![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 4 types of tissue?
|
epithelial, connective, muscle, nerve
|
|
|
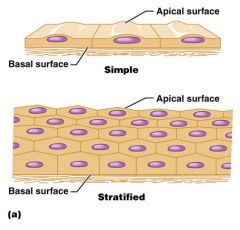
Epithelial tissue forms ______sheets held together by ______ ______ and ______
|
continuous, tight junctions, desmosomes
|
|
|
How is epithelial tissue supported?
|
by connective tissue
|
|
|
Epithelial tissue contains blood vessels. T or F?
|
False
|
|
|
Epithelial cells are regenerative. T or F?
|
True
|
|
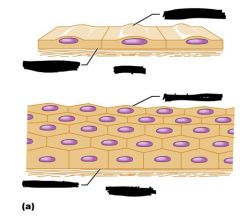
Name the blacked-out regions
|
Good Job!
|
|
|
What are the three classifications (shapes) of epithelia tissue?
|
Squamous, cubodial and columnar
|
|
|
What are the functions of simple squamous tissue cells?
|
1. diffusion and filtration
2. provides slick friction-reduction to linings |
|
|
Where can you find simple squamous tissue cells?
|
kidney, lining of heart, blood vessels, serosae
|
|
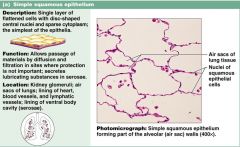
Know the info on this slide
|
Know the info on this slide
|
|
|
A simple cuboidial has a very small central nuclei. T or F?
|
False: very large central nuclei
|
|
|
What is the function of simple cuboidal cells?
|
secretion and absorbtion
|
|
|
Where can you find simple cuboidial cells?
|
kidney tubules, ovary surface, ducts and secretory portions of small glands
|
|
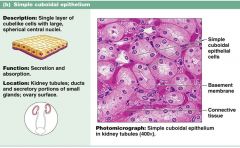
Kown the info on this slide
|
Kown the info on this slide
|
|
|
What shape of nuclei does a simple columnar cell have?
|
oval
|
|
|
What kind of cells are often found in the simple columnar layer?
|
goblet cells (mucus secreating)
|
|
|
There are both cilia simple columnar and non-cilia. Where is the purpose of each?
|
cilia: moves things thru passageways
non cilia - lines small bronchi, uterine tubes |
|
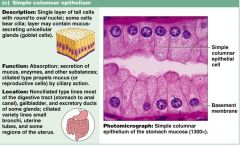
Know the info on this slide
|
Know the info on this slide
|
|
|
What is the function of pseudostratified columnar cells?
|
secretion and propulsion of mucus
|
|
|
Where can you find pseudostratified columnar cells?
|
male sperm-carrying ducts (non cilia) and trachea (cilia)
|
|
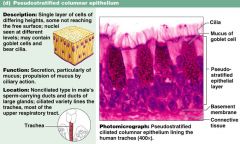
Know the info on this slide
|
Know the info on this slide
|
|
|
Stratified squamous is a thick membrane composed of several ______ of cells.
|
layers
|
|
|
What is the function of stratified squamous cells?
|
protection of underlying areas that are subject to abrasion
|
|
|
Where can stratified squamous cells be found?
|
1. external parts of skin
2, lining of esophagus, mouth and vagina |
|
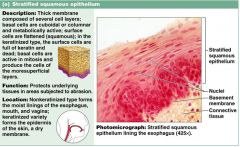
Know the info on this slide
|
Know the info on this slide
|
|
|
Stratified cuboidal and columnar a very common in the body. T or F?
|
False
|
|
|
Stratified cuboidal and columnar cells are typically ______ cell layers thick.
|
two
|
|
|
Where can stratified cuboidal and columnar cells be found?
|
pharynx, male urethra
|
|
|
What is the physicall appearance of transitional epithelia cells?
|
several layers w/ top layers dome shapped and bottom layers cuboidal
|
|
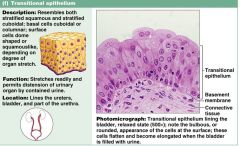
Know the info on this slide
|
Know the info on this slide
|
|
|
What is a gland?
|
One or more cells that makes and secretes an aqueous fluid
|
|
|
How do we classify glands?
|
Where their product is released (endocrine OR exocrine)
|
|
|
What are endocrine glands?
|
ductless glands that produce hormones
|
|
|
What do endocrine glands secrete?
|
amino acids, (glyco)proteins and sterioids
|
|
|
What is more numerous in the body...endocrine or exocrine glands?
|
exocrine
|
|
|
Where do exocrine glands secreate their products?
|
Onto the body surface OR into a body cavity
|
|
|
Give several examples of exocrine gland products.
|
mucous, sweat, oil, saliva
|
|
|
What is the important unicellular gland cell?
|
the goblet cell
|
|
|
Exocrine glands are composed of a ______ and ______ unit
|
duct, secretory
|
|
|
How can exocrine glands be classified?
|
simple OR compound duct types AND by the structure of their secretory units (tubular OR alveolar)
|
|
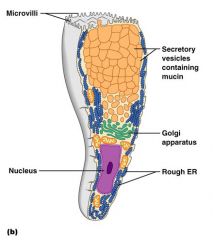
Image of a goblet cell
|
Image of a goblet cell
|
|
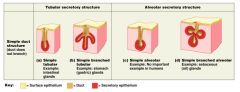
Chart of exocrine secretory STRUCTURES (tubular and alveolar)
|
Chart of exocrine secretory STRUCTURES (tubular and alveolar) SIMPLE only!
|
|
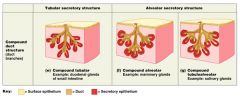
Chart of exocrine secretory STRUCTURES (tubular and alveolar) COMPOUND only!
|
Chart of exocrine secretory STRUCTURES (tubular and alveolar) COMPOUND only
|

