![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The ability to detect the external enviroment is accomplished by a series of a specialized structures called:
|
sensory receptors
|
|
|
The sense of smell is related to the first cranial nerve, which passes through the ethmoid bone into the nasal cavity, called the:
|
olfactory nerve
|
|
|
The normal adult possesses a number of cutaneous (exteroceptive) senses. Among these are:
|
pain, pressure and heat
|
|
|
The detection of certain low energy forms of electromagnetic radiation can be accomplished by photoreceptors located in the:
|
eye
|
|
|
The degree of distention is some muscular organs, such as the rectum and the urinary bladder, is accomplished by:
|
stretch receptors
|
|
|
The transparent outer portion of the eye that allows passage of light into the eye is called the:
|
cornea
|
|
|
The tympanic cavity is a small irregular space within the temporal bone that serves to house the structures associated with:
|
hearing
|
|
|
The specialized organs on the tongue for the detection of taste are called:
|
taste buds
|
|
|
The external funnel-like structure of the ear that helps to direct sound vibrations to the ear is called the:
|
auricle
|
|
|
The tympanic membrane is a thin membrane which separates the structures of the:
|
external and middle ear
|
|
|
Pressure differences in the middle ear must be maintained to prevent hearing impairment. The structure associated with this function is the:
|
Eustachian tube
|
|
|
The small bones of the middle ear that serve to transmit sound vibrations to the inner ear are the:
|
incus, stapes, malleus
|
|
|
The sense of equilibrium (balance) is controlled by a series of small fluid canals called the:
|
semicircular canals
|
|
|
The specialized receptor for hearing located on the basilar membrane of the cochlea is called the:
|
organ of Corti
|
|

stapes at oval window
|
A
|
|

cochlear nerve
|
E
|
|

vestibule
|
B
|
|

semicircular canals
|
C
|
|

cochlea
|
F
|
|

vestibular portion of the acoustic nerve
|
D
|
|
|
The membraneous labyrinth of the inner ear is surrounded by a protective fluid called:
|
perilymph
|
|
|
The action of otoliths on the hairlike extensions of the macula in response to gravity is interpreted by the brain to help control:
|
positional orientation
|
|
|
The tongue is able to detect four primary taste sensations. Among these is:
|
sweet, sour, salt, bitter
|
|
|
Visceral pain impulses may be felt at body parts other than where the stimulus is occurring. This phenonmenon is called:
|
referred pain
|
|
|
The upper eyelid that forms a protective covering for the eye also houses a small gland that produces tears called the:
|
lacrimal gland
|
|
|
The production of tears helps to moisten and protect the eye from bacterial infection and will drain into the nasal cavity through the:
|
nasolacrimal duct
|
|
|
The visual receptors cells are located on the back of the eye in the cellular layer called the:
|
retina
|
|
|
The amount of light passing through the pupil of the eye is controlled by a set of circular muscles called the:
|
iris
|
|
|
The majority of the eyeball is composed of a white, fibrous protective covering called the:
|
sclera
|
|
|
The impulses for visual sensation will pass into the occipital lobe of the brain by way of the second cranial nerve, which is also called the:
|
optic nerve
|
|
|
The action of the ciliary bodies control the shape of a transparent oval body called the _______ which serves to focus light on the back of the eye.
|
lens
|
|
|
Eye color is due principally to the appearance of a circular muscle called the:
|
iris
|
|
|
The retina is composed of two distinct types of cells called:
|
cones and rod
|
|
|
The point of the retinal surface with the greatest amount of visual acuity is the:
|
fovea centralis
|
|
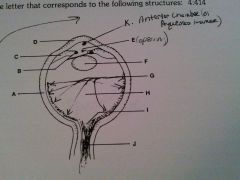
vitreous humor
|
H
|
|
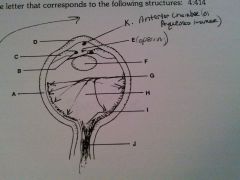
cornea
|
D
|
|
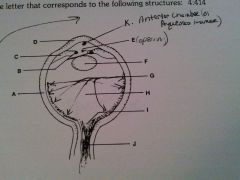
lens
|
F
|
|
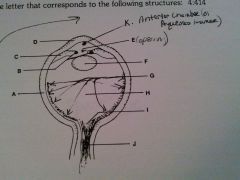
optic nerve
|
J
|
|
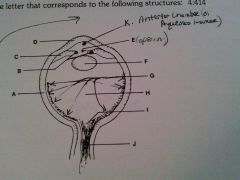
retina
|
G
|
|
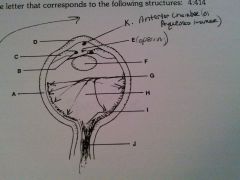
sclera
|
A
|
|
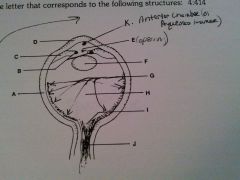
iris
|
B
|
|
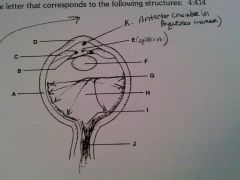
ciliary body
|
C
|
|
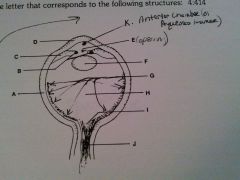
pupil opening
|
E
|
|
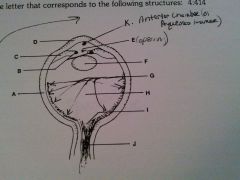
optic disc
|
I
|
|
|
The normal value for the interpupillary measurement is:
|
2.5" (6-7 cm)
|
|
|
High interocular pressure most commonly results from excessive amounts of _______ buildup in the anterior chamber.
|
aqueous humor
|
|
|
There are no photreceptors in the area where the optic nerve joins the posterior portion of the eye leaving a blind spot called the:
|
optic disc
|
|
|
The clouding of the lens of the eye is a common cause of blurred vision. This condition is called:
|
a cataract
|
|
|
The specialized cell of the retina that is primarily responsible for color vision is the:
|
cone
|
|
|
the principal muscle group responsible for eye movement are the:
|
rectus muscles
|
|
|
Differentiate between endocrine and exocrine glands.
|
endocrine- ductless
exocrine- ducts |
|
|
What is known as the "master gland of the body"?
|
pituitary
|
|
|
What is secreted by the adrenal medulla?
|
epinephrine
|
|
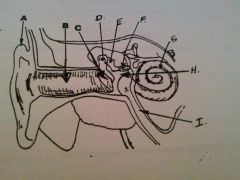
What is A?
|
auricle or pinna
|
|
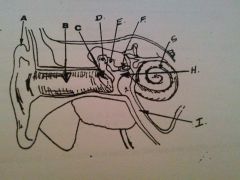
What is B?
|
EAM
|
|
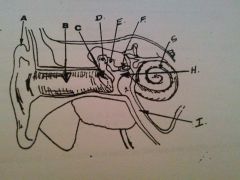
What is C?
|
tympanic membrane
|
|
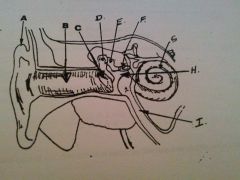
what is D?
|
malleus
|
|
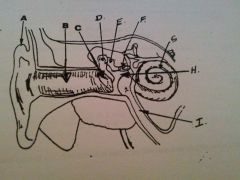
What is E?
|
incus
|
|
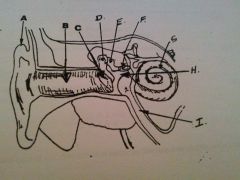
What is F?
|
stapes
|
|
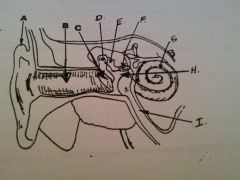
What is G?
|
cochlea
|
|
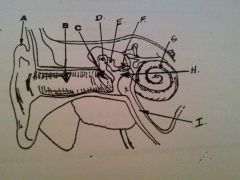
What is H?
|
tympanic cavity
|
|
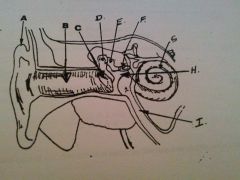
What is I?
|
Eustachian tube
|

