![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
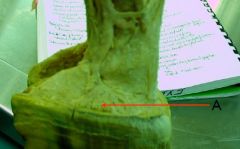
Which equine structure makes the first contact with the ground?
|
The frog (and basal border)
|
|
|
In the equid hoof capsule, how many primary laminae? Secondary laminae?
|
600; 100
|
|
|
What is the junction between the hoof and skin?
|
Coronet
|
|
|
What is the soft part of the hoof just proximal to coronet?
|
Periople
|
|
|
Which quarter is steeper, medial or lateral?
|
Medial
|
|
|
Which structures are involved in preventing venous pooling in the horse limb? (2)
|
Digital cushion
Collateral hoof cartilages |
|
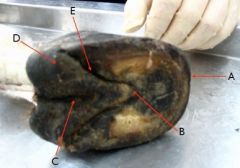
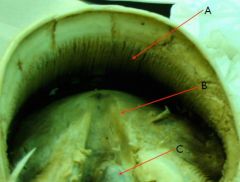
see pic
|
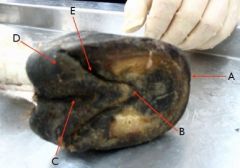
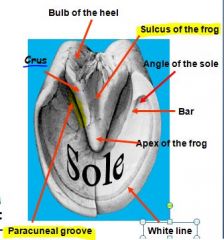
A - Toe
B - Apex of frog C - Sulcus of frog D - Bulb of the heel E - Paracuneal groove |
|

identify
|

A - Distal phalanx
B - Stratum medium C - Basal border of hoof D - Digital cushion E - Deep digital flexor tendon F - Navicular bone |
|
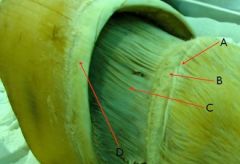
identify
|
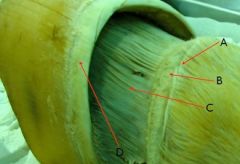
A - Perioplic dermis
B - Coronary dermis C - Laminar dermis D - Coronet |
|
|
which has broader toe: thoracic or pelvic limb?
|
pelvic limb
|
|
|
where does lamintis happen?
|
- inflammation of laminar dermis
- between laminae dermis and epidermis |
|
|
wall reflected at heels to form bars, separated from the frog by the
|
paracuneal grooves
|
|
|
Wall is thickest at
|
Wall is thickest at TOE, and thins progressively heel-ward
|
|
|
Which quarter has thicker wall: inner or outer (lateral)?
|
outer (lateral) quarter
|
|
|
angle between dorsal surface and ground surface (of fetlock) is normally
A. in forefoot B. in hind foot |
A. 45-50 degrees in (forefoot)
B. 50-55 degrees (hindfoot) |
|
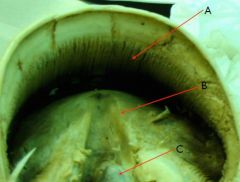
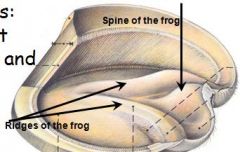
identify
|

A - Laminar epidermis
B - Ridges of the frog C - Spine of the frog |
|
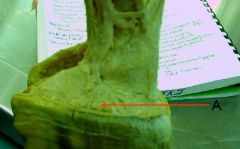
identify
|
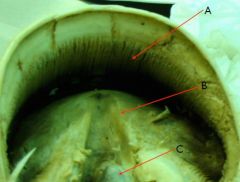
Coronary venous plexus
|
|
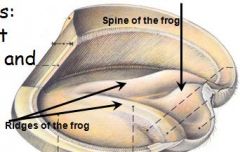
identify
|
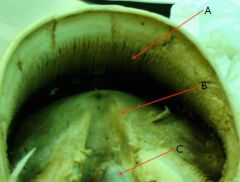
A - Laminar epidermis
B - Ridges of the frog C - Spine of the frog |
|
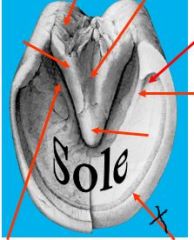
identify
|
see pic
|
|
|
does laminae dermis contain papillae?
|
No
|
|
|
what produces hoof wall?
|
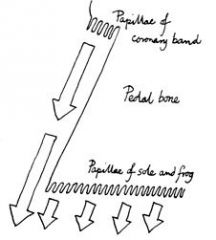
coronary dermis - produces hoof wall by means of papillae on their surfaces
|
|
|
Function of dermis:
|
1.highly vascular and sensitive
2. attaches hoof wall to internal foot structures 3. produces parts of wall via papillae (not laminae dermis) 4.provides wall with nourishment |
|
|
types of dermis
|
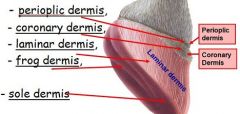
- perioplic dermis,
- coronary dermis - laminar dermis (no papillae) - frog dermis - sole dermis |
|
|
produce horn of periople and stratum tectorium?
Produces most of wall? |
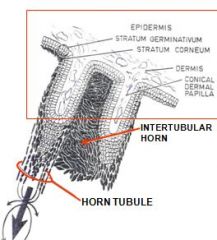
Papillae of Perioplic dermis
Coronary dermis; it produces stratum medium and internum |
|
|
which is more proximal, Coronary dermis OR Perioplic dermis?
|
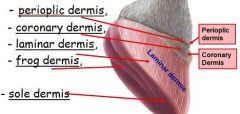
Perioplic dermis is more proximal
|
|
|
covers extensor tendon, cartilages of distal phalanx via subcutaneous tissue of the coronary cushion
|
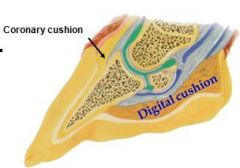
Coronary dermis
|
|
|
_____ of coronary dermis produces stratum medium of wall
also produces horny tubules |
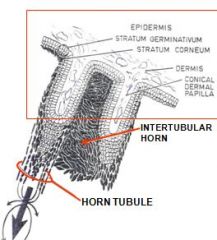
stratum germinativum
|
|
|
produce the tubular horn (horny tubules)
produce intertubular horn |
papillae cells of stratum germinativum
inter-papillar cells -> produce intertubular horn, this is the glue |
|
|
coronary venous plexus lies deep in ?
coronary venous plexus feeds/forms ? |
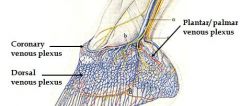
coronary cushion
med./lat. digital veins |
|
|
what happens if get a deep laceration in coronary border?
|
bleeds perfusely
|
|
|
degenerative condition of the frog, especially when animal is kept in moist or watery floor/ground
|
Thrush
|
|
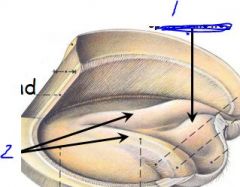
identify
|
see picture
|
|
|
True or False:
frog is completely keratinised |
False *****!
The frog is incompletely keratinised - softer (50% water content: sole -- 33%) than wall |
|
|
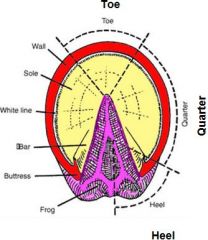
The white line visible at junction of ?
|
white line visible, white, at junction of wall and sole
|
|
|
Two parts of white line:
|
1. stratum internum
2. horny papillae OR pigmented horn FYI this straw colored (pigmented) amorphous horny material is produced by stratum germinativum overlying terminal papillae |
|
|
Where are terminal papillae located?
|
distal end of each laminae...i think
|
|
|
What do they do?
|
* fill space, glue between hoof wall (specifically the white line) and sole
|
|
|
Injuries to dermis
|
1. corn - bruised sole dermis at angle of sole
2. Canker - chronic hypertrophy of frog dermis - often due to infection. |
|
|
Name 3 plexuses of foot and location:
|
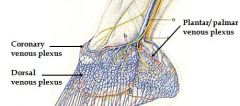
1. dorsal venous plexus - within cushion of laminae dermis
2. coronary venous plexus: in coronary cushion of cor.dermis 3. palmar/plantar venous plexus: in dermis of sole and on surfaces of cartilages of third phalanx. |
|
|
Do the 3 plexuses communicate?
|
Yes
|
|
|
What does digital cushion consist of?
It is part of ? |

fibroelastic tissue
Coronary cushion |
|
|
Why is it important to get horse exercise?
|
* each limb can hold a lot of blood via plexuses, etc.
* exercise innervates venous return and proper circulation * Blood may stagnate in the foot if horse is unable to shift foot or have adequate exercise. |
|
|
ungual cartilages may become ossified to be called ?
what is between them? |
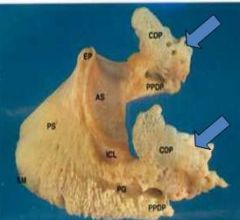
side bones
btw. is digital cushion, plantar venous plexous, etc. |

