![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
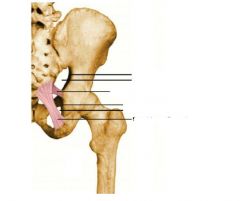
Label lines
|
|
|
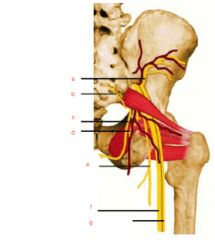
Name the nerves etc
|
a. superior gluteal nerve
b. inferior gluteal nerve c. pudendal nerve d. nerve to obturator internus e. posterior cutaneous nerve of thigh f. tibial branch of sciatic nerve g. common peroneal branch of sciatic nerve |
|
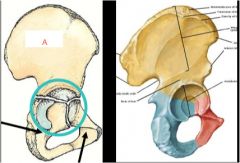
|
a. Ilium
Arrows left to right ischium, pubis |
|
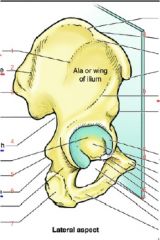
What are the labels?
|
1. anterior gluteal line
2. posterior gluteal line 3. posterior superior iliac spine (PSIS) 4. greater sciatic notch 5. ischial spine 6. lesser sciatic notch 7. ischial tuberosity a. iliac crest b. inferior gluteal line c. articular surface d. acetabular fossa e. acetabular notch f. obturator foramen |
|
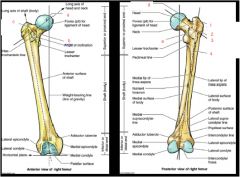
What are the markings? except 3?
|
a. head
b. neck c. greater trochanter d. trochanteric fossa e. intertrochanteric crest 1. greater trochanter 2. quadrate tubercle 4. gluteal tuberosity |
|
|
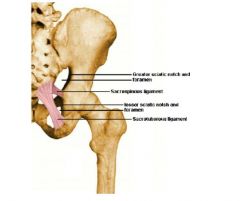
What are the two ligaments that form the two important foramina for the passage of structures into and out of gluteal region?
What are the two foramens? |
1. sacrospinous ligament
2. sacrotuberous ligament 1. greater sciatic foramen- all exit 2. lesser sciatic foramen- all enter |
|
|
What muscles does superior gluteal nerve supply?
What muscles does the inferior gluteal nerve innervate? |
Leaves superior to piriformis
gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, tensor faciae latae Leaves inferior to piriformis gluteus maximus |
|
|
What is the route and roots of sciatic nerve?
|
-Leaves pelvis inferior to pirformis
- divides 1/2 way down thigh to tibal and common fibular nerves - roots L4-S3 vetral rami |
|
|
Posterior hip disloation can cause damage to what nerve?
What may result in this type of injury? |
-paralysis of hamstrings and distal muscles to knee
- sensory changes in posterlateral parts of leg |
|
|
Describe roots and role of posterior femoral cutaneous nerve and pudendal nerve
|
S1-S3
- innervates skin of butt, thigh, and calf -S2-4 Most medial structure exiting greater sciatic foramen, re-enters pelvis via lesser sciatic foramen |
|
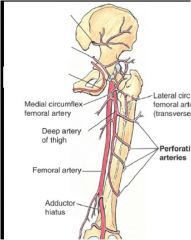
What are the three main arteries of the gluteal region? Where do these three arise from?
|
top left superior to inferior
(superior gluteal arter, inferior gluteal artery, internal pudendal artery) all arise from the internal illiac artery |
|
|
What does the pneumonic "I Love Going Places In My Very Own Underware" stand for?
|
branches of internal iliac artery
"I Love Going Places In My Very Own Underwear": Ileolumbar Lateral sacral Gluteal (superior and inferior) Pudendal (internal) Inferior vesicle (uterine in females) Middle rectal Vaginal Obturator Umbilical |
|
|
What muscles does the superior gluteal artery supply and where does it originate?
|
third and largest branch of internal iliac artery- gives blood to:
Superior gluteus maximus Deep branch: gluteus medius, minimus, tensor fascia lata |
|
|
What muscles does the inferior gluteal artery supply and what does it do in the thigh?
|
supplies:
gluteus maximus, small lateral rotators, superior hamstrings Involved with cruciate anastomosis of thigh: 1 medial circumflex femoral artery, 2. lateral circumflex of femoral artery 3. first perferating artery |
|
|
What is the significance of the cruciate anastomosis?
|
by passes an obstruction of the external iliac or femoral artery
|
|
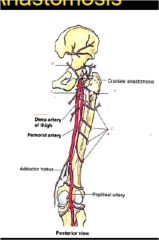
What are the points of the cruciate anastomosis?
|
a. lateral circumflex femoral artery (transverse branch)
b. interior gluteal artery c. perforating artery (first one) d. medial circumflex femoral artery |
|
|
What area of the gluteal region should intragluteal injections be made and why?
|
superior lateral quadrant avoiding sciatic nerve
|
|
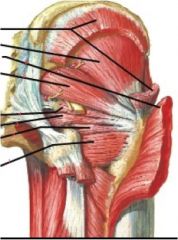
What main muscle does 2-4 form... label rest!
|
2-4 form the tricep cocci
1. quadratus femoris 2. inferior gemellus muscle 3. obturator internus muscle 4. superior gemellus muscle 5. piriformis muscle 6. gluteus maximus 7. gluteus minimus 8. gluteus medius muscle |
|
|
What are facts and innervations of the following muscles:
a. gluteus maximus b. gluteus minimus/medius |
a. inferior gluteal nerve L5-S1, largest gluteal muscle, chief extensor, lateral rotation, slight leg extension
b. medius is over minimus, thigh abduction and medial rotation Superior gluteal nerve (L5-S1) |
|
|
What are facts and innervations of the following muscles:
a. tensor fasciae latae b. function of iliotibial tract |
a. superior gluteal nerve (L4-S1)
abducts, medial rotates, flexes thigh, slight extension of knee b. assists decelerating adduction of thigh, stabilizes knee, stretch to treat chondromalacia patella |
|
|
If patient presents with waddling gait that is characterized by pelvis falling toward unaffected side what is it called?
Causes? |
called: limp or gluteal gait
also called positive trendelenburg's sign Causes- superior gluteal nerve injury to gluteus medius and minimus |
|
|
If person presents with positive trendelenburg sign what are muscles and nerves affected?
|
muscles- gluteus minimus and medius
nerve- superior gluteal nerve |
|
|
When leaning on left leg what does gluteus minimus and medius do?
If right side gluteus minimus and medius injured? |
keep trunk raised, body will fall toward left so compensation by leaning toward injured side- causing limp
|
|
|
What is the role of the piriformis?
|
Demarcates gluteal blood and vesses and nerve
nerve- nerve to periformis |
|
|
Describe the obturator internus and externus and how they relate and insert themselms...
|
part of triceps cocci
Internus- stopping up in |
|
|
Describe innervation of superior and inferior gemelli
|
Two nerves come from two long nerves
(N to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus and N to obturator internus and superior gemellus) |
|
|
Which of small lateral rotators are least effective when thigh is flexed?
|
?
|
|
|
Which artery is involved in the arterial anastomosis around the hip joint
|
medial circumflex femoral artery
|
|
|
What is the articularis genu and role?
|
small slips of vastus intermedius that raise the joint capsule/suprapatellar bursa during extension of the leg
|
|
|
What two nerves receive contribution from L2-L4?
Name the terminal branch of the femoral nerve... |
femoral and obturator
saphenous n. |
|
|
Which nerve innervates obturator internus?
In order from superior to inferior what muscles are below the piriformis in the gluteal region? |
nerve to obturator internus and superior gemellis
-ticeps coxae- (superior gemellis, obturator internus, inferior gemellis) |
|
|
What is the femoral sheath and what does it contain?
|
extension of transversalis fascia around femoral vessels and femoral canal
|
|
|
Where is the adductor hiatus?
Where do most posterior thigh muscles originate and which nerve supplies? |
distal/inferior aspect of adductor magnus also marks beginning of popliteal vessels
ischium, tibial portion of sciatic nerve |
|
|
Name all the vessels that contribute to the cruciate anastomoses
|
medial and lateral circumflex femoral, inferior gluteal, and first perforating artery of deep femoral
|
|
|
What three muscles form the pes anserinus?
What are the two terminal branches of the sciatic nerve? |
sartorius,
gracilus semitendinosis - tibial and common fibular |
|
|
What general structures are found in the popliteal fossa superior to inferior?
Which nerve travels with the small saphenous vein? what two nerves form it? |
tibial nerve, popliteal vein, popliteal artery
- sural nerve...formed from a. medial sural cutaneous and sural communicating branch (from lateral sural cutaneous) |

