![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
400 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
CNS/PNS (Composition) |
|
|
|
Sensory/Motor (Functions) |
|
|
|
Somatic/Visceral Sensory |
|
|
|
Somatic/Visceral Motor |
|
|
|
Sympathetic/Parasymapthetic |
Sympathetic: ventral root of spinal nerves T1-L2 Parasympathetic: ventral root of S2-S4 All other nerves must "catch a ride" |
|
|
Cell body/Soma |
|
|
|
Dendrites |
Directing info towards soma |
|
|
Axon |
Directing info away from soma |
|
|
Astrocyte |
Blood brain barrier Regulate fluid Structural support of CNS (Glue) |
|
|
Oligodendrocytes |
Produce myelin for CNS |
|
|
Microglial cells |
Destroy viruses and bacteria in CNS |
|
|
Ependymal Cells |
Line ventricles of brain Produces CSF with choroid plexi |
|
|
Schwann cells |
Produce myelin around axons in PNS |
|
|
Satellite cells |
Surround and separate cell bodies in ganglia Regulate nutrient and waste exchange |
|
|
Forebrain/Cerebrum 3 layers |
1: cortex (grey matter) 2: tracts (white matter) 3: deeper gray matter |
|
|
Cortex of the Cerebrum |
Outer covering |
|
|
Cerebral sulci |
Grooves the cortex |
|
|
Cerebral gyri |
Hills between the sulci |
|
|
Longitudinal fissure |
Separates two hemispheres |
|
|
Central sulcus |
Groove separating frontal lobe from parietal lobe |
|
|
Lateral sulcus |
Superior border of temporal lobe |
|
|
Parieto-occipital Sulcus |
Groove between parietal lobe and occipital lobe |
|
|
Insula lobe |
Deep to temporal lobe |
|
|
Pre/post central gyrus (location and function) |
Pre-central: gyrus in front of central sulcus; motor in function Post-central: gyrus behind central sulcus; sensory in function |
|
|
Association type tracts |
Join gyri in same hemisphere in cerebrum |
|
|
Commissural tracts |
Axons that join right and left hemispheres (ex. Corpus callosum) |
|
|
Projection tracts |
Axons that transmit sensory information between cortex and deeper brain |
|
|
Structures of the deeper gray matter |
Thalamus Hypothalamus Basal ganglia |
|
|
Thalamus |
Major relay center for all sensory information |
|
|
Hypothalamus |
Controller for autonomic nervous system and endocrine system |
|
|
Basal ganglia |
Group of cerebral nuclei that receive info from cortex to regulate skeletal movement |
|
|
Midbrain functions |
-Contains 2 nuclei of spinal nerves to control eyes -Visual and auditory reflex centers -Contain Superior cerebellum peduncles (tracts to the cerebellum) |
|
|
Peduncles (Superior/middle/inferior) |
Motor tracts that run back to the cerebellum Superior: midbrain Middle: Pons inferior: medulla oblongata |
|
|
Hindbrain structures |
Pons Medulla oblongata |
|
|
Pons (Functions) |
-Contain nuclei of cranial nerves 5-8 -regulate breathing rate and depth |
|
|
Medulla oblongata |
- Contain nuclei for cranial nerves 8-12 -Reflex centers that regulate cardiac, respiratory and blood pressure centers |
|
|
Cerebellum (Function) |
Co-ordinate motor movement |
|
|
Vermis |
Narrow band of cortex splitting the two halves of the cerebellum |
|
|
Arbor Vitae |
Myelinated axons in cerebellum resembling a tree |
|
|
Meninges (Layers) |
3 layers 1. dura mater 2. Arachnoid 3. Pia mater |
|
|
Falx cerebri |
Fold in the dura mater in the longitudinal fissure |
|
|
Falx cerebelli |
Fold of dura between the two cerebellar hemispheres |
|
|
Tentorium cerebelli |
Fold between the cerebellum and the occipital lobe |
|
|
Diaphragma sellae |
Roof of dura over the sella turcica |
|
|
Venous sinuses |
Flood filled spaces within the dural folds |
|
|
Superior Sagittal sinus |
Top edge of the falx cerebri |
|
|
Inferior Sagittal sinus |
Bottom edge of the falx cerebri |
|
|
Straight sinus |
Drains inferior Sagittal sinus into the confluence of sinuses (intersection of superior, straight, occipital) |
|
|
Occipital sinus |
Located in the falx cerebelli |
|
|
R/L Transverse sinus |
-Located in the tentorium cerebelli -Runs laterally -Drains the confluence of sinuses |
|
|
R/L Cavernous sinuses |
Located in the diaphragma sellae |
|
|
R/L inferior and superior petrosal sinuses |
Drain the cavernous sinuses |
|
|
Sigmoid sinus |
Drains the petrosal sinuses and the transverse sinuses |
|
|
R/L Internal jugular veins |
Drains the sigmoid sinuses |
|
|
Pathway of the sinuses |
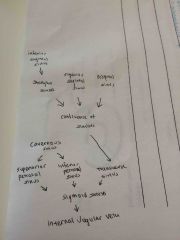
|
|
|
Trabeculae |
Strands connexting the arachnoid layer to the pia mater |
|
|
Subarachnoid space |
Space between the arachnoid layer and the pia mater |
|
|
Arachnoid granulations/villi |
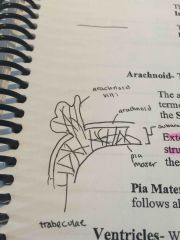
Extremely permeable extensions of the arachnoid into the superior Sagittal sinus |
|
|
Pia mater |
Delicate meningeal layer that follows all the contours of the cerebral cortex |
|
|
Ventricles |
Spaces/cavities that communicate with each other with CSF |
|
|
R/L Lateral ventricles (Location) |
Cerebrum |
|
|
Ventricles |
Spaces/cavities that communicate with each other with CSF |
|
|
Interventricular foramina |
Connects L/R lateral ventricles with the 3rd ventricle |
|
|
3rd ventricle (location) |
Thalamus |
|
|
Cerebral aqueduct (Function and location) |
- connects 3rd and 4th ventricle - midbrain region |
|
|
4th ventricle - apertures |
Allows communication with the subarachnoid space |
|
|
Central canal |
Continuation of the 4th ventricle of the spinal cord |
|
|
Choroid Plexus/Plexi |
Site of CSF formation |
|
|
CSF formation |
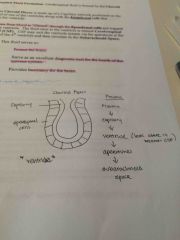
|
|
|
CSF Function |
1. Protect the brain 2. Diagnostic tool for the health of nervous system 3. Provides buoyancy for the brain |
|
|
Anterior/Posterior Median fissures |
Depressions on the surface of the spinal cord |
|
|
Conus medullaris |
Bottom of the spinal cord at the level of the 2nd lumbar vertebra |
|
|
Filum terminale |
Continuation of the pia mater from the conus medullaris, anchors the conus medullaris to the cocyx |
|
|
Posterior/Dorsal Horns |
Contains axons of sensory neurons, brings sensory info to posterior spinal cord |
|
|
Anterior/Ventral Horn |
Contains cell bodies of somatic efferent neurons (motor information) |
|
|
Lateral horn |
T1-L2 region: contains sympathetic neuron cell bodies S2-S4 region: contains parasympathetic neuron cell bodies |
|
|
Gray commissural |
Unmyelinated neurons that join the left and right halves of the cord |
|
|
Interneurons |
Join the anterior and posterior horns |
|
|
White matter of the spinal cord (function) |
Anterior: motor axons taking info down the cord Posterior: sensory axons taking info up the cord |
|
|
Spinal nerves (how many) |
31 pairs |
|
|
Dorsal root |
Afferent (sensory) axons into the posterior spinal cord |
|
|
Dorsal root ganglion |
Contain cell bodies of the Afferent nerves |
|
|
Ventral root |
(Lateral horn) Efferent neurons T1-L2: Sympathetic axons S2-S4: Parasympathetic axons
|
|
|
Posterior ramus of the spinal cord |
Distribution of afferent and efferent functions to the posterior of the body (ex. Posterior muscles) |
|
|
Anterior ramus |
The larger distribution of afferent and efferent functions to the anterior/lateral trunk and upper/lower extremities |
|
|
Spinal nerve plexi (4) |
Cervical Brachial Lumbar Sacral |
|
|
Cervical plexi (region and function) |
C1-C4 Sensory and motor functions of the neck region |
|
|
Phrenic nerve |
Nerve from cervical plexi that innervates the diaphragm |
|
|
Brachial nerves (region and function) |
C5-T1 Sensory and motor functions for the upper extremity |
|
|
Median nerve |
Nerve from brachial plexi that innervates the wrist and finger flexor muscles |
|
|
Ulnar nerve |
Nerve from brachial plexi that innervates the intrinsic muscles of the hand |
|
|
Radial nerve |
Nerve from the brachial plexi that innervates that muscles on the back of the arm, wrist and finger extensor muscles |
|
|
Thoracic nerves |
T1-T11 Do not form a plexus, individually come off the cord between ribs |
|
|
Lumbar plexi (region) |
L1-L4 |
|
|
Femoral nerve |
Nerve from lumbar plexi that innervates the quadriceps |
|
|
Oburator nerve |
Nerve from lumbar plexi that innervates the adductor muscle group |
|
|
Sacral plexi (region) |
L4-S4 |
|
|
Sciatic nerve |
Nerve from sacral plexus that travels down the posterior leg to innervates the hamstrings |
|
|
Common peroneal/fibular nerve |
Nerve split from the sciatic nerve to supply the lateral/anterior muscles of the leg |
|
|
Tibial nerve |
Branches from the sciatic nerve to supply all the posterior muscles of the leg |
|
|
Medial/Lateral plantar nerve |
Branches from the tibial nerve and supplies intrinsic muscles of the foot |
|
|
Parasympathetic cranial nerves (which numbers) |
3, 7, 9, 10 |
|
|
Vagus nerve/Cranial nerve 10 |
Parasympathetically innervates all the organs in the thorax and all the organs in the abdomen up to the splenic flextime of the LI. Slows down the SA node of heart. |
|
|
Paravertebral ganglia (chain) |
Cell bodies located outside the spinal cord in a chain |
|
|
Ganglia impar |
Where the left and right paravertebral ganglia chains unite at the level of the sacrum |
|
|
White ramus |
Myelinated pre-ganglionic axon from the ventral root of the spinal nerve |
|
|
Gray ramus |
Unmyelinated post-ganglionic axon |
|
|
What does it mean to" catch a ride" |
Nerve catches a ride on one of the arteries to desired destination |
|
|
Sympathetic pathways of spinal nerves |
1. Thoracocolumbar region 2. Above or below thoracocolumbar region 3. Nerves to the head |
|
|
Functions of sympathetic spinal nerves |
1. Vasoconstriction 2. Control of sweat glands 3. Control of smooth muscle of body hair |
|
|
Sympathetic Pathway: Thoracic organns |
Lateral horn -> white ramus -> travel up or down sympathetic chain slightly -> gray ramus (Heart, lungs) |
|
|
Collateral ganglia |
Sympathetic ganglia positioned around the 3 major arteries that supply abdominals |
|
|
Sympathetic pathways: abdominal organs |
Lateral horn -> white ramus -> bypasses sympathetic trunk without synapsing -> collateral ganglia -> catch a ride -> abdominal organs |
|
|
Circulatory System Functions (5) |
1. Transport nutrients/oxygen 2. Remove wastes 3. Maintain body heat 4. Carry hormones/drugs 5. Maintenance of proper fluid balances |
|
|
Mediastinum |
Cavity in the thorax that houses the heart |
|
|
Pericardial Sac |
Double layered membrane encasing the heart |
|
|
Parietal pericardium |
Double layer outer layer of pericardial sac. 1. Fibrous layer (outer) 2. Serous layer (inner) |
|
|
Pericardial cavity |
Space between the serous parietal pericardium and the visceral pericardium |
|
|
Visceral pericardium/epicardium |
Inner serous membrane layer of the pericardium |
|
|
Myocardium |
The actual heart muscle |
|
|
Endocardium |
Epithelial layer that lines the inside of the chambers of the heart and blood vessels. |
|
|
Coronary heart supply/circulation |

|
|
|
R/L Coronary arteries |
Come off the aorta to supply the myocardium |
|
|
Coronary sinus |
Drain the coronary veins on the posterior surface of the heart to the right atrium |
|
|
Superior Vena Cava |
Final vein that brings venous blood from areas above the heart and the upper extremity |
|
|
Inferior Vena Cava |
Final vein that brings venous blood from areas below the heart to the right atrium |
|
|
Pathway of blood through the heart |

|
|
|
Atrial septum |
Separates L/R atriums |
|
|
Fossa Ovale |
Depression in the atrial septum Remnant of fetal circulation |
|
|
Interventricular septum |
Separates L/R ventricles |
|
|
Chordae tendinae |
Collagen fibres attached to the inferior edge of valve cusps to prevent cusps from everting back up into atria |
|
|
Papillary Muscles |
Muscles on the ventricle wall that attach to the inferior edge of chordae tendinae to prevent cusps from everting back up into atria |
|
|
Right AV valve/Tricuspid valve |
3 cusp valve between the right atrium and ventricle |
|
|
Pulmonary Artery |
Artery that takes venous blood from the right ventricle to the lungs |
|
|
Pulmonary semilunar valve |
3 half moon cusps that prevent back flow from pulmonary artery to the heart |
|
|
Left AV valve/Bicuspid valve |
2 cusp valve between the left atrium and ventricle |
|
|
Aortic semilunar valve |
Valve that prevents back flow from aorta to the heart. Relaxation allows L/R coronary arteries to be filled up. |
|
|
Base (Heart) |
Superior border of the heart |
|
|
Apex (Heart) |
Inferior pointed end of the heart |
|
|
Coronary Sulcus |
External groove around the heart that houses the coronary sinus (Divides the atria from the ventricles) |
|
|
Anterior/Posterior interventricular sulci |
Houses anterior/posterior interventricular arteries (Marks the location of the interventricular septum) |
|
|
SA Node (sinoatrial) |
Pacemaker of the heart Location: junction of the SVC and R atrium |
|
|
AV Node (atrioventricular) |
Modified cardiac muscle located at the floor of the right atrium. Picks up signal from L/R atria and distributes it downwards. |
|
|
Bundle of His |
Receives signal from AV node and distributes down the interventricular septum to the apex |
|
|
Purkinje Fibres |
Fibres that course through myocardium of the ventricles |
|
|
3 Layers of Arteries |
1. Tunica Externa 2. Tunica Media 3. Tunica Interna |
|
|
Tunica Externa |
Outer areolar connective tissue layer of arteries. Anchors artery to other structures |
|
|
Tunica Media |
Middle smooth muscle layer of arteries Responsible for vasoconstriction and vasodilation |
|
|
Tunica Intima |
Inner areolar connective tissue of arteries Only layer that is present in capillaries (along with basement membrane) |
|
|
Arteries/Arterioles/Capillaries |
Arteries: Largest Arterioles: Smaller diameter arteries Capillaries: smallest blood vessel |
|
|
Veins/Venules |
Veins: Largest Venules: Smaller diameter veins |
|
|
Veins (Features) |
1. Thicker externa layer 2. Valves that prevent blood from back-flowing 3. Rely on massaging action of muscles to propel blood back to the heart |
|
|
Brachiocephalic Artery |
Comes off right arch of the aorta to bifurcate into R subclavian and R common carotid |
|
|
L common carotid |
Comes off middle arch of the aorta to bifurcate into L internal/external common carotid aa. (Splits at the level of the thyroid cartilage) |
|
|
R common carotid |
Comes off brachiocephalic aa to bifurcate into R internal/external common carotid aa. (Splits at the level of the thyroid cartilage) |
|
|
L subclavian aa |
Comes off the left branch of the aorta |
|
|
R subclavian aa |
Comes off the brachiocephalic aa |
|
|
R/L internal carotid artery |
Comes off the common carotid artery to supply the cranial activity INSIDE the skull |
|
|
R/L external carotid artery |
Comes off the common carotid artery to supply the outer surface of the face and skull |
|
|
R/L Superficial temporal aa |
Branches off from external carotid aa Level: Ramus of the mandible |
|
|
R/L maxillary aa |
Branches off from the external carotid aa Level: ramus of the mandible |
|
|
L/R vertebral artery |
Branches off from subclavian aa to supply cranial activity through foramen magnum |
|
|
L/R axillary aa |
Continuation of subclavian aa Level: after subclavian goes under clavicle and over the 1st rib |
|
|
L/R lateral thoracic aa |
Branch from axillary Supplies anterior thorax |
|
|
L/R subscapular aa |
Branch from axillary Supplies posterior surface of scapula |
|
|
L/R brachial aa |
Continuation of the axillary Level: Teres major insertion |
|
|
L/R deep brachial aa |
Branch from brachial artery that passes behind humerus |
|
|
L/R Radial aa |
Branch from brachial aa Level: Radial tuberocity Splits into deep and superficial aa |
|
|
L/R Ulnar aa |
Branch from brachial aa Level: radial tuberocity Splits into deep and superficial aa |
|
|
L/R Deep Palmar arch |
Loop of artery made up mostly of the deep radial aa (some contribution from ulnar) Located deep to the long tendons of the palm of the hand |
|
|
L/R Superficial Palmar Arch |
Loop of artery made up mostly of the superficial ulnar aa (some contribution from radial) Located superficial to the long tendons of the palm of the hand. |
|
|
L/R Digital branches |
Radiate from the superficial and deep palmar arches |
|
|
Visceral Type Branches (Arteries) |
Branches of the aorta that supply organs as it passes through the thorax |
|
|
Parietal Type Branches (Arteries) |
Branches of the aorta that supply muscles as it passes through the thorax Ex. Lumbar arteries, intercostal arteries |
|
|
3 Types of Visceral Type Branches of aa |
1. Celiac Trunk 2. Inferior Mesenteric aa 3. Superior Mesenteric aa |
|
|
Celiac Trunk (Location) |
Level: Just above the stomach |
|
|
Superior Mesenteric artery (Location) |
Level: Just below stomach (intestines, pancreas) |
|
|
Inferior Mesenteric Artery (Location) |
Level: just above the divide of the aorta to the lower extremities |
|
|
Arteries of Lower extremity (level of division from aorta) |
L4 |
|
|
L/R Common iliac aa |
Branches from aorta |
|
|
L/R internal iliac aa |
Branch from common iliac aa Supplies the pelvic |
|
|
L/R external iliac aa |
Branch from the common iliac aa |
|
|
L/R Femoral aa |
Continuation from the external iliac aa Level: after passing under inguinal ligament |
|
|
L/R Deep femoral aa |
Branch from the femoral aa Level: after passing under inguinal ligament |
|
|
L/R Popliteal artery |
Continuation from femoral aa that supplies the knee Level: Posterior/medial knee |
|
|
L/R Anterior Tibial artery |
Branch of Popliteal artery that passes over interosseus membrane Level: Bottom edge of popliteus muscle |
|
|
L/R Posterior Tibial aa |
Branch of popliteal artery that passes deep to the soleus Level: Bottom edge of popliteus muscle |
|
|
L/R Dorsalis Pedis aa |
Continuation of anterior tibial aa Level: Dorsal surface of foot |
|
|
L/R Peroneal (Fibular) aa |
Branch of the posterior tibial aa supplying lateral side of the leg |
|
|
L/R Lateral and Medial Arteries |
Branches of the posterior tibial aa that rejoin to form an arterial on the plantar surface of the foot Level: Passing behind the medial malleolus |
|
|
Deep Veins of the Upper Extremity |
Parallel in name and location with the arteries |
|
|
Superficial Veins of the upper extremity (2) |
1. Cephalic 2. Basilic |
|
|
L/R Cephalic vv |
Drains dorsal venous network of the hand, travelling up the lateral forearm to enter the axillary vv Level: between deltoid and pectoralis major |
|
|
L/R Basilic vv |
Drains dorsal venous network of the hand, travelling up the medial forearm to enter the axillary vv |
|
|
L/R Median cubital vv |
Bridges the cephalic vv and basilic vv Level: Elbow |
|
|
L/R External Jugular vv |
Drains venous blood from face and scalp to join the subclavian vv Travels down the sternomastoid muscle |
|
|
L/R internal jugular vv |
Drains venous blood from inside the cranial cavity to the subclavian vein Travels down along the common carotid artery |
|
|
L/R Brachiocephalic vv |
Continuation of the subclavian vein. L-R join to form the Superior Vena Cava |
|
|
Deep Veins of the Lower Extremity |
Parallel in name and location to the arteries. L-R common iliac vv join to form Inferior Vena Cava |
|
|
Superficial Veins of the Lower Extremity |
1. Great Saphenous Vein 2. Small Saphenous Vein |
|
|
L/R Great Saphenous Vein |
Drains venous network on the dorsal surface of the foot , travelling up the MEDIAL side of the leg to empty into the femoral vv Level: Just before the inguinal ligament |
|
|
L/R Small Saphenous Vein |
Drains venous network on the dorsal surface of the foot, travelling up the LATERAL side of the leg to empty into the popliteal vein Level: Just behind the knee |
|
|
Superior/Inferior Mesenteric Veins |
Parallel the Superior/Inferior Arteries |
|
|
Splenic Vein |
Drains the spleen |
|
|
Portal Vein |
Drains the Inferior/Superior mesenteric veins and the splenic vein Filtered through the liver |
|
|
Hepatic Veins |
Drains the filtered blood from the liver and continues as the IVC |
|
|
Azygous veins |
Drains small intercostal veins the right side of the thorax |
|
|
Hemiazygous/Accessory Hemiazygous veins |
Drains small intercostal veins on the left side of the thorax |
|
|
Airways for inhaled air |
1. Nose 2. Mouth |
|
|
Nasal Septum |
Divides the two nostrils Composed of cartilage, vomer, and perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone. |
|
|
Conchae |
Medial projections from the lateral walls of the nostrils Superior, Middle, inferior |
|
|
Meati |
Areas immediately lateral to the conchae (depressions) Superior, Middle, Inferior |
|
|
Functions of the nose |
1. Filtering 2. Humidifying/Moistening 3. Olfactory (smell) |
|
|
Olfactory Process |
1. Receptors at the top of the nose 2. Axons from receptors synapse with olfactory bulbs in the cranium |
|
|
Pharynx |
C shaped muscular tube that stretches from the back of the nose to the larynx |
|
|
3 Sections of the Pharynx |
1. Nasal 2. Oral 3. Laryngeal |
|
|
Eustachian/Auditory Tube (Location and function) |
Tube that connects the nasal pharynx with the middle ear. Equalize air pressure on either side of the ear drum |
|
|
Pharyngeal Tonsils/Adenoids |
Lymphatic tissues at the back of the nasal pharynx |
|
|
Paranasal Sinuses (Location and 4 types) |
Mucous lined cavities in the face and skull that connect to the nose 1. Frontal bone 2. Sphenoid 3. Ethmoid 4. Maxilla |
|
|
Oral Pharynx (Location) |
Back of the mouth |
|
|
Soft Palate (Location and function) |
Attached to the posterior edge of the hard palate Elevates to close off passage to the nasal pharynx when swallowing |
|
|
Palatine Tonsils (Location and function) |
Back lateral walls of the oral pharynx Lymphatic function - protect body from infection |
|
|
Laryngeal Pharynx |
Associated with the larynx and the esophagus |
|
|
Larynx Cartilages (4) |
1. Thyroid 2. Cricoid 3. Arytenoid 4. Epiglottis |
|
|
Larynx Composition Structures |
1. Cartilage 2. Membranes 3. Muscles |
|
|
Thyroid Cartilage |
Two cartilage plates that meet anteriorly to form the Adam's Apple Note: does not form a complete ring |
|
|
Thyroid Prominence |
Adam's Apple from the two thyroid cartilages that meet anteriorly |
|
|
Cricoid Cartilage (Location and shape) |
Immediately inferior to the thyroid cartilage Forms a complete ring with a wider posterior surface (signet ring) |
|
|
Inferior horn (Respiratory System) |
Articulation between the thyroid and cricoid cartilages |
|
|
Arytenoid Cartilage |
2 triangular shaped cartilage pieces that sit on top of the cricoid cartilage |
|
|
Vocal process |
Anterior point of the arytenoid cartilage |
|
|
Muscular process |
Posterior point of the arytenoid cartilage |
|
|
Epiglottis |
Paddle shaped cartilage attached to the inside surface of the thyroid cartilage |
|
|
Criothyroid membrane (attachments and function) |
2 Membranes that attaches the thyroid and cricoid cartilages Superior-posterior edge attaches to the vocal processes of the arytenoid cartilage Forms the true vocal cords |
|
|
Glottis |
The vocal cords plus the space in between them |
|
|
Laryngeal Muscles |
Attach to the muscular processes of the arytenoid cartilages and other cartilages Causes movement of the cartilage pieces = movement of the vocal cords |
|
|
Trachea |
Extension of the pharynx |
|
|
R/L Primary Bronchi |
Branches of the trachea Level: Sternal angle |
|
|
Secondary Bronchi (Quantity) |
Right: 3 Secondary bronchi Left: 2 Secondary bronchi |
|
|
Bronchioles |
Smaller branches from the bronchi |
|
|
Alveoli |
End of the conducting air pathway Site of gas exchange |
|
|
Pleural Serous Membrane |
Double layer membrane surrounding the lungs 1. Parietal 2. Visceral |
|
|
Parietal pleural membrane |
Lines the inside surface of the thoracic cavity Covers: rib cage, mediastinum, diaphragm |
|
|
Visceral pleural membrane |
Continuation of the parietal pleura Level: Root of the lung |
|
|
Root of the lung |
Location where the primary bronchus and pulmonary artery enter the lung and the pulmonary vein leaves the lung. |
|
|
Pleural cavity |
Space between the parietal and visceral pleural serous membranes |
|
|
Lung Lobes (Number) |
Right: 3 Left: 2 |
|
|
Number of teeth |
32 |
|
|
Central incisors |
2 |
|
|
Lateral incisors |
2 |
|
|
Canines |
2 |
|
|
Premolars |
4 |
|
|
Molars |
6 |
|
|
Parotid gland |
Salivary gland in a cavity just in front of the ear that pierces the cheek muscle to empty into the mouth |
|
|
Submandibular Gland |
Salivary gland on the inside of the mandible that empties into the mouth at the level of the frenulum |
|
|
Sublingual Gland |
Salivary gland that follows the lateral contours of the mandible and empties into the floor of the mouth |
|
|
Lingual frenulum |
Mucous membrane that anchors the tongue to the floor of the mouth |
|
|
Papillae |
Bumps on the dorsal surface of the tongue |
|
|
Esophagus |
Smooth muscle tube that empties into the stomach |
|
|
Greater Curvature |
Bottom curve of the pouch of the stomach |
|
|
Lesser Curvature |
Top curve of the pouch of the stomach |
|
|
Fundus of the stomach |
Superior/lateral dome shape portion of the stomach (near the esophagus) |
|
|
Body of the stomach |
Main portion of the stomach |
|
|
Pyloric region |
Distal end of the stomach where it narrows |
|
|
Pyloric sphincter/orfice |
Regulates the emptying of the stomach into the duodenum (smooth muscle) |
|
|
Cardiac sphincter/orfice |
Prevents stomach contents from regurgitating back into the esophagus (Smooth muscle) |
|
|
Gastric glands (location) |
Located in depressions in the stomach |
|
|
Mucous cells |
Cells in the gastric gland that secretes mucous to protect the stomach lining |
|
|
Parietal cells |
Cells in the gastric gland that secret HCl |
|
|
Chief cells |
Cells in the gastric gland that secrete digestive enzymes |
|
|
Duodenum |
C shaped first section of the SI; 10 inches Note: C shape cradles the pancreas |
|
|
Pancreatic duct |
Duct in the duodenum that connects to the pancreas |
|
|
Common bile duct |
Duct in the duodenum that connects to the liver Uses the same opening as the pancreatic duct |
|
|
Villi |
Inner lining of SI that increase SA |
|
|
Central lacteal |
Part of the lymphatic system within each villus of the SI |
|
|
Jejunum |
Middle portion of the SI; 7-8 feet |
|
|
Ileum |
End portion of the SI; 11 feet |
|
|
Iloececal Valve |
Regulates the emptying of SI into the LI |
|
|
Cecum |
First part of the LI |
|
|
Veriform appendix |
Small pouch attached to the medial part of the cecum |
|
|
Ascending colon |
Continuation of the cecum |
|
|
Hepatic/Right colic flexture |
90 junction between ascending and transverse colon Level: liver |
|
|
Transverse colon |
Continuation of the colic flexture |
|
|
Splenic/Left colic flexture |
90 junction between the transverse and descending colons Level: spleen |
|
|
Sigmoid colon |
S shaped continuation of the descending colon |
|
|
Rectum |
Continuation of the sigmoid colon Level: midline of the body |
|
|
Anal canal |
Last 1-1.5 inches of the rectum |
|
|
Internal anal sphincter |
Thickening of smooth muscle in the anal canal |
|
|
Levator Ani muscles |
Funnel shaped skeletal muscle that forms the posterior floor of the pelvis in the anal triangle |
|
|
External anal sphincter |
Skeletal muscle continuation from the levator ani muscles |
|
|
Accessory Digestive Organs (3) |
1. Pancreas 2. Gallbladder 3. Liver |
|
|
Pancreas functions |
Endocrine: produce Insulin and Glucagon hormones Exocrine: produce digestive enzymes to the SI |
|
|
Body/Tail of the pancreas |
Body: Main portion Tail: Distal end that touches the spleen |
|
|
Liver Function |
Production of bile |
|
|
Bile function |
Emulsification of fat in the duodenum |
|
|
R/L Hepatic ducts |
Transport bile from the L/R lobes of the liver |
|
|
Common hepatic duct |
Transport bile from the L/R hepatic ducts |
|
|
Gall Bladder function |
Smooth muscle pouch that stores bile |
|
|
Cystic duct |
Joins gall bladder with common hepatic duct |
|
|
Common bile duct |
Continuation of the cystic and common hepatic ducts |
|
|
Fundus, body, neck of the gall bladder |
Fundus: bottom rounded portion of the pear Body: Main wide portion of the pear shape Neck: Narrow portion of the pear |
|
|
Peritoneum |
Double layered serous membrane surrounding the abdominal cavity 1. Parietal 2. Visceral |
|
|
Parietal peritoneum |
Lines the inside of the abdominal cavity |
|
|
Visceral peritoneum |
Lines the intestines and abdominal organs |
|
|
Dorsal mesentery |
Serous membrane that joins the parietal peritoneum to the visceral peritoneum; supports the intestines Level: Middle posterior abdominal cavity |
|
|
Greater omentum |
Specific dorsal mesentery associated with the stomach |
|
|
Mesentery of the SI and LI |
Specific dorsal mesentery associated with the SI and LI |
|
|
Peritoneal cavity |
Space between the parietal and visceral membranes |
|
|
Kidney Function |
Filter and purify blood |
|
|
Kidney - Surround Structures (2) |
1. Fibrous protective capsule 2. Perirenal fat that surrounds the kidney that anchors kidney in place and protects it. |
|
|
Hilum |
Concavity on the medial border of the organ Location where vessels, nerves and ureter connect the kidney |
|
|
Renal Sinus |
Internal extension of the hilum |
|
|
Minor Calyx/Calyces |
Smallest of a tube system located in the renal sinus 8-15 minor calyces in the kidney |
|
|
Major Calyx/Calyces |
Structure in the renal sinus that drains the minor calyces 2-3 major calyces in the kidney |
|
|
Renal pelvis |
Structure in the renal sinus that drains the major calyces |
|
|
Ureter |
Tubular extension of the renal pelvis that transports urine from the hilum with the urinary bladder |
|
|
Urinary bladder |
Smooth muscle container that stores urine from ureters |
|
|
Kidney Layers (2) |
1. Cortex 2. Medulla |
|
|
Kidney Cortex |
Superficial layer |
|
|
Kidney medulla |
Deep layer; triangular in shape (running from superficial to deep) |
|
|
Papilla (kidney) |
The apex of the medulla triangle that projects internally towards the renal sinus |
|
|
Renal columns |
Kidney cortex tissues that extend inwards between medullary triangles |
|
|
Nephron |
Filtrating tubular unit of the kidney |
|
|
Kidney Blood supply (function) |
Transports blood to be filtered through the nephron |
|
|
Afferent arteriole |
Brings blood to the initial section of the nephron |
|
|
Glomerulus |
Capillary network supplied by the afferent arterioles |
|
|
Efferent arterioles |
Takes blood away from the glomerulus Origin for a network of capillaries that surround the nephron |
|
|
Bowman's capsule |
Initial section of the filtration tube that surrounds the Bowman's capsule Filters some blood from the glomerulus |
|
|
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (Location and function) |
Continuation of the filtration tube form the Bowman's capsule Filters blood from the peritubulular capillary network) |
|
|
Peritubular capillary network |
Network of capillaries that surround the proximal and distal convoluted tubules |
|
|
Loop of Henle (and the two parts of the loop) |
Continuation of the proximal convoluted tubule that is surrounded by capillaries Descending loop: Cortex to the medulla Ascending loop: Medulla back the cortex |
|
|
Distal convoluted tubule |
Continuation of the Loop of Henle Filters blood from the peritubular capillary network |
|
|
Collecting duct |
Receives the distal convoluted tubules from a number of nephrons Empties the urine at the apex of the medulla to the minor calyx Note: level at which filtrate becomes urine |
|
|
Urethra (Location and function) |
Muscular tube positioned at the bottom of the urinary bladder to transfer urine to the exterior of the body |
|
|
Internal Sphincter of the Urethra |
Thickening of smooth muscle as the urethra leaves the bladder |
|
|
Perineum |
The region of the body that forms the floor of the pelvis |
|
|
Conjoint ramus |
Formed by the ischial and pubis rami |
|
|
Perineum diamond boundaries |
Anterior point: Pubis symphysis Lateral lines: Conjoint rami Lateral points: Ischial tuberosity Posterior: Coccyx |
|
|
2 Triangles of the perineal diamond |
1. Anal triangle 2. Urogenital triangle Note: Women have wider triangles |
|
|
Sphincter urethra muscle |
Skeletal muscle in the urogenital triangle in which the urethra passes through Forms sphincters: 1. External sphincter for the urethra 2. Vagina |
|
|
External sphincter for the urethra |
Formed by the sphincter urethra muscle |
|
|
Perineal membrane |
Dense layer of connective tissue covering the inferior side of the sphincter urethra muscle |
|
|
Urogenital triangle composition |
1. Sphincter urethra muscle 2. Perineal membrane |
|
|
Deep perineal pouch |
Space directly above the perineal membrane that houses the sphincter urethra muscles |
|
|
Superficial perineal pouch |
Space directly below the perineal membrane |
|
|
Scrotum |
Skin covered double pouched sac that contains the testicles Provides cooler environment outside the body for sperm production |
|
|
Testicle |
Male gonad that produces sperm and testosterone |
|
|
Seminiferous tubules |
Initial section of the tubule system in the testicle |
|
|
Sperm production location |
Tubule system in the testicle |
|
|
Straight tubules |
Continuation of the seminiferous tubules to the rete testis |
|
|
Rete testis |
Continuation of multiple straight tubules to the efferent tubules |
|
|
Efferent tubules (male reproductive) |
Drain rete testis to the epididymus |
|
|
Epididymus |
Drains the efferent tubules to the ductus/vas deferens |
|
|
Ductus/Vas deferens |
Drains the Epididymus, travelling up the spermatic cord |
|
|
Spermatic cord |
Multilayered cord composed of blood vessels and Vas deferens that travels through the inguinal canal through the abdominal wall |
|
|
Accessory glands of the male reproductive system |
1. Seminal vesicles 2. Prostate gland 3. Bublourethral glands |
|
|
Seminal vesicles (Location and function) |
Two structures positioned behind the urinary bladder that produce fluid that is added to ejaculate and provides nutrients for sperm |
|
|
Ejaculatory Duct |
Continuation of the Vas Deferens and the seminal vesicles Pierces through the prostate gland |
|
|
Prostate gland (Location and function) |
Location: right below the urinary bladder Function: production of the fluid that helps supply nutrients for the sperm |
|
|
Prostatic urethra |
Name of urethra as it passes through the prostate gland |
|
|
Bulbourethral glands (location and function) |
Location: below the prostate gland in the sphincter urethra muscle Function: lubricant for sexual intercourse and cleansing of urine from the urethra |
|
|
Membranous urethra |
Name of the urethra as it passes through the sphincter urethra muscle |
|
|
2 Parts of the penis |
1. Root 2. Body |
|
|
2 Parts of the root of the penis |
1. Bulb 2. Crura |
|
|
Bulb of the penis |
Erectile tissue that is attached to the underside of the sphincter urethra muscle in the root of the penis Location of that bulbourethral ducts empty |
|
|
Crura of the penis |
Erectile tissue that is attached to the underside of the conjoint ramus |
|
|
2 Parts of the body of the penis |
1. Corpus spongiosum 2. Corpora cavernosa/corpus cavernosum |
|
|
Corpus spongiosum |
Continuation of the bulb of the root of the penis |
|
|
Glans |
Expanded end of the corpus spongiosum |
|
|
Spongy urethra |
Name of the urethra while in the corpus spongiosum |
|
|
Vagina |
Fibromuscular tube that connects the uterus to the outside of the body |
|
|
Uterus |
Thick walled smooth muscle organ in the female reproductive system that has a cavity |
|
|
Fundus of the uterus |
Top rounded portion of the uterus |
|
|
Body of the uterus |
Middle, main portion of the uterus |
|
|
Cervix |
Inferior portion of the uterus that protrudes into the vagina |
|
|
Uterine/Fallopian Tubes |
Hollow tubes that extend laterally to the side wall of the pelvis |
|
|
Infundibulum |
Expanded end of the fallopian tubes |
|
|
Fimbriae |
Finger like folds in the infundibulum |
|
|
Ovary |
Female gonad responsible for the production and ovulation of an oocyte |
|
|
Ligaments that support the uterus/ovary |
1. Broad ligament 2. Suspensory Ligament 3. Ovarian ligament 4. Round ligament |
|
|
Broad ligament |
Double layer section of the parietal peritoneum that falls over the uterus |
|
|
Suspensory ligement |
Lateral extensions of the broad ligament that attaches the ovary to the side wall of the pelvis Note: Artery and vein of the ovary runs in this ligament |
|
|
Ovarian ligament |
Runs from the ovary to and through the wall of the uterus (Posterior-->Anterior) |
|
|
Round ligament |
Continuation of the ovarian ligament on the anterior side of the uterus that courses through the abdominal wall and anchors the labia majora |
|
|
Labia majora |
Folds of skin and connective tissue that form the external genitila Note: homologous to the male scrotum |
|
|
Labia minora |
Folds of skin medial to the labia majora; form the boundaries of the vestibule |
|
|
Vulva |
Female external genitalia |
|
|
Vulva structures (4) |
1. Bulb 2. Crura 3. Labia majora 4. Labia minora |
|
|
Bulb of the vulva |
Erectile tissue attached to the bottom of the perineal membrane |
|
|
Crura of the vulva |
Erectile tissue attached to the conjoint rami |
|
|
Corpora cavernosa/corpus cavernosum of the penis |
Extension of the crura in the body of the penis |
|
|
Corpora cavernosa/corpus cavernosum of the vulva |
Meeting of the 2 crura |
|
|
Clitoris |
Meeting of the two copora cavernosa |
|
|
Vestibule |
Space in the vulva that contains the openings for the vagina and the urethra |
|
|
Greater vestibular glands (Location and function) |
Pair of glands located on the posterior lateral walls of the vestibule Function: secrete lubricant into the vagina Note: homologous to the male bulbourethral glands |
|
|
Female Breast/Mammary gland (composition) |
1. Adipose tissue 2. Lactiferous glandular tissue |
|
|
Base of the breast (boundaries) |
Vertically: 2nd rib to the 6th rib Horizontally: Medial margin of the ribs to the mid-axillary line Note: generally the same for all women |
|
|
Axillary tail |
Small portion of the breast that follows the lateral edge of the pectoralis Major upwards |
|
|
Lactiferous Ducts/Glands |
Produce and carry milk produced during lactation to the Nipple of the breast |
|
|
Areola |
Pigmented area surrounding the nipple |

