![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is Anatomy? |
It is the study of the structures of the body. |
|
|
|
The bending or decreasing of the angle between bones or parts of the body |
Flexion |
|
|
|
Straightening or increasing of the angle between bones or parts of the body |
Extension |
|
|
|
What is it called when a body part moves away from the median |
ABduction |
|
|
|
What is it called when a body part moves towards the median? |
ADduction |
|
|
|
What is it called when the thumb is positioned closer to the other fingers? |

Opposition |
|
|
|
What is it called when the thumb is positioned away from the other fingers, back in its original position? |

Reposition |
|
|
|
What is flexion of the ankle joint? |
Dorsiflexion |
|
|
|
What is it called when the foot or toes are turned towards the plantar surface? |
Plantar Flexion |
|
|
|
What is the extensionn of a limb beyond the normal limit? |
Hyperextension |
|
|
|
When you bring the the anterior surface of a limb towards the medial plane? |
Medial Rotation |
|
|
|
When you bring the anterior surface away from the medial plane? |
Lateral Rotation |
Say hi position with the shoulder |
|
|
What it called when a part moves superiorly? |
Elevation |
|
|
|
What it called when you move a part inferiorly? |
Depression |
|
|
|
What is it called when you move the sole away from the medial plane? |
Eversion |
|
|
|
What is it called when you move the sole toward the medial plane? |
Inversion |
|
|
|
What is the rotational movement of the forearm and hand that swings the radius medially around its longitudinal axis so that the palm of the hand faces posteriorly? |
Pronation |
|
|
|
What is the rotational movement of the forearm and hand that swings the radius laterally around its longitudinal axis so that the dorsum of the hand faces posteriorly? |
Supination |
|
|
|
What is protrusion? |
Movement anteriorly or forward |
|
|
|
What is protraction? |
Movement anteriorly or forward. |
|
|
|
What is retrusion? |
Movement posteriorly or backwards. |
|
|
|
What is retraction? |
Movement posteriorly or backwards |
|
|
|
Inferomedial means what? |
"Down" and "In" |
|
|
|
Superolateral means what? |
"Up" and "Out" |
|
|
|
What plane divides the body into anterior and posterior parts? |

The coronal plane. |
|
|
|
What plane divides the body into inferior and superior parts? |
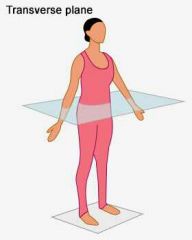
The transverse plane. |
|
|
|
What plane is known as the frontal plane? |
The coronal plane. |
|
|
|
What does ipsilateral mean? |
Occuring on the same side of the body as another structure. |
|
|
|
What plane is also known as the horizontal plane? |
The Transverse plane. |
|
|
|
Your right leg and right arm are what? |
Ipsilateral. |
|
|
|
What plane divides the body into top and bottom parts? |
The Transverse plane. |
|
|
|
Contralateral is what? |
When two structures occur on opposite sides of the body. |
|
|
|
The wrapping, packaging, and insulating materials of the deep structures of the body are known as what? |
Fascia |
|
|
|
Unilateral is what? |
When a structure occurs on only one side of the body. (i.e. the heart) |
|
|
|
What is the dense, organozed connective tissue layer, devoid of fat, that covers most of the body parallel to the skin and subcutaneous tissues? |
Deep Fascia. |
|
|
|
The skin provides what? |
Protection from environment Containment for body structures and vital substances Heat regulation through the evaporation of sweat and the dilation/constriction of blood vessels Sensation through nerves and their sensory endings Synthesis and storage of Vitamin D |
|
|
|
Deep Fascia has how many parts? |
Four: 1. Investing fascia- extensions invest deep structures (muscles and neurovascular bundles) 2. Intermuscular fascia- a layer of fascia that seperates muscles into compartments 3. Retinaculum- near certain joints, the fascia holds tendons on pakce where they cros the joint during flexion and extension 4. Subserous fascia- lies between the internal surfaces of the musculoskeletal walls and the seous membranes lining body cavities |
|
|
|
How does the skin regulate heat? |
Through the evaporation of sweat and the dilation/constriction of blood vessels |
|
|
|
Closed sacs of serous menbrane that are empty except dor a thin lubricating fluid secreted by te membrane are what? |
Bursae |
|
|
|
Skin consists of two layers called |
The Epidermis and the Dermis |
|
|
|
Bursae aid in what? |
Bursae enable one structure to move freely over another. In places of friction. |
|
|
|
Does the epidermis have blood vessels? |
No, it is avasculur. It has no blood vessels or lymphatics. It is nouroshed by the Dermis |
|
|
|
3 layers of Bursae |
1. Subcutaneous Bursae- occur in the subcutaneous tissues between skin and bony prominences 2. Subtendinous Bursae- facilitate the movement of tendon over bone 3. Synovial Tendon Sheaths- elongated bursae tat wrap around tendons, usually enclosing them as they traverse osseofibrous tunnels tat anchor the tendon in place |
|
|
|
Does the Dermis have blood vessels? |
Yes, it does. It is vascular. It provides the Epidermis with nourishment. |
|
|
|
What two fibres provide the Dermis with strength and flexibility? |
Collagen (strength) and Elastin (flexibility). |
|
|
|
Is the subcutaneous layer a skin layer? |
No. It is located between the dermis and the underlying deep fascia. |
|
|
|
Where is fat stored? |
In the subcutaneous layer. |
|
|
|
What do skin ligaments do? |
Hold the skin in place. It attaches the deep surface of the dermis to the underlying deep fascia. |
|

