![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The second type of connective tissue we will learn about is cartilage. There are three types...what are they?
|
hyaline, elastic and fibrocartilage
|
|
|
Describe characteristics of hyaline cartilage
|
1. supports, cushions and resists compression
2. found in embry skeleton, end of long bones, nose, trachea, larynx |
|
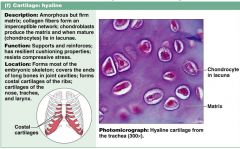
Connective tissue: HYALINE CARTILAGE
|
Connective tissue: HYALINE CARTILAGE
|
|
|
Describe characteristics of elastic cartilage.
|
1. similar to hyaline, but more elastic fibers
2. maintains shape and structure, but still flexible 3. external ear, epiglottis |
|
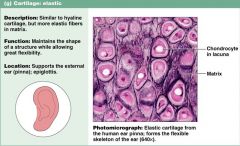
Connective tissue: ELASTIC CARTILAGE
|
Connective tissue: ELASTIC CARTILAGE
|
|
|
Describe characteristics of connective tissue: fibrocartilage
|
1. simliar to hyaline, but LESS firm
2. provide strength, absorbs shock 3. found in discs, and pubic symphysis |
|
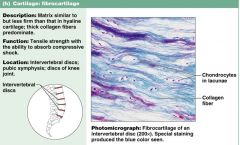
Connective tissue: FIBROCARTILAGE
|
Connective tissue: FIBROCARTILAGE
|
|
|
The third type of connective tissue we will learn about is bone. What are characteristics of bone?
|
1. hard, calcified matrix
2. supports, protects 3. stores calcium, minerals, fat 4. marrow: formation of blood cell components |
|
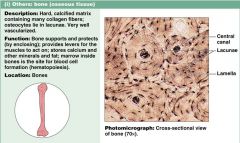
Connective tissue: BONE
|
Connective tissue: BONE
|
|
|
The 4th (and last) type of connective tissue we will learn about is blood. Describe characteristics of blood
|
1. red and white cells in fluid matrix (plasma)
2. found in blood vessels 3. transports respiratory gasses, nutrients, wastes |
|
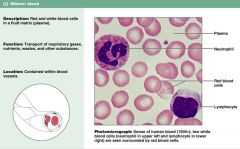
Connective tissue: BLOOD
|
Connective tissue: BLOOD
|
|
|
The third type of tissue we will learn about is nervous tissue. What are characteristics of nervous tissue?
|
1. branched neurons
2. transmits electrical signals 3. found in brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves |
|
|
The 4th (and last) type of tissue we will learn about is muscle tissue. There are 3 types. What are they?
|
skeletal
cardiac smooth |
|
|
What are characteristics of skeletal muscle?
|
1. long, cylindrical
2, initiates and controls voluntary movement 3. attached to bones or skin |
|

Muscle Tissue: SKELETAL
|
Muscle Tissue: SKELETAL
|
|
|
What are characteristics of cardiac muscle?
|
1. propels blood into the circulation
2. found in the walls of the heart |
|
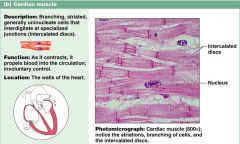
muscle tissue: CARDIAC
|
muscle tissue: CARDIAC
|
|
|
What are characteristics of smooth muscle?
|
1. sheets of spindle shapped cells
2. no striations 3. propels substance through passageways 4. found in walls of hollow organs |
|
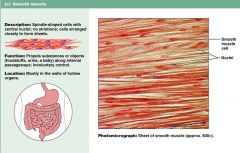
muscle tissue: SMOOTH
|
muscle tissue: SMOOTH
|
|
|
When tissue is tramatized, what happens?
|
1. becomes inflamed
2. dilation of blood vessels 3. redness, heat, swelling, pain |
|
|
What does the word "cutaneous" mean?
|
of, or relating to the skin
|
|
|
What is the cutaneous membrane?
|
This is our skin...the top layer
|
|
|
There are two types of mucous membranes. What are they?
|
mucous and serous
|
|
|
What is the mucous membrane?
|
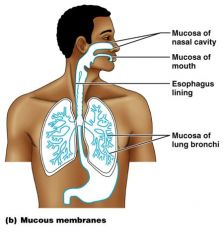
lines body cavities open to the exterior
|
|
|
What is the serous membrane?
|
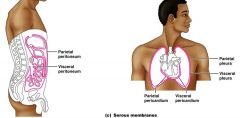
moist membrane found in CLOSED ventral body cavity
|
|
|
Phase 1 of tissue repair
|
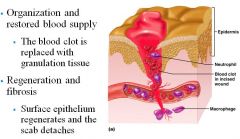
Phase 1 of tissue repair
|
|
|
Phase 2 of tissue repair
|
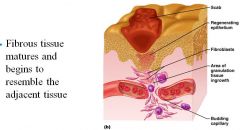
Phase 2 of tissue repair
|
|
|
Phase 3 of tissue repair
|
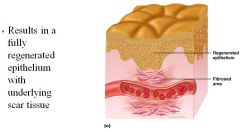
Phase 3 of tissue repair
|
|
|
In the very early embryo stage, there are three primary germ layers. What are they?
|
ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
|
|
|
What do the three primary germ layers evolve into?
|
the 4 primary tissues that we learned about
|
|
|
What does nerve tissue arise from?
|
ectoderm
|
|
|
What does connective and muscle tissue arise from?
|
mesoderm
|
|
|
What does epithelial tissue arise from?
|
all 3 germ layers
|
|
|
Illustration of the 3 germ layers
|

Illustration of the 3 germ layers
|
|
|
Complete breakdown of histology
|

Complete breakdown of histology
|

