![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
thick fibrous strand extending along the length of biceps brachii m. to insert on the extensor carpi radialis m. |
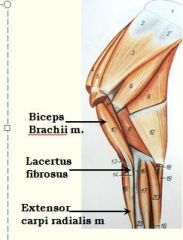
Lacertus fibrosus
|
|
|
Perineural anesthesia in the horses:
Palmar / Plantar digital nerve Anesthesia Site of injection ? |
1. Distal palmar/plantar digital nerve block
2. Proximal palmar/plantar digital nerve block |
|
|
Where is Distal palmar/plantar digital nerve block?
|
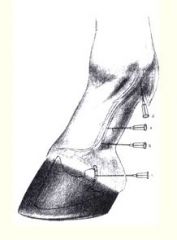
* Along the medial and lateral edges of the flexor tendons.
* At the level of pastern joint / just above the collateral cartilages of distal phalanx. * Can also be done just proximal to the previous site. |
|
|
Where is Proximal palmar digital nerve block?
What is purpose? |
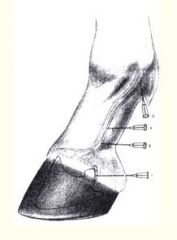
On the abaxial sides just below the proximal sessamoid bones
~desensitizes entire foot!!! |
|
|
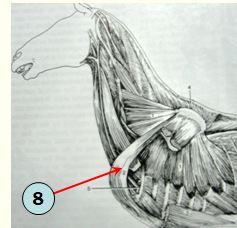
Structures desensitized by palmar digital nerve anesthesia (7)?
|
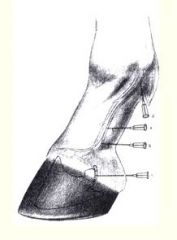
~desensitizes entire foot !
1. Navicular bone and bursa 2. Digital cushion 3. Palmar / plantar aspect of the sole and frog 4. Palmar / plantar aspect of the coffin bone 5. Palmar / plantar aspect of the pastern and coffin joint 6. Disal sessamoidean ligaments (PDB) 7. Distal Superficial and deep digital flexor tendons |
|
|
Ring (field) block
Site of injection? (this is for distal/proximal palmar/plantar digital nerve anesthesia) |
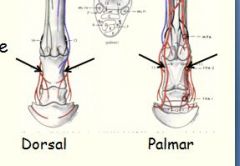
Redirect needle to the dorsal aspect of the digit
OR On both sides of the common/long digital extensor tendon at same level. |
|
|
For ring (field) block, how much in usually injected?
|
Inject 3-5 ml of anesthetic solution.
|
|
|
For ring (field) block what structures are desensitized?
|
* Structures desensitized by the palmar/plantar digital nerve block
* Complete analgesia of the foot distal to the site of injection. |
|
|
Four point palmar/plantar nerve block:
Where are injections? |
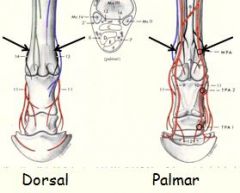
* this set of injection more are more proximal and done after ring field block
* distal ends of the lateral and medial splint bones (metacarpal 2&4) * couple inj. are deep to reach metacarpal nerves * others are sfc. to get med./lat. palmar nerves |
|
|
For HIGH Four point palmar nerve block:
Where are injections? |
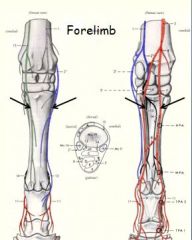
* Deep injection on inside of metacarpals 2&4 (splint bones)
* both sides of the flexor tendons to access palmar/plantar nerves |
|
|
What is used to block deep structures of the metacarpus / metatarsus region?
|
High 4 pt. block
|
|
|
Extensors of carpus and digits.
Arise from the______aspect of distal humerus: |
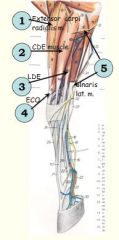
Extensors arise from craniolateral aspect of the distal humerus.
|
|
|
Extensors of carpus and digits insert...?
|
Extensors Insert either on carpus/metacarpus or digits
|
|
|
Extend what joints?
|
carpus as well as digits
|
|
|
Extensors of carpus and digits are supplied by ?
|
Extensors of carpus and digits
are all supplied by the radial nerve. |
|
|
Easy question:
Flexors of the carpus and digits Arise from the ____ aspect of the humerus. Occupy ___part of forearm. |
Flexors Arise from CAUDOMEDIAL aspect of humerus!
Occupy the CAUDAL part of the forearm |
|
|
Name the Flexors of the carpus and digits
|
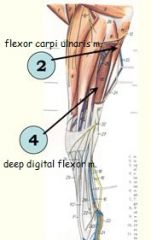
Flexor carpi radialis m.
Flexor carpi ulnaris m. Superficial digital flexor m. Deep digital flexor m. |
|
|
Flexors secured by ?
|
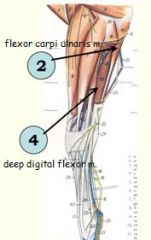
Flexors of carpus and digits secured by flexor retinaculum at the caudal aspect of the carpus.
|
|
|
Muscles are secured at the carpus by extensor retinaculum? (5)
|
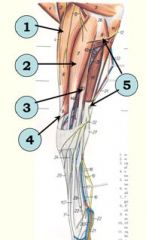
1. Extensor carpi radialis m.
2. Common digital extensor m. 3. Lateral digital extensor m. 4. Extensor carpi obliquus m. originates on shaft of radius 5. Ulnaris lateralis m. (other name??)– opposite action –- FLEXION of carpus |
|
|
What is retractor of the forelimb – antagonist of the brachiocephalicus m.
* innervated by _____. |
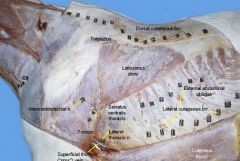
Latissimus dorsi m.
Thoracodorsal nerve. |
|
|
Adduction of the forelimb.
|
Pectoral muscles
|
|
|
flexors of digits and carpus are innervated by?
|
median and ulnar n.
therefore these nerves must pass thru caudolateral part of antebrachium |
|
|
what muscles are innervated by radial n.?
|
Extensors of carpus and digits.
* Arise from the craniolateral aspect of the distal humerus. * run C/L |
|
|
Which muscle is present in extensor retinaculum and extensor groove (on C/L aspect) but is flexor of carpus?
|
Ulnaris lateralis m.
(also innervated by radial n.) |
|
|
Prime advancer of the forelimb – neck is fixed
Turns the neck to the side – forelimb is fixed |
Brachiocephalicus m.
|
|
|
Complements action of the brachiocephalicus m
|
Omotransversarius m.
|
|
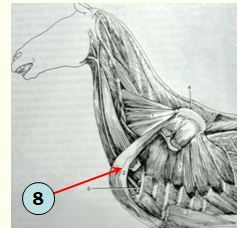
identify muscle
what innervates it? |
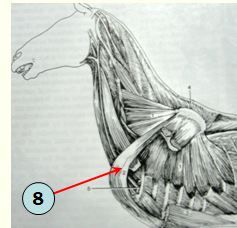
subclavius m. : originates just cranial to the deep pectoral on sternum (hence the muscle was previously considered as part of the pectoral m.)
Pectoral n. |
|
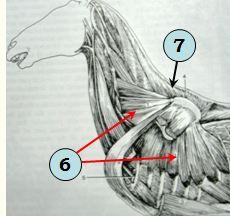
identify muscles
|
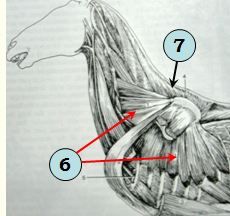
Serratus ventralis m.
Rhomboideus m. |
|
|
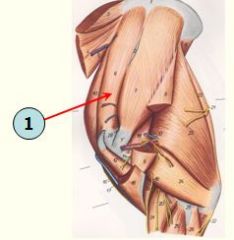
Well developed and lies cranial to the supraspinatus m.
Originates just cranial to the deep pectoral on sternum |
Subclavius muscle
Originates just cranial to the deep pectoral on sternum (hence the muscle was previously considered as part of the pectoral m.) |
|
|
what nerve is at risk if humerus breaks?
|
radial n., runs right on bone
|
|
|
Where are flexors of carpus and digits located on forearm?
Which flexor has 3 heads? |
caudomedial aspect, in "flexor groove"
flexor carpi radialis, FCU, SDF, DDF (3 heads) FYI: 1 of 3 heads of DDF is actually superficial to SDF? |
|
|
This is an important component of the forelimb stay apparatus.
|
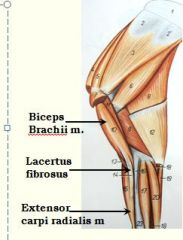
Lacertus fibrosus
: a thick fibrous strand extending along the length of biceps brachii m. to insert on the extensor carpi radialis m. main function is to keep shoulder joint and carpus extended at same time |
|
|
Major flexors of shoulder joint?
(and innervations) |
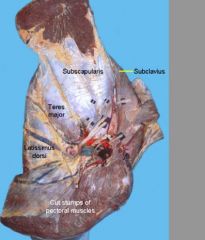
teres major m. (axillary n.)
long head of triceps brachii m. (deep branch of median n. - check this because says radius n. online) |
|
|
Major extensors of shoulder joint?
(and innervations) |
Supraspinatus m. (suprascapular n.)
biceps brachii m. (musculocutaneous n.) |
|
|
which head of triceps is absent in horse?
|
accessory head
|
|
|
how many bursa are associated with triceps?
|
2; deeper, congenital bursa bew. bone and muscle
2nd superficial bursa betw. skin and tendon of insertion, which is acquired - known as capped elbow. |
|
|
Coracobrachialis muscle action and relative location?
|
small musc. just inside (closer to center of limb) of biceps brachii which helps adduct limb
|
|
|
thickening of deep fascia that connects to medial side of carpus and accessory carpal bone. With the carpal bones it forms the carpal canal.
|
flexor retinaculum
|
|
|
what passes thr. carpal canal?
|
SDF and DDF?
|
|
|
Which is present in forelimb, common digital extensor or long digital extensor?
|
common digital extensor m.
|
|
|
another name for proximal check ligament?
|
accessory ligament of SDF
~tendinous band that connects SDF to radius; part of stay aparatus |
|
|
where does common digital extensor insert?
|
P3 (distal phalanx)
|
|
|
where does lateral digital extensor insert?
|
P1
|
|
|
what nerve innervates extensors of digits?
what nerve innervates flexors of digits? |
radial n.
mostly ulnar n. |
|
|
DDF inserts?
|
P3
|
|
|
SDF inserts?
|
after it forks around DDF (creating manica flexorium) it inserts on P1 and P2.
|
|
|
Serratus Ventralis m. (originating from both C3-7 and Ribs 1-7/8) and inserts on _______, contains sheets (plural) of fibrous tissue known as the _______?
|
Serratus Ventralis m., which originates from both C3-7 and Ribs 1-7/8 and <inserts on serrated face of the scapula>, contains sheets of fibrous tissue known as <dorsoscapular ligament>
|
|
|
ulnar nerve divides into ?
|
dorsal br. of ulnar nerve
palmar br. of ulnar nerve |
|
|
damage to this nerve can lead to shoulder sweeney, what is it called?
|
Suprascapular n.
|

