![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Sialocele
|
a.k.a. Salivary mucocele
Submucosal accumulation of salivary secretions due to damage to salivary gland or duct |
|
|
Tracheal intubation - how?
|
placement of flexible tube into trachea to maintain open airway or to serve as a conduit
Pull tongue Push soft palate up Hold epiglottis down Tube between vocal cords |
|
|
blepharospasm
|
Tonic blinking
|
|
|
Inflammation of conjunctiva?
|
Conjunctivitis
|
|
|
Prolapse of 3rd eyelid?
|
Cherry eye or haws
|
|
|
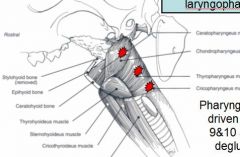
Pharyngeal mm. driven by
|
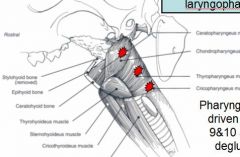
9&10 for 2nd stage of deglutition
|
|
|
(CrN 4)
|
Trochlear
smallest cranial n. Somatic motor: dorsal oblique m. Midbrain: Brain connection |
|
|
Cr N 7 Facial
|
Motor to muscle of facial expression
ANS motor to lacrimal gland, salivary glands |
|
|
CrN 5
|
Trigeminal n.
largest cranial nerve Sensory to most of head & face Motor to muscles of mastication |
|
|
CrN 8
|
Vestibulocochlear
Special sensory Hearing & equilibrium |
|
|
Causes dropped jaw
|
Paralysis CrN 5 trigeminal
|
|
|
Facial n. paralysis – what is most important?
|
Dry eye – lacrimal & obicularis oculi not facial paralysis
|
|
|
Clinical use of auriculopalpebral deficit?
|
VII – paralyze eyelids – lg animals
|
|
|
CrN 9
|
Glossopharyngeal n – group with X
Motor: Pharyngeal mm. Laryngeal & esophageal mm. |
|
|
CrN XII
|
Hypoglossal
Somatic motor to muscles of the tongue Paralysis of tongue… what nerve? Hypoglossal – motor to tongue How test? Nerve or neurotic? Pull on tongue |
|
|
Inflammation of iris and ciliary body?
|
IN Vascular tunic
Anterior uveitis |
|
|
Pupils of different size?
|
Anisocoria
|
|
|
Posterior malformation of eye in collies?
|
Collie eye
|
|
|
Palpebrae
Inversion of margins? Eversion of margins? Misplaced eyelash? Inflammation of eyelid? |
Entropion
Ectropion Ectopic cilia Blepharitis |
|
|
Problems in Fibrous tunic
Inflammation of cornea? Dry eye? Absence of corneal epithelium? Corneal ulcer think? |
Keratitis
Keratoconjunctivitis sicca (KCS) Corneal ulcer No steroids |
|
|
Problems in chamber of eye:
Increased intraocular pressure? Opacity of lens? |
Glaucoma
Cataract |
|
|
Dilates eyes with?
|
Atropine!
(by blocking Ach receptors from parasympathetic innervation of iris constrictor m.) Paralyzes ciliary mm. |
|
|
Absence of pain perception
|
Analgesia
|
|
|
Weakness?
Lack of coordination or irregularitys of muscular activity |
Paresis
Ataxia |
|
|
Sensing movements & part positioning
|
Proprioception?
|
|
|
Where do neoplasia metastasize through lymph channels?
|
Neoplasia is abnormal growth
Metastasis is spread of a disease from one organ to another, e.g. in malignant tumor cells Through heart to lungs |
|
|
How do neck wounds reach the thorax (mediastinum)?
What IDs ventral midline of larynx? |
Fascial planes
Cricothyroid muscle |
|
|
What is the incision site of a pharyngostomy tube?
|
Pyriform recess of laryngopharynx
|
|
|
shortened jaw also called?
|
Mandibular Brachygnathia
Parrot mouth |
|
|
Long-headed breeds
Prone to? |
Dolichocephalic
Nasal infections |
|
|
Short-headed breeds
Problems associated with them? Anatomical reason behind problem? |
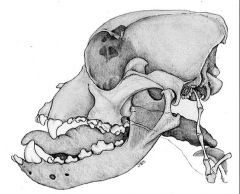
Brachycephalic
Breathing problems Brachycephalic airway syndrome elongated soft palate stenotic nares, etc. Prognathism (jaw protrudes) Upper brachygnathia (short upper jaw) Crowding of teeth or Malocclusion of teeth |
|
|
What is difficult breathing?
What is inflammation of nasal cavity? |
Dyspnea
Rhinitis |
|
|
Periodontal Disease
|
Periodontal (gum) diseases, including gingivitis and periodontitis, are serious infections that, left untreated, can lead to tooth loss. Word periodontal literally means "around tooth." Periodontal disease is a chronic bacterial infection that affects gums & bone supporting teeth. Periodontal disease can affect one tooth or many teeth. Begins w/bacteria in plaque causes gums to become inflamed.
|
|
|
Endodontal Disease
|
Disease of dental pulp
e.g. if tooth gets fractures and then infected |
|
|
parts of tooth from inside, out
|
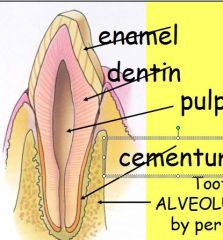
pulp cavity
dentin cementum (below gum line and enamel above) |
|
|
incisors & all canines have how many roots?
|
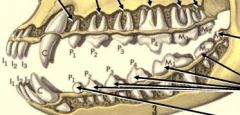
single
|
|
|
3 tunics: of eye
|
fibrous (the capsule): Sclera (DCT capsule)
and cornea vascular (uvea) : Iris (shutter) Ciliary body & processes Choroid (vessels, pigment) nervous tunic (retina). |
|
|
conjunctiva
|
mucous membrane lines inside of eye lid and also covers sclera
so coats inner surfaces of eyelids and outer surface of the eye. |
|
|
What DV skull projections good for?
|
view for symmetry by comparing one side to other
|
|
|
Where are the cell bodies of optic nerve?
|
retina of eyeball
|
|
|
Cerebral lesions
|
-changed behavior
- seizures - normal gait w/abnormal postural reactions -loss of vision |
|
|
Diencephalon (hypothalmus + thalmus) lesions produce what signs?
|
-cerebral signs (similar)
-autonomic and endocrine abnormalities (e.g. polyuria, polydipsia (excessive thirst), altered sleep patterns also possible |
|
|
Brainstem lesions
|
-decreased levels of consiousness from R.A.S.
-deficits in CN's III-XII as they arise from brainstem -proprioreceptive deficits and gait signs (this gets complicated) |
|
|
Brainstem includes?
|
midbrain, pons, medulla obl.
|
|
|
Cerebellar lesions:
|
-incoordination of mov't (ataxia), initiation tremors, and abnormal mov't of head
-vestibular disease signs: including nystagmus and head tilt |
|
|
Vestibular system lesions:
|
-affects posture in relation to gravity, eye mov't in relation to head
-head tilt, nystagumus, asymmetric ataxia, w/possibly circling and vestibular strabismus IF central vestibular disease in addition to above will have -paresis/weakness, UMN -depression IF have peripheral disease, besides head tilt with NOT produce UMN signs (NO paresis) -will have postural deficits b/c of balance NOT proprioreceptive disruption |
|
|
What is autonomic function of oculomotor nerve?
|
-Motor involuntary/smooth mm. of eye (near focus lens & constrict pupil)
|
|
|
With what does the vestibular branch of the vestibulocochlear nerve deal ?
With what does the cochlear branch of the vestibulocochlear nerve deal ? |
Special Sensory: equilibrium/ motion
Special Sensory: hearing - so sensory to auditory portion of the inner ear. - core component is the Organ of Corti, the sensory organ of hearing |
|
|
polydipsia
|
excessive thirst
|
|
|
Outline the pathway of the sympathetic innervation to the head.
|
Nerves from hypothalamus (UMN) down cervical cord to lateral (intermediolateral) gray column to T1-T4, preganglionic fibers over communicating branches & up SNS trunk to cranial cervical ganglion; Postganglionic fibers through middle ear, cranial cavity & orbit over CrNs
|
|
|
Through what head structures do sympathetic fibers to the eye pass?
|
Middle ear, cranial cavity & orbit
|
|
|
special sensory afferent CN's?
|
1 (smell), 2 (vision),8 (hearing)
(also 7,9,10 for taste) |
|
|
What are the most clinically important ANS fibers in the head?
|
CrN7 to lacrimal gland & sympathetic to eye (Horner's syndrome)
~see page 483 |
|
|
What does stimulation of sympathetic fibers of the eye cause?
|
dilation of pupil, widening of palpebral fissure, protrusion of eyeball
~page 483 |
|
|
what is main cavity of eye called?
|
vitreous chamber
|
|
|
inflammation of inner ear is know as?
|
otitis interna
can affect balance, resulting in vestibular signs (head tilt, circling), ataxia, nystagmus |
|
|
What are the signs of Horner's Syndrome? Horner's Syndrome
The classic signs of Horner's Syndrome occur on the same side of the face as the injury, and include: |
(1)Small pupil size (miosis) (2)Protrusion of 3rd eyelid
(3)Drooping of upper eyelid (ptosis) (4)Sunken appearance to the eye (enophthalmos) (5)Dilation of blood vessels on affected side of the face, which makes the area feel warmer to the touch >caused by loss of sympathetic innervation to eye, so parasympathetic NS takes over. >eye constrict, muscle around eye go limp |
|
|
The classic signs of Horner's Syndrome occur on the same side of the face as the injury, and include?
|
1. Ptosis (dropping eyelid)
2. Enophthalmos (sinking of eye) 3. Myosis (pupil constriction) 4. Protruding 3rd eye lid/nictating membrane caused by loss of sympathetic innervation to eye, so parasympathetic NS takes over. eye constrict, muscle around eye go limp |

