![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
143 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the Bohr Effect? |
A decrease in pH and an increase in CO2 will cause O2 and Hb to separate. |
|
|
Haldane Effect |
Hb will become saturated with Oxygen but when the PO2 becomes low enough Hb will bind to CO2 |
|
|
How is oxygen carried in the blood? |
1.5% dissolves in plasama 98.5% in the rest of the body |
|
|
How is carbon dioxide carried in the blood? |
5% dissolves in plasma
20% dissolves in blood 60-80% as bicarbonate |
|
|
Somatic system how many neurons? neurotransmitters? effect? (excite/inhibit) |
1 neuron acetylcholine excite |
|
|
Parasympathetic how many neurons? neurotransmitters? effect? (excite/inhibit) |
2 neurons acetylcholine excite/inhibit |
|
|
Sympathetic how many neurons? neurotransmitters? effect? (excite/inhibit) |
2 neurons acetycholine excite *exception innovation of adrenal gland: norepinephrine and epinephrine |
|
|
A man weighs 200 lbs. his breathing rate is 10 breaths/min. tidal volume = 500mL calculate his minute ventilation rate |
min ventilation rate= tidal vol x rate 500 x 10= 5000 mL |
|
|
A man weighs 200 lbs .his breathing rate is 10 breaths/min. tidal volume = 500mL calculate his alveolar ventilation rate |
alveolar vent. rate= (tidal vol-dead space) x rate (500-200) x 10= 3000 mL |
|
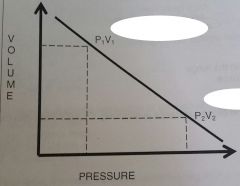
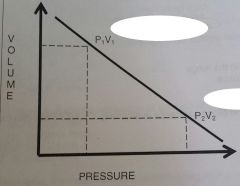
What law is associated with the relationships shown? |
Boyle's Law |
|
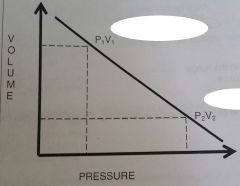
Describe how this graph relates to the mechanics of ventilation |
As pressure increases volume decreases in expiration
|
|
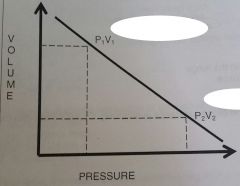
What causes air to enter the lungs what causes air to flow out of the lungs? |
because the atmospheric air pressure is slightly higher than alveolar pressure and creates a pressure gradient. |
|
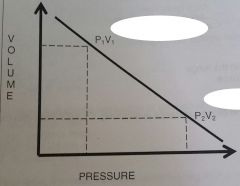
what muscle activity contributes to increased ventilation? |
external intercostals
|
|
besides pressure and volume, describe one other factor that can affect the amount of air reaching the alveoli |
diameter of airway
|
|
|
during quiet or resting expiration the diaphram |
relaxes
|
|
|
during expiration the alveolar pressure is |
greater than the barometric pressure |
|
|
alveolar ventilation is the |
amount of air available for gas exchange
|
|
|
if the PO2 in the alveoli is 104mmHg and the PO2 in the blood capillaries is 40mmHg, O2 will diffused into the blood according to whos law? |
Henry's law |
|
|
the partial pressure of CO2 in the venous blood is _____ than the alveoli |
greater than |
|
|
The partial pressure of oxygen in the blood is established by the amount of oxygen |
dissolved in plasma |
|
|
the chloride shift |
promotes the transport of CO2 in the blood Occurs when Cl- ions replace HCO3- in the red blood cells maintains the electrical neutrality between red blood cells and the blood |
|
|
Parasympathetic ganglia |
are usually close to or embedded in target organs |
|
|
Hb is saturated when it carries __ molecules in O2; Myoglobin is saturated when it carries __ |
4;1 |
|
|
acetylcholine is released by the _______ neurons to ________ heart rate |
parasympathetic; increase |
|
|
sympathetic innervation of the heart results from neurons with roots from |
T1-5 |
|
|
most organs of the body |
receive dual innervation from the psns and sns |
|
|
the major pathway for parasympathetic outflow from the cranial region is the |
vagus nerve |
|
|
the preganglionic cell bodies of sympathetic neurons are located in the ____ of the spinal cord |
lateral horn |
|
|
at sea lvl the most important factor leading to the increase in breathing rate and depth is blood lvls of |
carbon dioxide |
|
|
inspiratory reserve volume |
oxygen intake when you take a deep breath |
|
|
residual volume |
regular air exchange |
|
|
expiratory reserve volume |
oxygen that is forcable pushed out of lungs |
|
|
viral capacity |
total exchangeable air |
|
|
terminal ganglia |
ganglia at target organ |
|
|
Haldane Effect |
Co2 and O2 wont bind to Hb at the same time |
|
|
carbaminohemoglobin |
CO2 bound to Hb |
|
|
carbonic anhydrase |
critical for synthesis of bicarbonate |
|
|
herring-breuer reflex |
prevents over-inflating lungs |
|
|
Dalton's law |
sum of partial pressure |
|
|
henry's law |
gas dissolves in fluid |
|
|
Bohr Effect |
increase temperature and co2, decrease pH |
|
|
respiratory centers |
pons and medulla |
|
|
nerve roots t1-L2 |
sympathetic nervous system |
|
|
cranial nerves; sacral roots |
parasympathetic nervous system |
|
|
The stomach has an area closest to the duodenum called the |
pyloric region
|
|
|
the gallbladder releases bile in response to |
cholesystokinin |
|
|
pancreatic bicarbonate is secreted by the |
intercalated duct cells |
|
|
Pepsinogen, a digestive enzyme |
chemically digest proteins is secreted by the chief cells of the stomach |
|
|
Amylase, an enzyme that breaks down carbs, is secreted bt |
salivary glands and pancreas |
|
|
amino acids and glucose are absorbed into the ___ while lipids are absorbed into the ___ |
blood; lymph |
|
|
the targets of human growth hormone is/are |
all are targets
bone muscle liver adipose tissue.. |
|
|
hydrochloric acid is secreted by the ___ cells of the stomach |
parietal |
|
|
there are three phases of gastric secretion, the cephalic phase occurs |
even before food enters the stomach
|
|
|
when it comes to movement of food through the digestive tract...order |
esophagus, cardiac sphincter, pyloric sphincter, ileum, descending colon |
|
|
production of thyroxine by follicular cells in the thyroid requires iodine and |
tryosine |
|
|
if an incision is made completely through the wall of the ileum, the last layer to be cut is the |
mucosa |
|
|
nutrient rich blood from the sm intestines enters the ___ by the way of the ___ |
liver; hypatic portal vein |
|
|
the secretion of the thyroid hormones T3 & T4 is controlled by TSH from the: |
anterior pituitary |
|
|
# of hormones produced by the posterior pituitary |
2 |
|
|
chemical signaling of nearby but different cells is called |
paracrine |
|
|
second messenger systems such as cAMP is characteristics of |
protein based hormones |
|
|
if an autoimmune disorder targets beta cells of the pancreas, the production of which hormone is affected |
insulin |
|
|
which of the following is a steroid hormone? human growth hormone insulin thyroxine cortisol |
cortisol |
|
|
the substance that stimulates the pancreas to release enzymes and the gallbladder to release bile: |
cholecystokinin |
|
|
calcitonin comes from the |
thyroid |
|
|
bicarbonate is secreted by |
exocrine pancreas - digestive enzymes |
|
|
mucous is secreted by |
goblet cells
|
|
|
hydrochloric acid is secreted by |
stomach |
|
|
melanocyte-stimulating hormone is secreted by |
pars intermediate |
|
|
aldosterone is secreted by |
adrenal cortex |
|
|
antidiuretic hormone is secreted by |
posterior pituitary |
|
|
cholecystokinin is secreted by |
duodenum
|
|
|
gastrin is secreted by |
stomach |
|
|
cortisol is secreted by |
adrenal cortex |
|
|
thyroid hormone releasing hormone |
hypothalamus |
|
|
human growth hormone is secreted by |
anterior pituitary |
|
|
ACTHis secreted by |
anterior piruitary |
|
|
androgens is secreted by |
adrenal cortex |
|
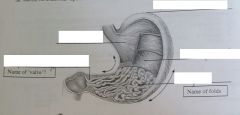
|
fundus cardiac oblique muscle pyloric sphincter rugae |
|
|
describe the chemical reaction that is used to produce hydrogen ions (to make hydrochloric acid) and to produce bicarbonate ions in digestion |
CO2 diffuses across membrane CO2+H2O >> carbonic anhydrase carbonic anhydrase >> H2O3- bicarbonate Cl- exchanges for H+ |
|
|
identify the cells and organs specifically responsible for producing hydrochloric acid and bicarbonate |
hyrdochloric acid- stomach, parietal cells bicarbonate- pancreas, intercalated ducts |
|
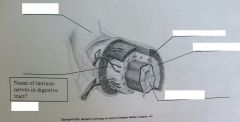
|
serosa muscularis submuscularis mucosa entric nerves |
|
|
3 ways that secretion rate for a given hormone may be controlled |
Neural hormonal humoral |
|
|
3 ways that secretion rate for a given hormone may be controlled- Neural |
Neural- stimulation by nervous system on endo-gland ex: adrenal gland release of epinephrine and norepinephrine |
|
|
3 ways that secretion rate for a given hormone may be controlled- Hormone |
Hormone- stimulation of one endocrine gland on another ex: anterior pituitary secrets TSH to thyroid |
|
|
3 ways that secretion rate for a given hormone may be controlled - Humoral |
humoral- stimulation by something other than hormone on endo-gland ex PTH is released when blood calcium is low |
|
|
Compare homeostatic regulation by the nervous and endocrine system |
specialized centers effects: quick specific short-lived amplitude modulated |
|
|
Compare homeostatic regulation by the nervous and endocrine system |
glands
hormones effects: slow general long lasting frequency modulated |
|
|
Gallbladder identify and fnx |
small organ found on liver
fnx: stores bile |
|
|
Pancreas identify and fnx |
organ with endo- and exocrine fnx fnx: endo- controls regulation of insulin and glucagon exo- secretes digestive enzymes |
|
|
Live identify and fnx |
largest organ has two major lobes L & R lobes Fnx: detox synthesis, bile production |
|
|
list all nine hormones of the pituitary |
Pars Melanocyte stimulating hormone anterior Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) Luteinising hormone (LH) Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) Prolactin Growth hormone (GH) posterior oxytocin Antiduritic hormone (ADH) |
|
|
Water is reabsorbed all except from the |
ascending loop of henle |
|
|
the blood vessels that exit the glomerulus are called the |
effernt arterioles |
|
|
under normal conditions blood cells are not found in the |
proximal convoluted tuble |
|
|
the glomerulus contains_______ capillaries and adjacent cells called______ |
fenestrated; nephrons |
|
|
the primary force that pushes water and solute out of the blood across the filtration membrane is |
the glomerular hydrostatic pressure |
|
|
the renal corpuscle is made up of |
bowamn's capsule and the glomerulus
|
|
|
what is a stimulus for micturition |
filling and stretching of the bladder wall |
|
|
renin is released in response to |
decreased blood pressure |
|
|
if an incision is made into a kidney, the first layer to be cut is the |
renal capsule |
|
|
which of the following is a potent vasocontrictor? insulin angiotensin II atrial natriuretic hormone renin |
angiotensin II
|
|
|
the filtration membrane includes all of the following except: |
renal pelvis |
|
|
what is an example of insensible water loss from the body |
breathing |
|
|
the term water intoxication is also called |
hyponatremia |
|
|
hyponatremia results from |
drinking large amounts of fluids low in sodium |
|
|
Respiratory alkalosis can occur when: |
a person travels to altitudes- above 3000m-starts breathing rapidly |
|
|
which of the following two organs fnx as important physiological buffer systems? |
lungs and kidneys |
|
|
while chloride is the main anion (-) in the exrtracellular fluid_________ is the main intracellular anion |
phosphate |
|
|
intracellular fluid in the human body is composed of |
fluid in cell cytoplasm |
|
|
blood pH varies _____ with CO2 lvls but_______ with bicarbonate lvls. |
inversely; directly |
|
|
the largest amount of water leaves the body through |
urine |
|
|
Renal pelvis |
drains into the ureter |
|
|
Retro-peritoneal |
describes location of kidneys in the body |
|
|
juxtoglomerular cells |
helps adjust GFR |
|
|
mascula densa cells |
found in distal convoluted tuble |
|
|
Trigone |
urethra, plus two ureter openings |
|
|
renal medulla |
location of lowest point of loop of henle |
|
|
renal cortex |
lighter, outer tissue layer |
|
|
urethra |
transports urine from bladder to outside of the body |
|
|
renal pyramid |
cone-shaped tissue in medulla |
|
|
fibrous capsule |
outermost layer of kidney |
|
|
per-renal fat |
cushions; protects |
|
|
bladder |
contains transitional epithelia |
|
|
explain the role of these hormones in regulation of Na+, H2O blanace, and/or blood pressure: Renin |
|
|
|
explain the role of these hormones in regulation of Na+, H2O blanace, and/or blood pressure: Aldosterone |
causes renal tubles to retain Na+ bp decrease H2O decrease |
|
|
explain the role of these hormones in regulation of Na+, H2O blanace, and/or blood pressure: Atrial Natriuretic Hormone |
produced by <3 when bp increases |
|
|
explain the role of these hormones in regulation of Na+, H2O blanace, and/or blood pressure: Anti-diuretic hormone |
|
|
|
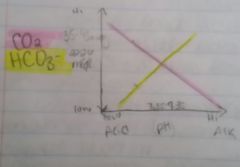
range of acidosis-alkilosis |
pH 7.35-7.45 |
|
|
PCO2 range |
respiratory system 35-45 mmHg |
|
|
HCO3- range |
metabolic 22-26 |
|
|
|
|
|
Define Euhydration |
total amount of water in body that stays constant |
|
|
primary mechanisms of fluid loss for the human body |
urination sweat insensible (breathing) |
|
|
primary sources of fluid |
food
ingested fluid cell metabolism |
|
|
4 primary ways that the body releases heat into the environment |
Evaporation
Radiation conduction convection |
|
|
Evaporation |
the transfer of heat by the evaporation of water. |
|
|
Radiation |
occurs between any two objects when their temperatures diffes |
|
|
conduction |
the transfer of heat by two objects that are in direct contact` |
|
|
convection |
the transfer of heat to the air surrounding the skin |
|
|
What is our normal glomerular filtration rate |
125 mL/min |
|
|
What are the mechanisms controlling GFR |
myogenic mechanism (auto regulatory) tubuloglomerular (autoregulatory) neural control renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system |
|
|
total energy expenditure 20min x 10kcal/min=200kcal total heat produced 200kcal x .8=160kcal heat loss from sweat 580 kcal/L sweat needed to prevent heat gain 160/580 = .28L of sweat |
|

