![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
129 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

What is a Meatus? Name them
|
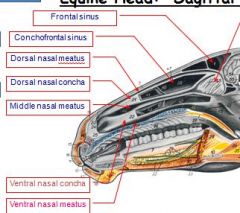
a natural body opening or canal
(dorsal, middle, ventral) |
|
|
What is a Concha?
Name them |
Nasal concha (or turbinate) is a long, narrow and curled bone shelf (shaped like an elongated sea-shell) which protrudes into the breathing passage of the nose. Turbinate bone refers to any of the scrolled spongy bones of the nasal passages in vertebrates.
|
|
|
which conchae is associated with frontal sinus?
|
dorsal concha
|
|
|
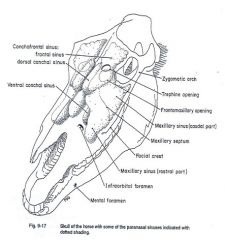
Surgical limit of maxillary sinus:
Rostrally? Caudally? |
Rostrally: a vertical line through the infraorbital foramen.
Caudally: a vertical line through the middle of the eye. |
|
|
Surgical limit of maxillary sinus:
Dorsally? Ventrally? |
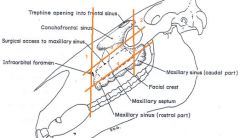
Dorsally: a line from the infraorbital foramen to eye.
Ventrally: border along facial crest |
|
|
Viborg’s triangle: 3 boundaries (clinical significance)
a. rostral border? b. ventral border? c. dorsocaudal border? |
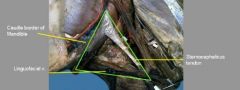
a. Rostral – caudal margin (ramus) of the mandible
b. Ventral – linguofacial vein c. Dorsocaudal – tendon of insertion of sternocephalicus muscle * One of the approaches to the guttural pouch for surgical intervention. |
|
|
Site of surgical entry into guttural pouch:
|
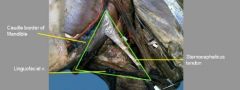
Viborg's triangle
|
|
|
• Parotidoauricularis muscle covers ?
|
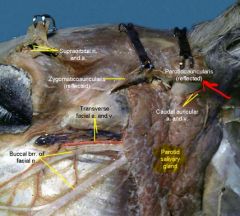
Parotidoauricularis muscle covers the parotid gland (check on this)
(important in operations for drainage of infections of external ear in dog) |
|
|
Pupil of horse is normally
|
transversely oblique in shape
|
|
|
The master lymph node of the head of the horse is the :
|
- medial retropharyngeal
|
|
|
There is a bony plate that divides the maxillary sinus into medial and lateral parts, what canal is transmitted through this bony plate?
|
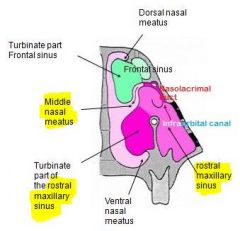
transmits the infraorbital canal on its dorsal border
|
|
|
A long bony ridge on the lateral part of the head of the horse that is an important practical or clinical landmark is:
|
facial crest
|
|
|
In the horse vomit passes through nasal cavity because?
(check on this) |
- long soft palate separates the oropharynx from the nasopharynx
(but i thought horses can't vomit?) |
|
|
The following muscle is unique to the horse:
oc____ muscle |

occipitomandibularis muscle
(don't confuse with digastricus m.) |
|
|
Links the frontal sinus directly with the (caudal) maxillary sinus.
|
frontomaxillary opening
|
|
|
Which roots of the upper cheek teeth project into maxillary sinus in the horse?
|
- last 2 or 3
|
|
|
Name 2 important canals that pass through or close to maxillary sinus of the horse
|
nasolacrimal canal - runs on dorsolateral aspect of maxillary sinus
infraorbital canal - |
|
|
True or False: concerning the maxillary sinus of the horse
- it has 2 main divisions (rostral and caudal)? |
True
|
|
|
The frontal sinus of the horse communicates with the nasal cavity how?
|
- indirectly through the maxillary sinus
|
|
|
Main bone which forms roof of the cranium of the horse:
|
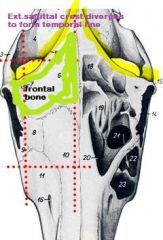
parietal
|
|
|
Concerning the azygos vein of the horse, what side(s) can it be found on?
|

- it is only present on the right
|
|
|
The roof of the equine cranium is formed by the _?
(in ruminant?) |
The roof of the cranium is formed by the occipital, parietal and interparietal bones, and rostrally, by the frontal bones.
(c.f. ox – the cranium is formed by the frontal bone which displaces the parietal bones, laterally and caudally) |
|
|
from ext. occipital prot. runs cranially , in the midline, diverges to form the temporal line, on either side, before joining the zygomatic process of the frontal bone.
|
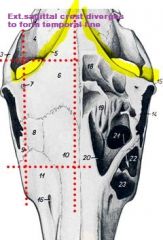
external saggital crest
diverges to form the temporal line, on either side, before joining the zygomatic process of the frontal bone. (not in ruminants) |
|
|
_____ pierces the root of the zygomatic process of the frontal bone
|
supraorbital foramen
pierces the root of the zygomatic process of the frontal bone |
|
|
occipital bone forms most of the caudal part of the skull, and it projects DORSALLY to form the ____?
|
form the nuchal crest
|
|
|
Prominent ridge on lateral portion of skull – ______, a major landmark
|
the facial crest
|
|
|
_______ lies between the nasal and incisive bones
|
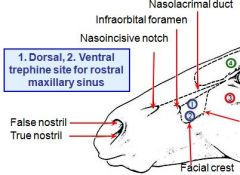
nasoincisive notch lies between the nasal and incisive bones
|
|
|
separates cranial cavity (cerebrum) from caudal part (cerebellum)
|
tentorium cerebelli osseum
|
|
|
The external nose is supported:
Rostrally? Laterally? Dorsally, medially and ventrally? |
Rostrally, by the median nasal septum,
Laterally, by dorsolateral nasal cartilage Dorsally, medially and ventrally, by the alar cartilage |
|
|
_____ comprises a dorsal, flat and broad lamina, and a narrow, curved ventral cornu (horn).
|
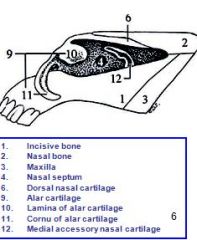
Alar cartilage
|
|
|
T/F Laterally, the nostril has cartilaginous support via dorsolateral nasal cartilage.
|
False: that supports lateral nose, not the nostril itself
Laterally, the nostril has no cartilaginous support. |
|
|
large, oval, opening - in floor of frontal sinus, and situated between the median plane (huh?) and the orbit.
|
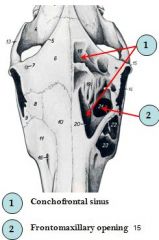
frontomaxillary opening
|
|

Identify
|
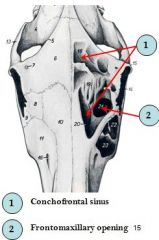
see pic
|
|
|
essentially and developmentally, invaginations of the nasal mucosa into the bones
|
PARANASAL SINUSES
|
|
|
nasal mucosa innervation
|
ophthalmic and maxillary br. of trigeminal n.?
|
|
|
bone found only in horse and cat btw 2 parietal bones, rostral to occipital bone.
|
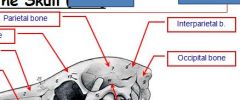
Interparietal bone
|
|
|
T/F Bony orbit is complete in ruminants but not horse
|
False complete in horse and ruminant, NOT in carnivores
|
|
|
All permanent horse teeth are ?
|
hypsodont
All equine teeth, except canine and P1, are hypsodont (erupt throughout life) and cheek teeth are anisognathous. Cheek teeth? |
|
|
Duct running from parotid gland to oral cavity?
(if you get this wrong, drop out of vet school!) |
parotid duct
|
|
|
Masseter muscle is dominant in ?
|
in herbivore
origin on maxillary region and zygomatic arch, insert on caudal part of mandible; adapted for chewing and small lateral mov't |
|
|
Temporalis muscle is dominant in ?
|
in carnivore!
higher on head (frontal bone and temporal fossa) than masseter, also covers coronoid process on mandible therefore better for scissorlike mov't or biting |
|
|
Muscles of mastication (4 and 1 extra)
|
temporalis, MASSETER, pterygoideus medialis/lateralis
~digastricus helps open mouth, it is on ventral portion of mandible, caudal to T/M joint |
|
|
Comparatively, frontal bone what size in equine (in proportion to its skull, etc.)?
|
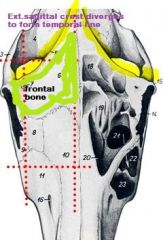
Frontal is smaller in equine, b/c it is rostral to temporal fossa and temporal line.
Largest in ruminant |
|
|
name for 1st premolars which usually do not develop, but if present are in UPPER archade, and smallish
|
wolf teeth
note: dental formulas P 3/3 shown in next question does not include wolf tooth, but wolf tooth is always PM1; if name specific premolar e.g. premolar after wolf is called PM2 even if wolf not present. |
|
|
Permanent Dental Formula in horse
|
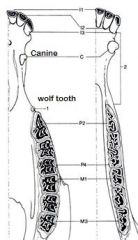
Incisor 3/3
C1/1 (male only, sometimes in female but appear under- developed) P3/3 M3/3 X 2 (for left and right)= 40 teeth total) |
|
|
* Masticatory / occlusal surface / table is flat, and changes shape with age, from oval, rounded, triangular and back to oval.
* For cropping/cutting of grass |
Incisors
|
|
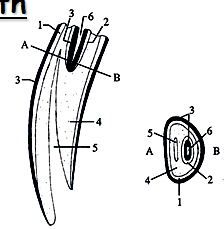
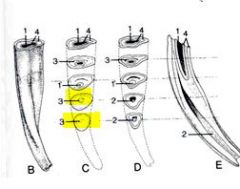
identify
name for masticatory surface? |
1. External Enamel
2. Central Enamel 3. Cement 4. Dentine 5. Dental Cavity 6. Infundibulum dentis >masticatory surface known as "occlusal surface" |
|
|
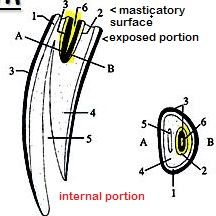
What is the central cleft of incisor teeth?
|
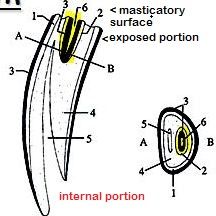
Central cleft – infundibulum, lined by cementum.
(yellow) |
|
|
Where is the site of the pulp cavity, where the darker, secondary dentine has been laid down in the incisors?
|
Dental star
infundibulum gradually filled in by secondary dentine (occludes central cavity) |
|
|
What side of the lower cheek teeth wear faster?
|
Vestibular side wear faster than lingual side
|
|
|
What side fo the upper cheek teeth wear faster?
|
Lingual side (inner surface) wear faster than vestibular side in upper teeth
|
|
|
sphenopalatine and middle conchal sinuses both drain into the ?
|
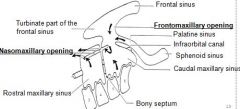
sphenopalatine and middle conchal sinuses both drain into the "caudal maxillary sinus"
|
|
|
Only the _____ sinuses communicate directly with the nasal cavity
|
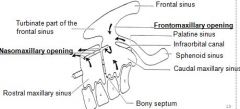
Only the communicate directly with the nasal cavity
|
|
|
Both (cranial and caudal) maxillary sinuses open into _____ through the ______?
|
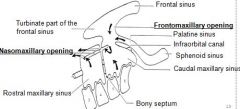
Both (cranial and caudal) maxillary sinuses open into:
the nasal cavity (middle nasal meatus) through the common, slit-like nasomaxillary opening, |
|
|
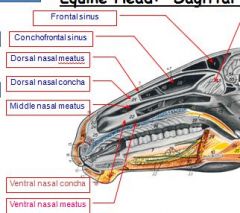
difference betw. frontal sinus and conchofrontal sinus
|
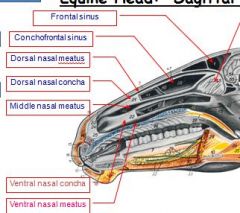
see pic
|
|
|
rostral and caudal maxillary sinuses are seperated by ?
direct communication btw. ? |
oblique septum
therefore no direct communication btw. the two |
|
|
Dr Aires said "rostral part of maxillary sinus incorporates ____?"
|
rostral part of max.sinus incorporates the caudal part of ventral conchae
|
|
|
which part of maxillary sinus is larger?
|
caudal part
|
|
|
What must be careful of when removing last 3 or 4 cheek teeth which project into maxillary sinus?
|
cutting infraorbital canal (infraorbital nerve), runs parallel to facial crest
|
|
|
runs on dorsolateral aspect of maxillary sinus?
|
nasolacrimal
|
|
|
Inflammation of nasal mucosa of maxillary sinus can occlude the ____?
|
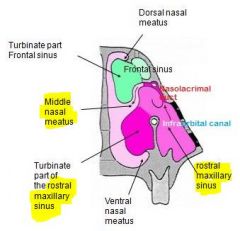
nasomaxillary opening (narrow slit)
|
|
|
why must horse eat with head at ground level?
|
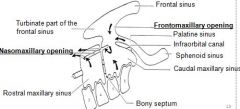
to ensure adequate drainage maxillary sinus
because floor of MS in below nasomaxillary opening |
|
|
innervates occipitomandibulatris m?
origin? insertion? |
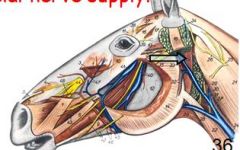
facial nerve
paracondylar process caudal border of mandible |
|
|
Which tooth erupts first i1 or i3?
|
generally I1 emerge first, I3 last of incisors to develop
therefore I3 (on bottom) often used for age determination |
|
|
what separates the cranial half of the ventral turbinate from the caudal, sinusal half?
|
Complete, bony septum
|
|
|
What does abnormal pigmentation of the tongue in a horse mean?
|
Indicative of a malignant tumor
|
|
|
What dorsal, palpable cartilagenous cord is present in the median plane of the horses oral cavity?
|
Dorsal lingual cartilage
|
|
|
What forms the clinical root in hypsodont teeth?
|
Reserve crown + true root = clinical root
(Reserve crown is proximal part near socket) |
|
|
Very long crowns of hypsodont teeth
the distal part above gum line = |
distal part above gum line = clinical crown
|
|
|
Enamel forms raised ridges on the cutting surface.
|
(enamel crests)
|
|
|
What side of the lower cheek teeth wear faster?
|
Vestibular (outer) side wear faster than lingual side
|
|
|
What side fo the upper cheek teeth wear faster?
|
Lingual (inner) side wear faster than vestibular side
|
|
|
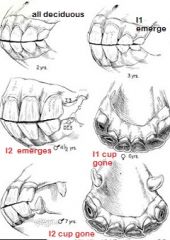
I1 emerges after?
I2 emerges after? I3 emerges after? |
I1 emerges after 2.5 yrs.
I2 emerges after 3.5 yrs. I3 emerges after 4.5 yrs. |
|
|
1. What 3 bones form the hard palate?
|
The hard palate is formed by the maxillary, palatine, and incisive bones.
|
|
|
The frontal sinus communicates with what two sinuses?
|
The frontal sinus communicates with the caudal maxillary sinus and dorsal conchal sinus.
|
|
|
What 3 muscles are used to close the jaw?
|
Pterygoid, masseter, and temporalis muscles close the jaw.
|
|
|
What age do cups wear down?
|
Mandibular:
* first cup to wear down is mandibular I1 at 6 years. * I2 cup gone at 7 years * I3 cup is gone at 8 years. |
|
|
Lower incisors flat after ?
Incisors level after? |
5 years
7 years (check these numbers) |
|
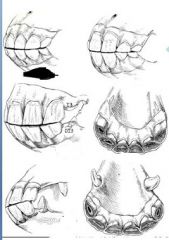
Guestimate age based on picture
|
on exam always say approximately
|
|
|
Dental star presence first appears in upper corner incisor at?
|
7-year hook (upper corner),
(according to colostate.edu says dental star first appears on I1 at 8 yrs. maybe on bottom) |
|
|
Galvayne's groove (on upper corner, etc.) appears at?
|
Galvayne’s groove appears on the third incisor at age 10
|
|
|
Galvayne's groove disappears over time; what age is half gone?
what age is groove completely gone? |
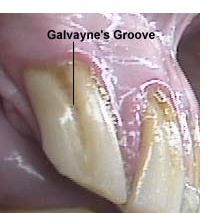
age 15
age 30 |
|
|
What is the reason that sharp edges and points develop in cheek teeth?
How is this fixed???? |
Differential wearing of teeth surfaces, fixed by floating
|
|
|
Where can a swelling of the guttural pouch be palpated on the horse?
|
In the Viborg's triangle
|
|
|
62. What shape is a new tooth? What are the next 3 successive shapes and at what ages?
|
New tooth: oval. 10 years: round. 16 years: triangle. 20 + years: oval
|
|
|
63. What causes uneven wear in equine teeth? Where do the sharp points form on the mandibular and maxillary teeth?
|
The lower jaw is narrower than the upper jaw, causing uneven wear. Sharp points form on the lingual side of the mandibular cheek teeth and on the buccal side of the maxillary cheek teeth.
|
|
|
What are the possible reasons that the parotid region of the horse may be inflamed?
|
Swollen medial retropharyngeal lymph node
Accumulation of secretory material in guttural pouch Air |
|
|
intubation are difficult b/c ?
how done? |
* mouth doesnt open wide, narrow rima oris
(commisure more rostral than dog) * done blindly * extend head slightly to align axis |
|
|
23. What is “crib-biting”,
|
Also known as wind-sucking. When bored prone to vices. Flexes neck and tenses caudo-ventral hyoid and sternocephalic muscles.
pharynx dilated and animal swallows air |
|
|
how do you correct this “crib-biting”,?
|
resecting the omohyoid, sternocephalic, and sternothyroid muscles
also have collars can put on horse |
|
|
What structures make contact with the roof of the guttural pouch?
|
Foramen lacerum
Tympanic bulla Cranial nerves 9-12 Chorda tympani Cranial cervical ganglion Internal carotid artery |
|
|
What two spaces does the auditive tube connect?
|
Middle ear
Nasopharynx |
|
|
How fast does air move through the larynx during physical exertion in the horse?
|
180 km/h
|
|
|
Where does the duct of the mandibular salivary gland open into?
|
Sublingual caruncle
|
|
|
Why is the horse an obligatory nasal breather?
|
Soft palate of horse is long and wraps around base of epiglottis
Can only raise it to swallow |
|
|
What is the ventrocaudal diverticulum/evagination of the auditive tube that is only in the horse?
|
Guttural pouch
|
|
|
In the larynx what fills the gap formed by incomplete thryroid cartilage?
|
Cricothyroid membrane
|
|
|
What is the name of the laryngeal entrance?
|
Aditus laryngis
|
|
|
What is the term for the deep, blind mucosal sac in the lateral wall of the larynx? Where is it's opening?
|
Laryngeal ventricle, opens between the vestibular and vocal folds
|
|
|
What is the respiratory rate of a horse at rest?
|
8-12 per minute
|
|
|
What is the respiratory rate of a horse during physical exertion?
|
About 150 per minute
|
|
|
What processes take place during physical exertion to ensure the horse gets enough air?
|
Nostrils dilate maximally
Vasoconstriction of cavernous tissue Arytenoid cartilages are maximally abducted Vestibular and vocal folds are in full abduction |
|
|
how is roaring in horse corrected; like what procedure called?
|
ventriculectomy
- remove laryngeal ventricle to widen lumen |
|
|
What is the function of the granula iridica of the eye in the horse?
|
Produce aqueous humor
Protect eye from bright light (cast shadows on retina) |
|
|
T/F Third eyelid not found in horse?
|
False; being an ungulate third eyelidis well developed.
|
|
|
What veins form the linguofacial vein?
This vein feeds INTO what ?????????????? |
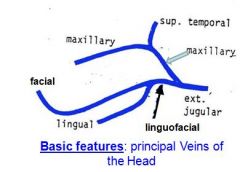
Facial veins
Lingual veins In the horse, both the facial and lingual v. form tributary (linguofacial vein). of the external jugular vein |
|
|
What veins help in assisting venous return from head?
|
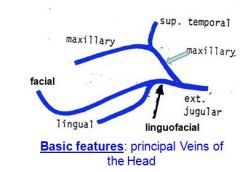
Veins running through masseter muscle
1. Transverse facial vein (joins the facial vein, rostrally) 2. Deep facial vein (enlarges to become the deep facial vein sinus) 3. Buccal vein |
|
|
Arises in pterygopalatine fossa, and drains the nasal cavity, palate, periorbita, etc.
|
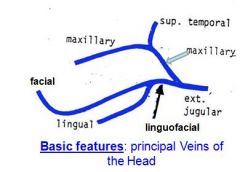
deep facial vein.
~deep to the masseter muscle. |
|
|
What vein is enlarged below the facial crest to form the transverse facial vein sinus?
|
Transverse facial vein
|
|
|
What are the lymph nodes of the horse head?
|
Parotid lymph node
Mandibular lymph node Lateral and medial retropharyngeal lymph nodes |
|
|
What is relationship between parotid and mandibular and retropharyngeal L.N.?
|
efferents from parotid and mandibular empty into retropharyngeal L.N.
|
|
|
What structures does the parotid lymph node drain and where do its efferents go?
|
Drains eye, ear, lips, rostral and dorsal superficial muscles
Efferents go to the retropharyngeal lymph node |
|
|
Relationship between Lateral and medial retropharyngeal lymph nodes
|
lateral R/Ph drains into medial R/Ph
|
|
|
What does mandibular drain?
|
Drain all areas NOT drained by the parotid ln.: nostrils, palate, tongue and jaws
Efferents go to retropharyngeal lnn. and cranial deep cervical lnn. |
|
|
How many rows of mandibular L.N are there?
|
2
|
|
|
Drain deep parts pf the head
|
Lateral retropharyngeal lnn
Efferents go to medial retropharyngeal lnn, cranial deep cervical and tracheal duct. |
|
|
A chain of lnn. along the external carotid artery on the lateral wall of the guttural pouch, and medial to the occipito-mandibularis muscle
|
Lateral retropharyngeal lnn
|
|
|
Efferents on what lymph node anastomose to form the tracheal duct.?
|
Medial retropharyngeal lnn.:
|
|
|
What do the two rows of the mandibular lymph node form?
|
V shape
|
|
|
What do minor salivary glands secrete?
|
Mucous secretions
|
|
|
What do major salivary glands secrete?
|
Serous or serous-mucous secretions
|
|
|
What side of the larynx is usually paralyzed in roaring in the horse?
|
Left
|
|
|
How do you enter the laryngeal ventricle in a ventriculectomy operation?
|
Through the cricothyroid membrane
|
|
|
Where is the most common site of damage for the facial nerve?
|
Over the caudal border of the mandible
Where the buccal branches run over the masseter muscle |
|
|
What are some negative effects of facial nerve paralysis?
|
Nostrils cannot dilate
Blink reflex lost Eyelids cannot close Lower lid droops Ear hangs and pulled back Prehension of lips impeded Drinking is impeded |
|
|
What is a consequence of bilateral paralysis of the mandibular nerve?
|
Lower jaw drops
|
|
|
What nerve must you block to anesthetize all teeth of the maxilla?
Name for this nerve block? |
Maxillary nerve (Peterson block)
|
|
|
What nerve must you block to anesthetize all teeth of the mandible?
|
Inferior alveolar nerve
|
|
|
T/F Sublingual salivary gland is monostomatic.
|
False; Sublingual, a minor sal.gland – has only the minor, polystomatic portion.
|

