![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the major components of blood plasma? |
Water – 91% Proteins – 7% All other solutes – 2% |
|
|
Antibodies on each blood type: A B AB O |
B A none both |
|
|
Antigens on each blood type A B AB O |
A B both none |
|
|
structure of RBC |
- Biconcave discs - Contractile proteins – help a red blood cell contract - No nucleus – anucleaus |
|
|
What are the differences between the pulmonary and systemic blood circuits? |
Pulmonary - carries blood to the lungs, from the heart is deoxygenated Systemic - goes to the body |
|
|
Five WBC and functions - |
1. Neutrophil - phagocytize bacteria 2. Eosinophil - they digest parasitic worms 3. Basophil -histamine and heparin which are important in inflammatory process; 4. Monocytes - phagocytize everything 5. Lymphocytes - produce T and B cells |
|
|
• If NFP is positive, if NFP is _negative, |
- fluid is driven out of the capillary • fluid is drawn back into the capillary |
|
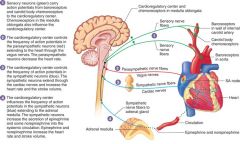
Green dots - top green line - red line - blue line - |
Baroreceptors/ chemoreceptors - sensory receptors vagus nerve cardiac nerves |
|
|
What effect does aldosterone have on blood pressure? |
lowers blood pressure by water and sodium reabsoprtion |
|
|
What are the name and the basic characteristics of the heart's pacemaker? |
a. Sinoatrial (SA) node 70-80 bpm |
|
|
How does blood move within veins toward the heart? |
blood is drained into cardiac veins, which join to form the coronary sinus, this leads to the right atrium |
|
|
Short-term BP controls work more on _________ while long-term BP controls work on __________. |
- peripheral resistance - blood volume |
|
|
What is the vasomotor center and how does it work? |
– cluster of Sympathetic neurons in medulla oblongata - • vasomotor nerve fibers innervate smooth muscle of small arteries and arterioles• these fibers release Norepinephrine, which cause vasoconstriction => rising BP |
|
|
What happens to blood flow with temperature change, anemia and polycythemia? |
Higher temperature - higher blood flow anemia - low blood flow polycythemia - low blood flow |
|
|
What structure filters blood to remove pathogens and also breaks down dead/damaged RBC’s? |
spleen |
|
|
What are the major functions of dendritic cells, reticular cells, lymphocytes and macrophages in the lymphatic system? |
dendritic - foreign antigen recognition Reticular - supports other cell types. Lymphocytes - make B and T cells - immune resp Macrophages - ; surveillance for foreign cells |
|
|
What is the correct sequence of structures in the flow of lymph from smallest to largest? |
Lymphatic capillaries, vessels, nodes, trunks, ducts. |
|
|
How does lymph enter and remain in lymph vessels? |
Enter in lymph vessels and only flow in one direction |
|
|
What is the equation for cellular respiration that explains the importance of the respiratory system? |
C6H12O6+ 6 O2 <-->6 CO2+ 6H2O + 36ATP’s |
|
|
What pressure change occurs in our chest to cause inhalation? |
• Pressure in the intrapleural space and lungs drops by 1 cm H2O;pressure inside the lungs becomes negative compared to outside (atmospheric) air |
|
|
Under what conditions would O2 normally be bonded tightly to Hemoglobin so it will NOT move into body cells? |
decreasing temperature decreasing H+ in blood (higher pH) decreasing Pco2 decreaseing BPG in blood |
|
|
What is the “respiratory membrane” where gas exchange occurs |
Alveolus |
|
|
What are the meanings of deglutition, mastication, peristalsis and segmentation? |
swallowing chewing rhythmic contraction of food in the GI tract mixing of food backwards and forwards in small intestine |
|
|
What nervous systems control digestion |
enteric and autonomic |
|
|
Reactions that occur as nutrients are chemically digested are essentially _______ reactions. |
metabolic |
|
|
How do the products of digestion: lipids, amino acids and monosaccharides, enter capillaries? |
amino and mono - by facilitated diffusion lipids - simple diffusion, then out by exocytosis |
|
|
What ions are involved with each phase of cardiac muscle contraction? |
Depolarization - voltage Na open, voltage K close, and voltage Ca start to open Platuea - voltage Na close, some voltage K open, Ca still open Repolarization - More voltage K open, Ca close |
|
|
what are their functions: sarcolemma, SR, T tubule, mitochondria and nucleus. |
- muscle contraction - SR - stores calcium - even contractions by allowing action potential - makes ATP - stores DNA |
|
|
What is the role of calcium in excitation-contraction coupling in a cardiac muscle cell? |
Ca+ binding to troponin, causing exposure of binding sites on actin, cross bridge pulling of myofilaments (power stroke), and contraction |
|
|
Nervous stimulation causes the contraction of the appropriate muscles, which causes the size of the chest cavity to ____, and the lungs then change in size the same way. This size change causes the pressure in the lungs to _____, so the pressure inside the lungs becomes ________ with respect to outside air. This pressure difference causes air to rush in and fill the lungs, thus causing inhalation. Exhalation occurs when the nerve stimulus to the relevant muscles stops, thus allowing these muscles to relax. The chest cavity returns to its normal size, and therefore the pressure in the lungs _____; it becomes ______ with respect to outside air. This allows air to rush out of the lungs - you exhale. |
increase decrease negative increase positive |
|
|
Name the two MOST IMPORTANT types of phagocytic cells that participate in the body’s immune responses. |
Neutrophils Macrophges |
|
|
. List five examples of nonspecific barriers in the 1st line of immune defense |
1. Intact skin and mucous membranes 2. Secretions from glands in the skin 3. Saliva and tears 4. Muco-ciliary escalator system in the respiratory tract 5. Acidic fluid in the stomach and vagina; urine is acidic. |
|
|
Identify the specific immune response which targets body cells that are infected or abnormal and the immune system cells responsible. |
cell-mediated immune response |
|
|
List the anterior pituitary hormone(s) released by these hypothalamic hormones and their target gland or organ: CRH GHRH TRH PRH GnRH |
- Adenocorticotropic hormone - adrenal cortex - Growth Hormone - bones and muscles - Thyroid stimulating hormone - thyroid gland - Prolactin - mammary glands - Follicle -stimulating hormone/ Lutinizing hormone- gonads/gonads |
|
|
Thyroid hormone acts through __________________ feedback on the release of hormones by the ________________________ pituitary and hypo______________________. |
negative anterior hypothalamus |
|
|
State how the half-life of a hormone may be increased. |
binds to Tyroid-binding globulin;TBG |
|
|
The endocrine system communicates with target cells by way of __________________messengers in the ______________________________. |
chemical bloodstream |
|
|
Sensory receptors for smell are classified as ________________receptors. |
olfactory |
|
|
Differentiate between rods and cones by shape, location on the retina and by function. |
rods - rod shaped/surrounding blind spot/dim light cones - cone shapped/ontop of blind spot/ color vision/acuity |
|
|
What Cranial Nerves relay taste information [Fig. 15.7]? |
5, 7, 9, 10 |
|
|
The hair cells for hearing are stimulated due to vibration of the ___________________Membrane. |
tympanic |

