![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
125 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Superior |
Above
|
|
|
Inferior
|
Below
|
|
|
Medial
|
Toward the midline
|
|
|
Lateral
|
Away from midline
|
|
|
Superficial
|
Toward the surface
|
|
|
Deep
|
Toward the core
|
|
|
Anterior
|
To the front
|
|
|
Posterior
|
To the back
|
|
|
Ventral
|
belly side
|
|
|
Dorsal
|
Back side
|
|
|
Proximal
|
nearest to an extremity's attachment to the trunk
|
|
|
Distal
|
furthest from an extremity's attachment to the trunk
|
|
|
Parietal
|
closer to the body wall or on the body wall
|
|
|
Visceral
|
Closer to an internal organ or on the organ
|
|
|
Ipsilateral
|
on the same side of the body
|
|
|
Contralateral
|
on the opposite side of the body
|
|
|
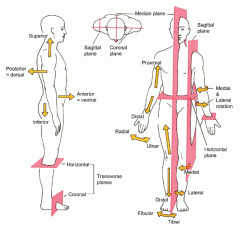
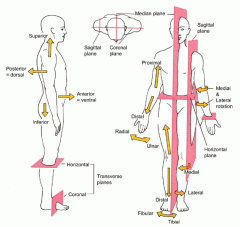
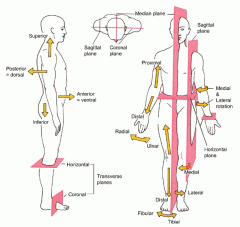
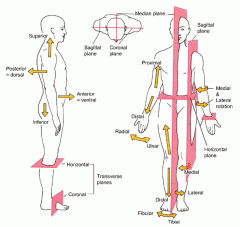
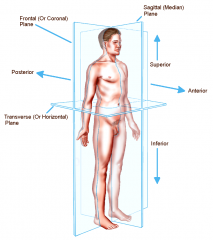
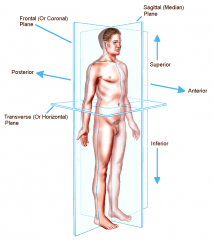
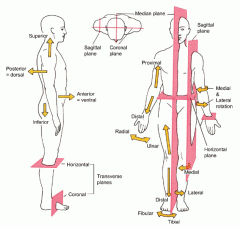
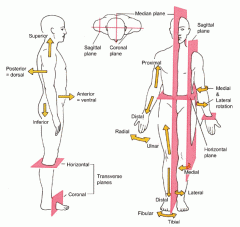
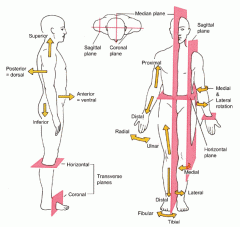
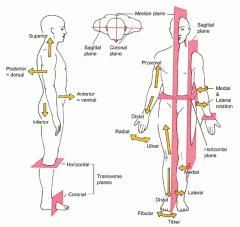
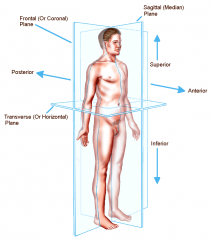
Coronal or Frontal plane
|
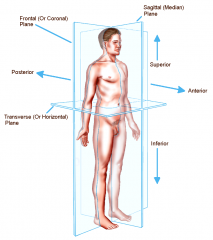
divides the body into anterior or posterior portions
this type of cut would leave the face untouched |
|
|
Midsagittal plane
|
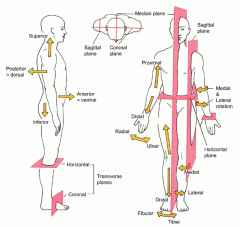
divides the body into equal left and right halves
|
|
|
Sagittal plane
|
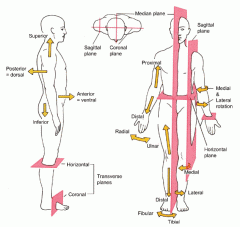
divides the body into unequal left and right halves
|
|
|
Parasagittal plane
|
any other sagittal plane
|
|
|
Transverse or horizontal plane
|
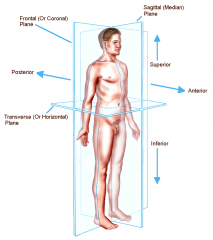
divides the body into a superior and inferior portion
view represented by a CT scan |
|
|
Dorsal Cavity consists of what?
|
cranial cavity and spinal cavity as known as vertebral canal
|
|
|
Ventral Cavity consists of what?
|
thoracic cavity and abdominal cavity
|
|
|
Cephalic
|
head
|
|
|
Cranial
|
Skull
|
|
|
Frontal
|
Forehead
|
|
|
Ocular, Orbit
|
eye
|
|
|
Otic
|
Ear
|
|
|
Buccal
|
cheech
|
|
|
Mental
|
Chin
|
|
|
Nasal
|
Nose
|
|
|
Oral
|
Mouth
|
|
|
Cervical
|
Neck
|
|
|
Thoracic
|
Chest
|
|
|
Sternal
|
referring to the middle of the chest
|
|
|
Pectoral
|
indicating the lateral musculature
|
|
|
Abdominal
|
anterior body trunk inferior to the ribs
|
|
|
Umbilical
|
naval
|
|
|
Coxal
|
hip
|
|
|
Inguinal
|
Groin
|
|
|
Pubic
|
Genital
|
|
|
Vertebral
|
region of the vertebral column
|
|
|
Scapular
|
Shoulder blade
|
|
|
Lumbar
|
Lower back
|
|
|
Sacral
|
area below lover back at start of gluteal cleavage
|
|
|
Gluteal
|
buttocks
|
|
|
Dorsum
|
Back
|
|
|
Acromial
|
Shoulder
|
|
|
Axillary
|
Armpit
|
|
|
Brachial
|
Arm
|
|
|
Antebrachial
|
Forearm
|
|
|
Cubital, Antecubital
|
front of elbow
|
|
|
Olecranal
|
back of elbow
|
|
|
Carpal
|
wrist
|
|
|
Manual
|
Hand
|
|
|
Digital, Phalangeal
|
fingers
|
|
|
Pollex
|
thumb
|
|
|
Coxal
|
hip
|
|
|
Femoral
|
thigh
|
|
|
Patellar
|
front of knee
|
|
|
Popliteal
|
back of knee
|
|
|
Crural
|
front of lower leg
|
|
|
Sural
|
back of lower leg
|
|
|
Tarsal
|
ankle
|
|
|
Pedal
|
foot
|
|
|
Calcaneal
|
heel
|
|
|
Hallux
|
Great Toe
|
|
|
Anatomical position Is a standardized method of observing and describing regions or parts of the human body when it is
|

in a SPECIFIC STANCE
|
|
|
Standard Anatomical position - 5 characteristics
|

i. Body is erect and facing forward – standing ii. Arms at side of body, iii. Palms facing forward, iv. Feet flat on the floor – parallel with the floor
|
|
|
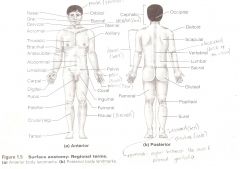
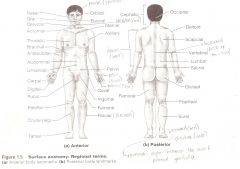
REGIONAL NAMES - PRINCIPAL REGIONS OF THE HUMAN BODY Head
|
Saphallic
|
|
|
REGIONAL NAMES - PRINCIPAL REGIONS OF THE HUMAN BODY Neck
|
Cervical
|
|
|
REGIONAL NAMES - PRINCIPAL REGIONS OF THE HUMAN BODY Trunk
|
Trunk
|
|
|
REGIONAL NAMES - PRINCIPAL REGIONS OF THE HUMAN BODY Upper Limbs
|
Upper Limbs
|
|
|
REGIONAL NAMES - PRINCIPAL REGIONS OF THE HUMAN BODY Lower Limbs
|
Lower Limbs
|
|
|
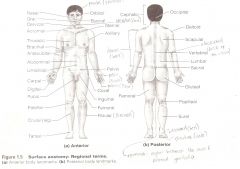
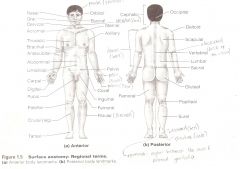
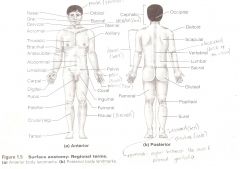
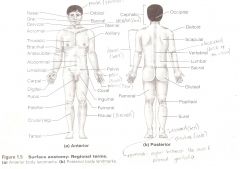
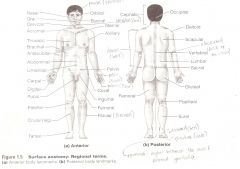
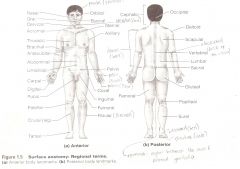
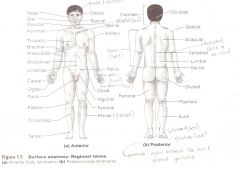
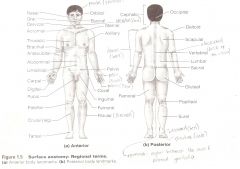
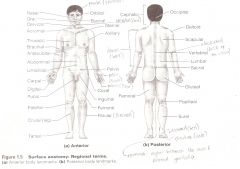
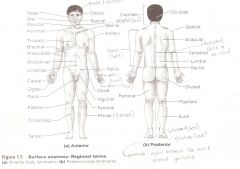
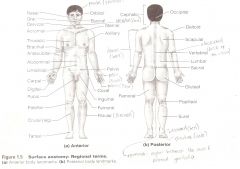
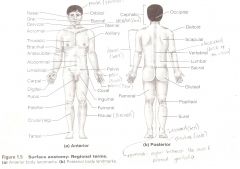
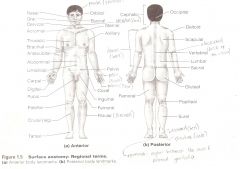
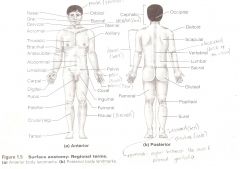
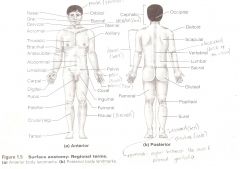
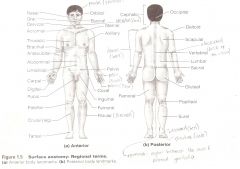
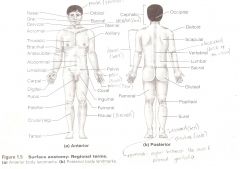
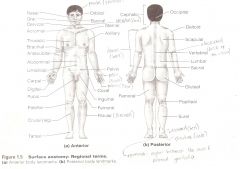
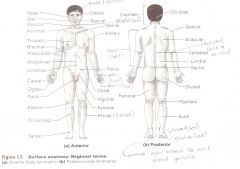
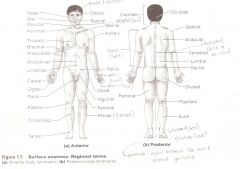
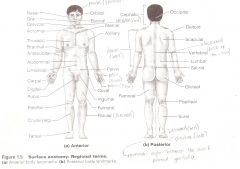
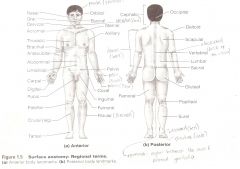
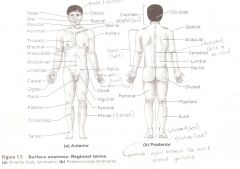
Anatomical Terms
|
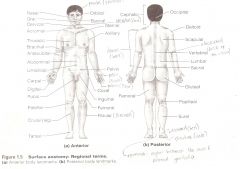
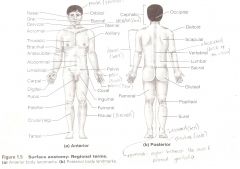
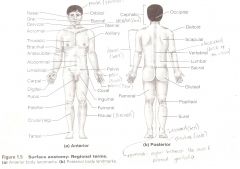
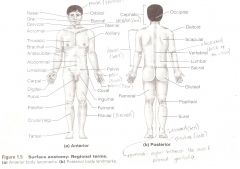
Are terms used to describe major parts of the body. - See Fig. 1.5 in your textbook.
|
|
|
Directional Terms are terms used to
|
describe the location of one part of the body relative to another part of the human body.
|
|
|
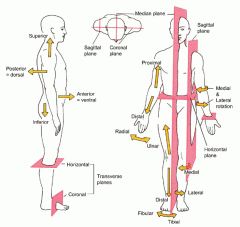
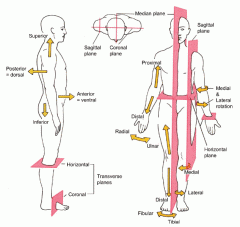
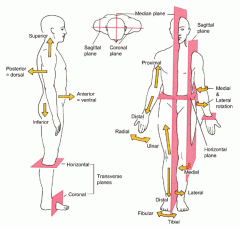
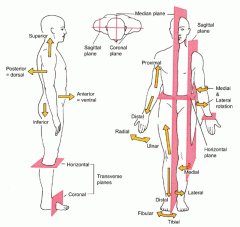
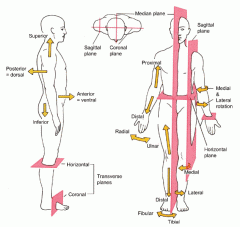
Directional Terms - superior refers to
|
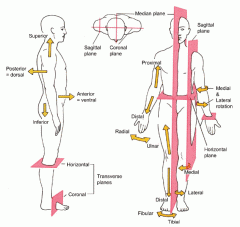
a part located toward the head or upper part of a structure.
|
|
|
Directional Terms - inferior refers to
|
a part located away from the head or toward the lower part of a structure.
|
|
|
Directional Terms - anterior refers to
|

a part which is nearer to or at the front of the body.
|
|
|
Directional Terms - posterior refers to
|

a part which is nearer to or at the back of the body.
|
|
|
Directional Terms - medial refers to
|
a part which is nearer to the imaginary midline of the body.
|
|
|
Directional Terms - lateral refers to
|

a part which is farther from the imaginary midline of the body.
|
|
|
Directional Terms - intermediate refers to
|

a structure which is located between two other structures.
|
|
|
Directional Terms - ipsilateral refers to
|
a structure which is located on the same side of the body as another structure.
|
|
|
Directional Terms - contralateral refers to
|
a structure which is located on the opposite side of the body from another structure.
|
|
|
Directional Terms - bilateral refers to
|
a structure which is located on both sides of the body.
|
|
|
Directional Terms - proximal refers to
|
a structure which is nearer to the point of attachment to the limb or to the trunk; nearer to the origination of a structure. Primarily used for limbs
|
|
|
Directional Terms - distal refers to
|
a structure which is farther from the point of attachment to a limb or to the trunk; farther from the origination of a structure. Primarily used for limbs
|
|
|
Directional Terms - superficial refers to
|
structures which are closer towards or on the surface of the body or other structure.
|
|
|
Directional Terms - deep refers to
|
structures which are farther away from the surface of the body or structure.
|
|
|
Directional Terms - prone refers to
|
the position of the body when the individual lies anterior side down.
|
|
|
Directional Terms - supine refers to
|
the position of the body when the individual lies anterior side up.
|
|
|
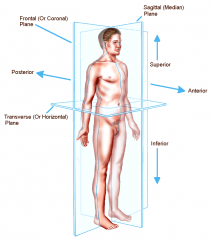
Planes and Sections
|
Imaginary flat surfaces that may be passed through the body or organs to divide it into parts.
|
|
|
Planes and Sections - Sagittal plane section or plane is used to divide the body
|
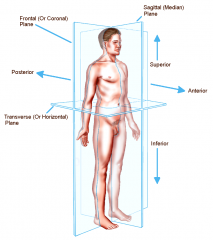
vertically into right and left sections.
|
|
|
Planes and Sections - midsagital section or plane is used to divide the body
|
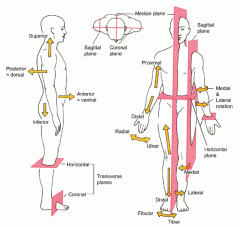
along the midline resulting in bilateral symmetry.
|
|
|
Planes and Sections - parasagital section or plane is a
|
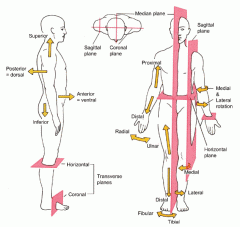
vertical division but is located off-center of the midline in either direction.
|
|
|
Planes and Sections - frontal section or plane may also be referred to as
|
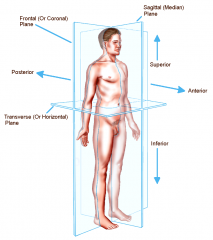
a coronal section or plane occurs at a right angle to the sagittal plane and it divides structures into anterior (front) and posterior (back) sections.
|
|
|
Planes and Sections - oblique section or plane occurs
|

at a slant or diagonal usually about 45 degrees to either a sagittal or frontal plane.
|
|
|
Planes and Sections - transverse section or plane is a
|

horizontal section or plane which divides the body or structure across the short axis resulting in superior(higher) and inferior (lower) sections.
|
|
|
Planes and Sections - Longitudinal section or plane refers to any division of the body or structure in
|
the direction of the long axis of a structure.
|
|
|
The term Anatomy is
|
the study of body structures and the relationships that exist among them.
|
|
|
Embyology: refers to the study of
|
structures of a fertilized egg through the eighth week in utero
|
|
|
Developmental Biology structures emerge from
|
fertilized egg to the adult form
|
|
|
Histology:
|
microscopic structure of tissues
|
|
|
Surface Anatomy:
|
anatomical landmarks on the surface of the body through visualization and palpation
|
|
|
Gross Anatomy:
|
structures which can be examined without the use of a microscope
|
|
|
Systemic anatomy:
|
structure of specific systems of the body
|
|
|
Regional Anatomy:
|
specific regions of the body
|
|
|
Radiographic:
|
body structures visualized with x-rays
|
|
|
Pathological:
|
structural changes associated with disease
|
|
|
The term Physiology is
|
the study of body functions or how the body parts work.
|
|
|
Neurophysiology:
|
functional properties of nerve cells
|
|
|
Endocrinology:
|
hormones and how they control body functions
|
|
|
Cardiovascular:
|
functions of heart and blood vessels
|
|
|
Immunology:
|
defense systems against disease-causing agents
|
|
|
Respiratory Physiology :
|
functions of air passageways and lungs
|
|
|
Metabolism
|
Defined as the sum of all chemical processes that occur within the body.
|
|
|
catabolic is the breakdown of
|
chemical substances and/or macromolecules into simpler compounds and/or monomers.
|
|
|
anabolic is the
|
synthesis(building) of complex chemical substances and/or macromolecules from smaller, simpler components and/or monomers.
|
|
|
Responsiveness
|
Refers to the ability of the organism to detect and respond to changes in both the internal and external environment. – goes Hand in Hand with Homeostasis
|
|
|
Movement
|
Includes motion of the whole body, individual organs, single cells, and structures inside the cells.
|
|
|
Growth
|
Refers to an increase in the size of the organism through an increase in cell size, the number of cells or both.
|
|
|
Differentiation
|
A process in which unspecialized cells change into cells with specialized functions and structures.
|
|
|
Precursor cells which can divide and become specialized cells through differentiation are called
|
stem cells
|
|
|
Reproduction
|
Refers to either the Formation of new cells responsible for growth repair or replacement. cell division/cell replication formation of new cells or cell replacement. The production of a new individual.
|

