|
What two organs release secretions into the small intestine that aid in the digestion of lipids?
|
Liver and pancreas
|
|
|
What are the two secretions that the liver and pancreas release and what function do each perform?
|
Liver: makes bile and gallbladder releases it; emulsifies fat and breaks down into smaller droplets
Pancreas: makes enzymes that attack smaller fat droplets |
|
|
Where are the lipids absorbed in our digestive system?
|
Villi in the small intestines
|
|
|
Briefly state what the basal metabolic rate (BMR) tells you about the human body.
|
Energy needed to keep body functioning at a basic level
|
|
|
For the experimental subject in the video, what was her measured BMR?
|
6,200 kJ
|
|
|
What happened to her BMR when she began wiggling her hands and feet?
|
It went up; needed more energy
|
|
|
Where is the major site of fat deposition in females?
|
Hips
|
|
|
Where is the major site of fat deposition in males?
|
Waist
|
|
|
What are some of the functions of stored fat in our bodies?
|
Insulation and protection
|
|
|
What are the four layers of the digestive system tube (i.e. four tunics?)
|
Mucosa (innermost)
Submucosa Muscularis Serosa (outermost) |
|
|
What are the general properties of the mucosa layer of the digestive system?
|
Innermost lining
Epithelium resting on lamina propria and a small amount of smooth muscle (muscularis mucosa) Simple columnar epithelium |
|
|
What are the general properties of the submucosa layer of the digestive system?
|
Beneath the mucosa
Layer of connective tissue containing blood vessels, nerves and glands [esp. nerve plexuses like Meissner's plexus) |
|
|
What are the general properties of the muscularis layer of the digestive system?
|
Several layers of smooth muscle beneath the submucosa
An inner circular and outer longitudinal layer In the stomach, there is an additional oblique layer Peristalsis occurs here Nerve plexuses (Meissner's plexus) present |
|
|
What are the general properties of the serosa (adventitia) layer of the digestive system?
|
Outermost layer of connective tissue (adventitia) or simple epithelium (serosa)
|
|
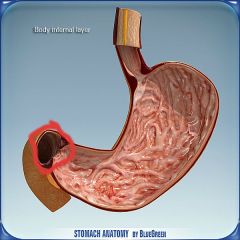
What is this?
|
Pyloric sphincter
|
|
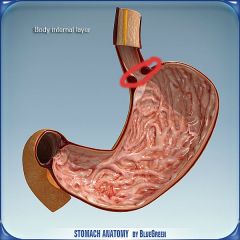
What is this?
|
Cardiac sphincter
|
|
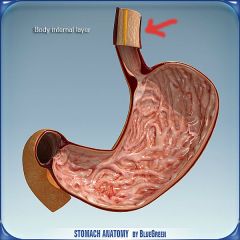
What is this?
|
esophagus
|
|
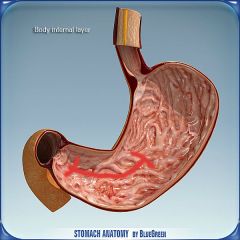
What is this?
|
Pyloric region of the stomach
|
|
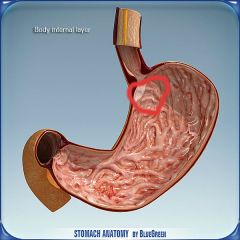
What is this?
|
Cardiac region of the stomach
|
|
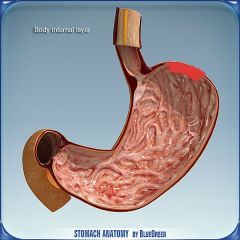
What is this?
|
Fundus region of the stomach
|
|
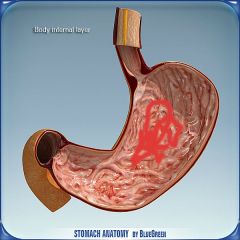
What is this?
|
Body region of the stomach
|
|
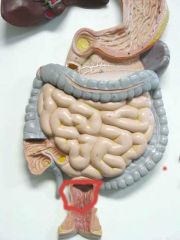
What is this?
|
Rectum
|
|
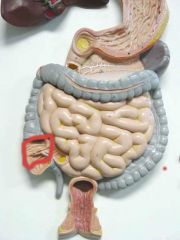
What is this?
|
Cecum
|
|
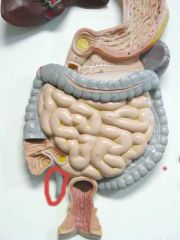
What is this?
|
Appendix
|
|
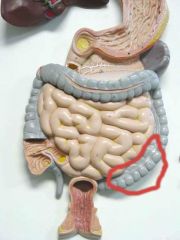
What is this?
|
Sigmoid colon/large intestine (part where it curves in)
|
|
What is this?
|
Ileum of the small intestine
|
|
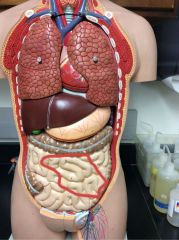
What is this?
|
Jejunum of the small intestine
|
|
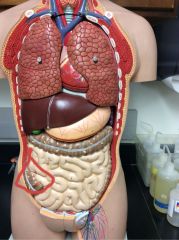
What is this?
|
Ascending colon/large intestine
|
|
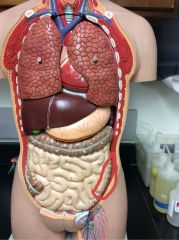
What is this?
|
Descending colon/large intestine
|
|
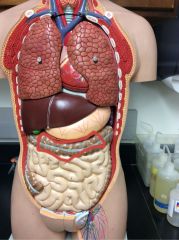
What is this?
|
Transverse colon/large intestine
|
|
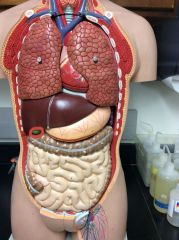
What is this?
|
Gallbladder
|
|
What is this?
|
Liver
|
|
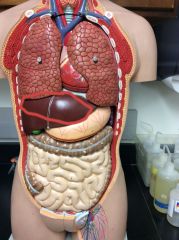
What is this?
|
Esophagus
|
|
What is this?
|
Parotid gland
|
|
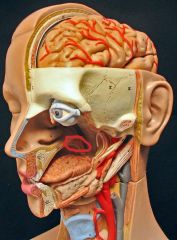
What is this?
|
Soft palate
|
|
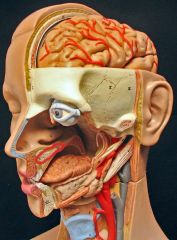
What is this?
|
Hard palate
|
|
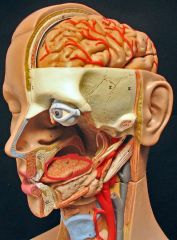
What is this?
|
Tongue
|
|
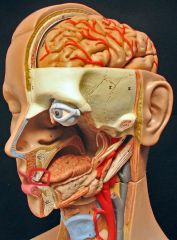
What is this?
|
Teeth
|
|
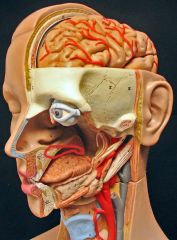
What is this?
|
Oral cavity
|
|
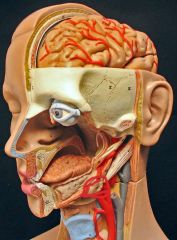
What is this?
|
Submandibular salivary gland
|
|
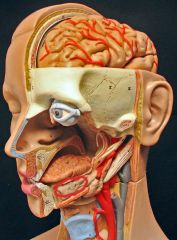
What is this?
|
Sublingual salivary gland
|
|
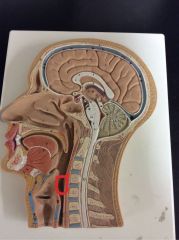
What is this?
|
Laryngopharynx
|
|
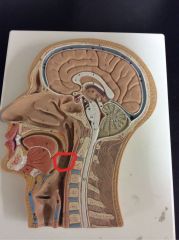
What is this?
|
Oropharynx
|
|
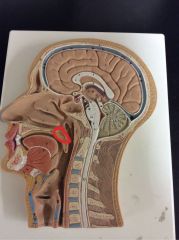
What is this?
|
Soft palate
|
|
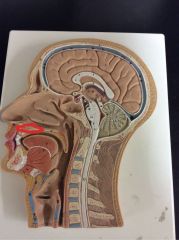
What is this?
|
Hard palate
|
|
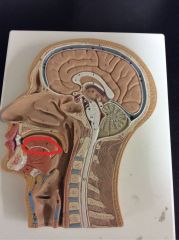
What is this?
|
Tongue
|
|
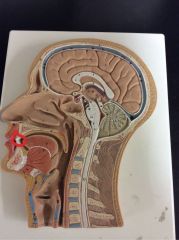
What is this?
|
Teeth
|
|
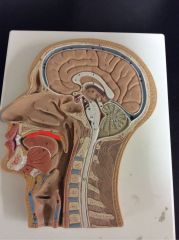
What is this?
|
Oral cavity
|
|
|
How can you distinguish the stomach slides?
|
Gastric pits on low power
Mucosa with simple columnar epithlieum and lamina propria NO GOBLET CELLS |
|
|
What do the chief cells of the stomach make? Parietal cells?
|
Chief=pepsinogen, gastric lipase
Parietal=HCl and intrinsic factor |
|
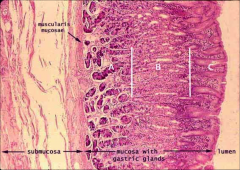
What is this a slide of?
|
The stomach
|
|
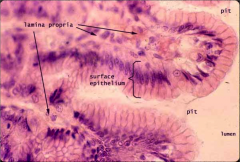
What is this a slide of?
|
The stomach
|
|
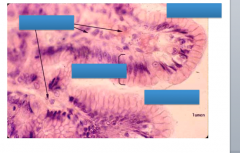
Label: gastric pits, simple columnar epithelium and lamina propria
|
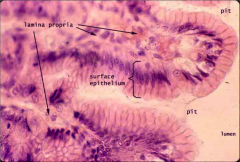
|
|
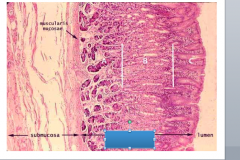
Label: mucosa with gastric pits
|
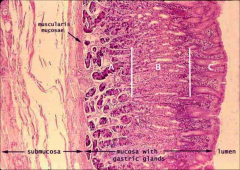
|
|
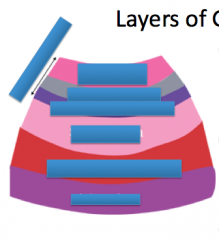
Label the layers of the gastrointestinal tract
|
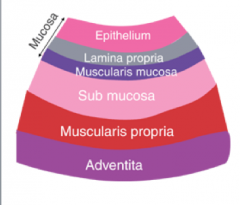
|
|
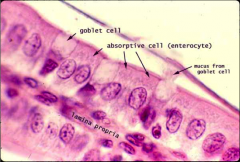
What is this?
|
Small intestine (high power)
|
|
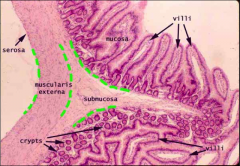
What is this?
|
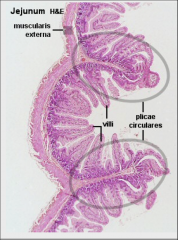
Small intestine (low power)
|
|
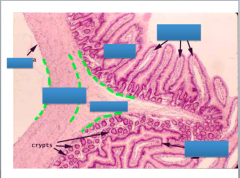
Label the four tunics:
Mucosa Submucosa Muscularis (with circular and longitudinal muscle layers) Serosa And the villi |
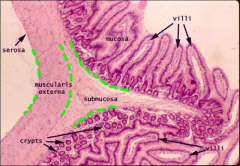
Lamina propria are the little blue dots with the crips
Circular muscle above longitudinal muscle |
|
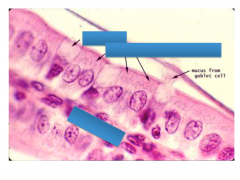
Label simple columnar epithelium with goblet cells
|
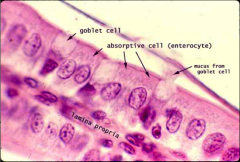
Absorptive cell=simple columnar epithelium
|
|
|
What distingushes a small intestine slide?
|
Crypts (pits) and villi
Goblet cells |
|
|
What do the crypts do (of small intestine)?
|
Provide protection for stem cells
|
|
|
What do villi do?
|
Increase surface area for nutrient reabsorption
|
|
|
What are the key identifiers of a colon slide?
|
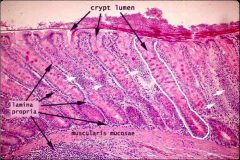
Crypts, but no villi!
|
|
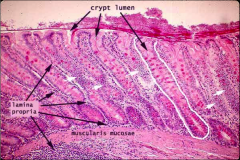
What is this?
|
A colon slide (low power)
|
|
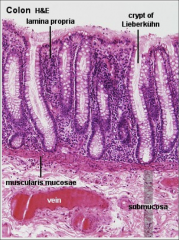
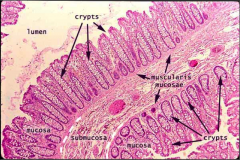
What is this? What do we need to label?
|
Colon slide, high power
Intestinal glands (light colored pockets) |
|
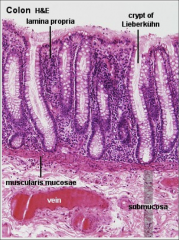
Where is the simple columnar epithelium with many goblet cells?
|
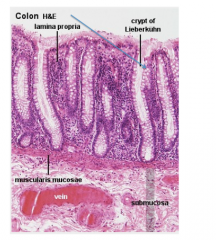
Just pointing to one
Goblet cell=clear circle |
|
|
Why do the large intestines not need villi?
|
Small intestines need to absorb small molecules and nutrients
Large intestines only absorb water...don't need a whole lots of room for that |
|
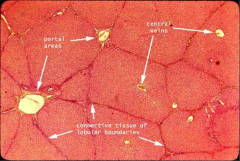
What is this a slide of?
|
The liver, on low power
|
|
|
What is present in the portal triads of a liver lobule?
|
Bile duct
Hepatic artery Hepatic vein Lymphatic vessels (not always present) |
|
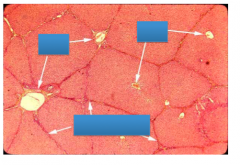
Label the liver lobules with hepatocytes, central vein and portal triad area
|
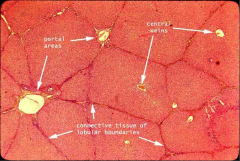
See here
|
|
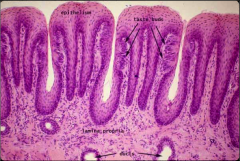
What is this a slide of?
|
The tongue, low power
|
|
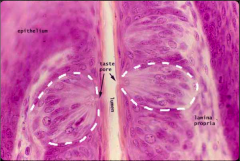
What is this a slide of?
|
The tongue, high power
|
|
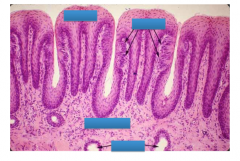
Where are the taste buds? Where are they located?
|
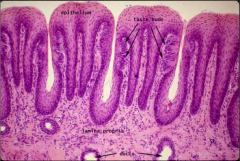
Surface epithelium of the tongue
|
|
|
What are the exocrine cells of the pancreas?
|
Acinar cells
Release digestive enzymes Look like clusters of grapes |
|
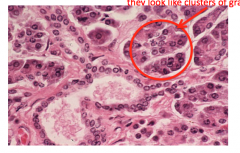
What slide is this and what is circled?
|
Pancreas
Pancreatic acini (exocrine) cells |
|
|
What are the endocrine cells of the pancreas?
|
Pancreatic islets
"islets of Langerhans" release endocrine hormones They are less defined and lighter and than acini...acini surround them |
|
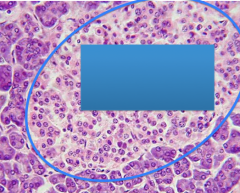
What slide is this and what is circled?
|
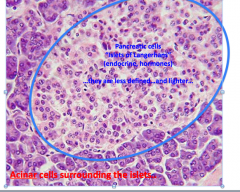
Pancreas
Pancreatic islets |
|
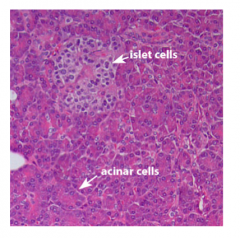
What is this a slide of?
|
The pancreas
|
|
|
List, in order, the structures of the gastrointestinal tract that food passes through beginning with the oral cavity and ending with the anus.
|
1. Oral cavity
2. Pharynx 3. Esophagus 4. Stomach 5. Small Intestine 6. Large Intestine 7. Anus OPE SSLA |
|
|
The liver and pancreas are sometimes termed accessory digestive organs. What are the major functions of these organs in the digestive process?
|
Liver: metabolizes fats and produces bile that emulsifies fats
Pancreas: gland that secretes pancreatic juice into the duodenum where it mixes with bile to digest food (breaks down proteins) |
|
|
Trace the path of blood that leaves the digestive tract (starts with hepatic portal vein)
*MOST digestive products |
Hepatic portal vein --> Blood to liver --> Liver capillaries --> Heaptic vein --> vena cava --> right atrium of heart
|
|
|
What happens to blood if it goes in lacteal system?
|
Lacteal system bypasses liver; carries contents more directly to the right atrium
|
|
|
Which products of digestion are carried in the blood to the liver?
|
Amino acids, carbohydrates, and simple sugars
|
|
|
Which products of digestion are carried via the lacteal system?
|
Fatty acids
|
|
|
During the first hour after a heavy meal, how does the concentration of glucose in the blood going from the small intestine to the liver compare to the concentration entering the right side of the heart?
|
Glucose concentrations will be higher going to the liver and lower going to the heart
|
|
|
In what specific layer of the tongue do you find the taste buds?
|
Surface epithelium
|
|
|
What specific tissue type lines the lumen of the esophagus?
|
Stratified squamous epithelium
|
|
|
Why is this tissue type well adapted for its location?
|
Keratinized so waterproof from liquids
Also has many layers, so regenerates quickly when food brushes past the cells and tears them off |
|
|
What is the purpose of cuboidal epithelium?
|
Glands/secretion
|
|
|
What is the purpose of squamous epithelium?
|
Perfussion of all tissues; liquid diffuses from one cell to the next easily
|
|
|
What is the purpose of columnar epithelium?
|
Absorption
|
|
|
What germ layers do the four main tissue types come from?
|
Nervous tissue: ectoderm
Epithelial tissue: ectoderm Connective tissue: mesoderm Muscle tissue: mesoderm |
|
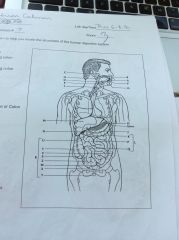
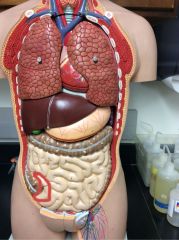
Label:
Anus/appendix/ascending colon/cecum/descending colon/duodenum/esophagus/gall bladder/ileum/jejunum/large intestine or colon/lips/liver/oral cavity/pancreas/parotid glands/pharynx/rectum/sigmoid colon/small intestine/stomach/sublingual glands/submandibular glands/teeth/tongue/transverse colon |

|

