![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Lymph nodes of head (Nodi lymphoidei capitis)
|
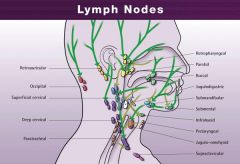
1. Occipital nodes (Nodi occipitales)
(<- posterior scalp, -> superior deep lateral cervical)(close to trapezius) 2. Mastoid\Retro-auricular (<- pinna\auricle, posterior scalp, -> superior deep cervical, esp jugulodigastric) 3. Deep & superficial parotid\pre-auricular (middle scalp, skin of temple, pinna\auricle, parotid gland, posterior orbit) (-> superior deep cervical, esp jugulo-omohyoid) 4. Facial nodes (Nodi faciales) (eyelids, nose, cheek, lip, gums. -> submandibular nodes) 5. Lingual nodes (along vein, <- tongue (except tip), -> submandibular nodes) 6. Submental nodes (anterior tongue, floor of mouth, lower incisor and canine teeth, lower lip, skin of anterior chin) (-> deep lateral cervical, esp retropharyngeall) 7. Submandibular nodes (upper lip, cheek, nose, forehead & anterior scalp, middle tongue, lower molar and premolar, all upper teeth, sublingual & submandibular gland, anterior half of nasal cavity and nasal sinuses) (-> superior deep cervical, esp. jugulodigastric) |
|
|
Anterior cervical group (of lymph nodes) (Nodi lymphoidei cervicales anteriores)
|
1. Superficial nodes
2. Deep nodes a. Infrahyoid b. Pre-, paratracheal (hypopharynx, larynx, trachea, thyroid, parathyroid) c. Retropharyngeal (Rouviere node) (pharynx) |
|
|
Lateral cervical group (of lymph nodes) (Nodi lymphoidei cervicales laterales)
|
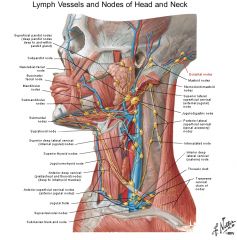
1. Superficial nodes
2. Deep nodes a. Jugulodigastric node (Kuttner node) (below digastric anterior to internal jugular vein) (palatine tonsil (Wood node), upper pharynx, posterior tongue) b. Juguloomohyoid node (above intermediate tendon of omohyoid and anterior to internal jugular vein) (posterior half of nasal cavity, palate (soft and hard, submental, submandibular, deep anterior cervical, -> deep lateral cervical) c. Supraclavicular nn (Virchow-Troisier nodes) (inferior deep lateral cervical (below inf. belly of omohyoid), <- mediastinum, -> subclavian trunk) d. Accessory nn (along accessory nerve, -> supraclavicular) |
|
|
Nodi lymphoidei membri sup.\Lymph nodes of upper limb
|
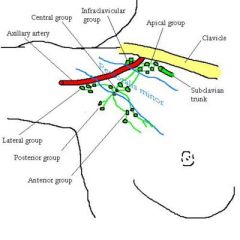
1. Axillary (-> subclavian lymph trunk)(APICAL mnemonic)
a. apicales b. centrales c. humerales\lateral (arm, forearm, hand) d. subscapulares\posterior (posterior thoracic wall, tail of breast, upper posterior abdominal wall) e. pectorales\anterior (Sorgius node) (breast, anterior thoracic wall, upper anterior abdominal wall) f. infraclavicular (skin of shoulder, skin of lower neck, skin of anterior upper thoracic wall, breast) 2. interpectorales (between pectoralis minor & major, <- muscles, mammary gland, -> axillary) 3. deltopectorales 4. brachiales\humeral axillary (along brachial vein, <- most of the upper limb -> central axillary lymph nodes) 5. cubitales (superficial & deep, along basilic vein above medial epicondyle, <- ulnar side of hand & forearm, -> brachial nodes |
|
|
Thoracic lymph nodes (nodi lymphoidei thoracis)
|
1. Paramammarii
(on lateral side of mammary gland, -> axillary pectoral group) 2. Parasternales (lie along course of internal thoracic vessels. <- anterior intercostal, pericardium, diaphragm, liver, medial mammary gland, -> bronchomediastinal trunk) 3. Intercostales (<- parietal pleura, intercostal space, posterior body wall, -> thoracic duct (upper), descending intercostal trunk to cisterna chyli (lower) 4. Phrenic sup\supradiaphragmatic (ant., middle, post., <- liver (bare space), diaphragm, intercostal, subphrenic spaces -> parasternal or posterior mediastinal) 5. Prepericardiaci 6. Pericardi lat. (along the pericardiophrenic vessels, <- pericardium, -> parasternal) 7. Tracheobronchiales sup. & inf. (<- heart and all layers of pericardium, lungs and visceral pleura, extrapulmonary bronchi, trachea, thymus, (thyroid isthmus), 8. Bronchopulmonales (in the hilum, <- pulmonary nodes, -> tracheobronchial) 9. Interpulmonales 10. Juxtaesophageals (<- esophagus, lungs, -> thoracic duct) 11. Prevertebrales\Posterior mediastinal (along thoracic aorta, <- esophagus, diaphragm, liver, pericardium, -> thoracic duct, bronchomediastinal lymphatic trunks) Anterior mediastinal lymph nodes: parasternales, prepericardiaci Posterior mediastinal nodes: juxtaesophageales, prevertebrales |
|
|
Parietal abdominal lymph nodes (nodi lymphoidei abdominis parietalis)\Lumbar lymph nodes
a. Members b. Together drain |
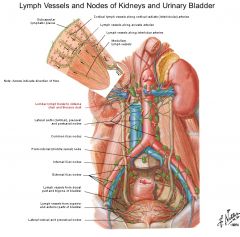
a.
1. Right lumbar (associated with IVC, lateral caval (right) precaval and postcaval) 2. Left lumbar (associated with aorta, lateral aortic (left) preaortic, postaortic) 3. Intermediate lumbar (between) b. <- 1. Lower rectum & pectinate line 2. Bladder 3. Urethra, lower urether (4. female: uterus, cervix, upper vagina, clitoris, labia minor, ovary) (5. male: vas deferens, seminal vesicle, prostate, bulk of penis, testis) |
|
|
Visceral abdominal lymph nodes
|
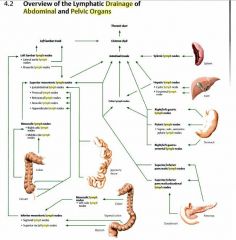
1. Celiac (-> intestinal trunks -> cisterna chyli)
a. Gastric (right, left) b. Pyloric (supra-, sub-, retropyloric) c. Gastroomental (right, left) d. pancreatic (sup, inf) e. spleen f. pancreaticoduodenal (sup, inf) g. hepatic (cystic, foraminal) 2. Superior mesenteric (-> intestinal trunks -> cisterna chyli) a. juxtaintestinal b. prececal c. retrocecal d. ileocolic e. appendicular f. mesocolic (right colic, middle colic) 3. Inferior mesenteric (-> superior mesenteric \ -> lateral aortic -> left lumbar trunk) a. sigmoid b. superior rectal c. mesocolic (left colic) |
|
|
Visceral pelvic lymph noeds
|
1. Paravesical
(around urinary bladder and prostate, pre-, lateral, postvesicular, -> internal iliac) 2. Parauterine a. Bayer node (parauterine node) (on either side of uterus, -> internal iliac, lumbar nodes( via ovarian artery) 3. Paravaginal (-> internal iliac) 4. Pararectal (on either side of rectum, -> middle (-> internal iliac) & superior rectal nodes (-> inf. mesenteric) |
|
|
Parietal pelvic lymph nodes
|
1. Common iliac (-> lumbar)
(5 groups: intermediate (between a v), lateral, medial, promontorial, subaortic (bifurcation)) 2. External iliac (<- inguinal, lower abdominal wall, pelvic viscera, -> common iliac) (intermediate (between a v), lateral, medial (to vein) 3. Internal iliac a. Gluteal (inferior, superior) b. Sacral (rectum, posterior pelvic wall) |
|
|
Lower limb lymph nodes
|
1. Deep (include Cloquet\Rosenmuller) inguinal
(deep structures of lower limb, glans penis&clitoris, superficial inguinal) (divisions: proximal, intermediate, distal) 2. Superficial inguinal (along great saphenous vein, via saphenous opening -> Cloquet) (uterine fundus (via round ligament), skin of penis, labia minora\scrotum, skin of buttock, skin of lower abdominal wall to umbilicus, skin of thigh, anterior skin of calf, dorsum of foot, skin of anterior perineum) 2. Popliteal (skin of sole of foot, skin of posterior calf) |
|
|
Wood lymph node
a. name b. group c. location d. <- |
a. Tonsillary lymph node
b. Lymph nodes of superior deep lateral cervical region c. At level of C3 d. From tonsilla palatine (inflammation) |
|
|
Bayer lymph node
a. name b. group c. location |
a. Parauterine lymph node
b. Parauterine lymph nodes c. At crossing of uterine a and ureter |
|
|
Sorgius lymph node
a. group b. location d. drain |
a. pectoral nodes
b. most crainal node from the group, at 2nd\3rd digitation from m. serratus anterior c. from breast |
|
|
Kuttner lymph node
a. name b. group c. location |
a. Jugulodigastric node
b. Superior deep lateral cervical nodes c. At crossing of internal jugular vein and posterior belly of digastric |
|
|
Cloquet\Rosenmuller node
a. name b. group c. location |
a. proximal node
b. deep inguinal nodes c. Most crainal node from the group, in lacuna vasorum (vascular space) |
|
|
Virchow-Troisier node
a. group b. location c. <- |
a. Supraclavicular nodes
b. Connected with arch of thoracic duct c. Respiratroy organs\GIT organs. Left side more frequently |
|
|
Rouviere node
a. group b. from |
a. deep anterior cervical nodes
b. From pharynx (inflammation, tumor) |
|
|
Sentinel lymph node
|
The first lymph node to receive lymphatic drainage from a malignant tumor
(identified as the first to take up a radionuclide or dye injected into the tumor) |
|
|
Deep nodes follow ..., superficial nodes follow ...?
|
Deep nodes follow arteries, superficial ones follow veins.
|
|
|
Cisterna chyli
a. what b. what opens into it |
a. A dilated sac at the lower end of the thoracic duct
b. The intestinal trunk and the two lumbar lymphatic trunks opens (Inconsistent, located posterior to aorta on anterior aspect of L1-2) |
|
|
Thoracic duct
a. <-, -> b. receives c. drains |
a. -< cisterna chyli, -> left venous angle (left subclavian w internal jugular)
b. left jugular trunk, left subclavian trunk, cisterna chyli, most thoracic lymhpatics (except right upper thorax) c. all body tissue below the diaphragm, left arm, left head & neck, left thorax, lower right thorax |
|
|
Right lymphatic duct
a. -> b. receives c. drains |
a. -> right venous angle
b. right subclavian trunk, right jugular trunk, right bronchomediastinal trunk (right upper thorax) c. right head and neck, right arm, right upper thorax |
|
|
Pharyngeal lymphatic ring\Tonsillar ring
a. what b. formed of c. synonym |
a. The broken ring of lymphoid tissue
b. Formed of lingual, palatine, and pharyngeal tonsils c. Waldeyer throat ring |
|
|
Bronchomediastinal lymphatic trunk
a. from b. special with left side |
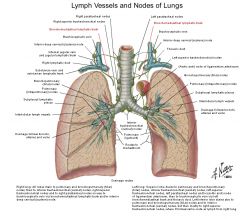
a. From union of efferent lymphatics from tracheobronchial and mediastinal nodes on either side
b. on the left side it may largely be replaced by direct drainage into the thoracic duct |
|
|
Lumbar lymphatic trunks
a. <- b. -> |
a. Two lymphatic ducts conveying lymph from
1. The lower limb 2. Pelvic viscera and walls 3. Large intestine 4. Kidneys 5. Suprarenal glands b. -> They discharge into the cisterna chyli |
|
|
Venous angle
a. what b. what empty into it c. what converge toward it d. synonym |
a. The junction of the internal jugular and subclavian veins
b. thoracic duct in the left, right lymphatic duct in the right c. external and anterior jugular veins and vertebral veins d. Pirogoff angle |
|
|
Drainage pattern of axillary lymph nodes: lateral\humeral, posterior, anterior, brachial, cubital, anterior, lcentral, apical, infraclavicular, subclavian lymph trunk
|
1. cubital -> brachial -> lateral\humeral
2. lateral\humeral, posterior\subscapular, anterior\pectoral -> central 3. Central, infraclavicular -> apical 4. Apical -> subclavian lymph trunk |
|
|
Testis & scrotum - lymphatic drainage
|
Testis -> paraaortic
Scrotum -> superficial inguinal |
|
|
60% of carcinomas of the mammary gland develop in which quadrant
|
Upper outer
|
|
|
Lymphatic drainge of the mammary gland
|
1. Axillary nodes (3\4 of drainage)
a. Pectoral group (pass around edge of pectoralis major) b. Apical nodes (route through the pectoral muscles) 2. Parasternal (follow blood vessels through the pectoralis major) 3. Contralateral breast (across the median plane) 4. Sheath of rectus abdominis & subperitoneal and subhepatix plexuses Also free communication exists between nodes below and above the clavicle (supraclavicular: inferior deep lateral cervical, infraclavicular: superficial) and between the axillary and cervical nodes |
|
|
Sappey's (subareolar) plexus
a. what b. drain by |
a. A network of lymphatics in the areola of the nipple
b. Drain by collecting trunk mainly to axillary nodes |
|
|
Breast cancer
a. cancer incidence among women b. types |
a. 10% (2nd most common after skin cancer, 5th most common cause of cancer death, 100 x as common in females)
b. ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) (local), invasive carcinoma (also graded according to dependence on hormone to grow: ER, PR. ER carcinomas can be treated by estrogen blockers such as tamoxifen or aromatase ihnibitors such as anastrozole), cyclophosphamide) (chemo: most common is AC: adriamycin(doxorubicin)(antineoplastic antibiotic, intercalate DNA) with cyclophosphamide (nitrogen mustard alkylating agent, form covalent cross links between DNA strands) |
|
|
Lymphatic drainage of mammary gland
|
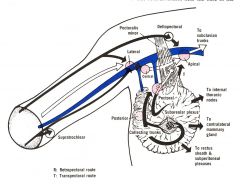
1. 3\4 of lymphatic drainage via axillary nodes
a. pectoral nodes (pass around the edge of pectoralis major) b. apical nodes (through pectoralis minor & major 2. parasternal (follow blood vessels through pectoralis major) 3. Contralateral place (across the median plane) 4. Rectus sheath, subperitoneal & subhepatic plexuses It should also be noted that free communication exists between nodes below and above the clavicle and between the axillary and cervical nodes |
|
|
Occipital nodes
a. <- b. -> c. group |
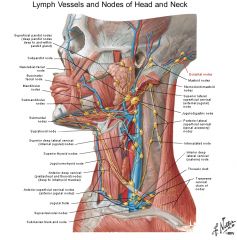
a. <- posterior scalp
b. -> superior deep lateral cervical (close to trapezius) c. lymph nodes of head (1-2 small, most posterior nodes of the pericervical collar of lymph nodes of head and neck) |
|
|
Mastoid\Retroauricular nodes
a. <- b. -> c. group |
a. <- pinna\auricle, posterior scalp
b. -> superior deep lateral cervical, esp. Kuttner n. (Jugulodigastric n.) c. lymph node of head (2-3) |
|
|
Deep & superficial parotid pre-auricular lymph nodes
a. <- b. -> c. group |
a. <-
1. Middle scalp, skin of temple 2. Parotid gland 3. Posterior orbit b. -> superior deep cervical, esp. jugulo-omohyoid node c. Nn. of head |
|
|
Facial nodes
a. <- b. -> c.group |
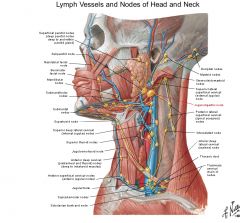
a. <-
1. Eyelids 2. Nose 3. Cheek 4. Lip 5. Gums b. -> Submandibular nodes c. Nn. of head (Chain) |
|
|
Lingual nodes
a. <- b. -> c. group |
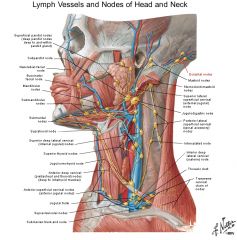
a. <- Tongue, except tip
b. -> Submandibular nodes c. Nn. of head (chain) |
|
|
Submental nodes
a. <- b. -> c. group |
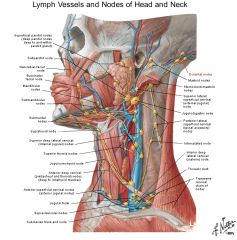
a. <-
1. Anterior tongue 2. Floor of mouth 3. Lower incisor and canine teeth 4. Lower lip 5. skin of anterior chin b. -> Deep lateral cervical, esp. Rouviere nn. (retropharyngeal nn) c. Nn. of head (small, superficial to mylohyoid, most anterior of pericervical collar of lymph nodes that initially receives drainage from the head) |
|
|
Submandibular nodes
a. <- b. -> c. group |
a. <-
1. Upper lip 2. Cheek 3. Nose 4. Forehead & anterior scalp, 5. middle tongue, 6. Lower premolar & molar 7. all upper teeth 8. Sublingual & submandibular glands 9. Anterior half of nasal cavity and nasal sinuses b. -> superior deep lateral cervical, esp. jugulodigastric node c. Nn of head (4-5, part of pericervical collar of nn that initially receive drainage from the head) |
|
|
Pre- and paratracheal nodes
a. <- b. group c. -> |
a.
1. Hypopharynx 2. Larynx 3. Trachea 4. Thyroid 5. Parathyroid b. Deep anterior cervical group c. -> 1. -> deep lateral cervical group 2. ->parasternal nodes |
|
|
Retropharyngeal nodes
a. synonym b. <- c. group |
a. Rouviere nodes
b. <- 1. Nasopharynx 2. Auditory tube 3. Atlanto-occipital & atlantoaxial jj c. Deep anterior cervical group |
|
|
Jugulodigastric node
a. Synonym b. Group c. <- d. -> |
a. Kuttner n
b. Deep anterior cervical group c. <- 1. Upper pharynx 2. Posterior tongue 3. Palatine tonsil (via Wood n) d. -> deep lateral cervical group\parasternal nn |
|
|
Juguloomohyoid node
a. Group b. <- c. -> |
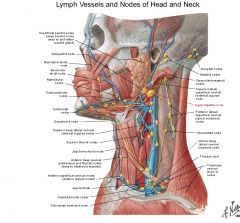
a. Deep lateral cervical group
b. <- 1. Posterior half of nasal cavity 2. Palate (soft & hard) 3. Submental & submandibular nn 4. Deep anterior cervical group c. -> Deep lateral cervical (Above intermediate tendon of omohyoid and anterior to internal jugular vein) |
|
|
Supraclavicular nodes
a. Group b. <- c. -> d. name of a firm supraclavicular palpable node, esp. on the left side, old eponym, signal for |
a. Inferior deep lateral cervical group (those below inf. belly of omohyoid)
b. <- Mediastinum c. Subclavian trunk d. Signal lymph node\Virchow node\Troisier ganglion\Virchow-Troisier node (may be the first recognized presumptive evidence of a malignant neoplasm in one of the viscera) |
|
|
Subscapular\posterior nodes
a. Group b. <- c. -> |
a. Axillary nn
b. <- 1. Posterior thoracic wall 2. Tail of mammary gland 3. Upper posterior abdominal wall c. -> central -> apical -> subclavian lymph trunk |
|
|
Pectoral lymph node
a. Synonym b. Group c. <- d. -> |
a. Sorgius node
b. Axillary nn c. <- 1. Breast 2. Anterior thoracic wall 3. Upper anterior abdominal wall c. -> central -> apical -> subclavian lymph trunk |
|
|
Interpectoral node
a. Group b. <- |
a. Axillary nn
b. <- 1. Muscles 2. Mammary gland |
|
|
Parasternal nn
a. Group b. <- c. -> |
a. Thoracic nn
b. <- 1. Anterior intercostal 2. Pericardium 3. Diaphragm 4. Liver 5. Medial mammary gland c. -> Bronchomediastinal trunk (Along course of internal thoracic veins, chain) |
|
|
Intercostal nn
a. Group b. <- c. -> |
a. Thoracic nn
b. <- 1. Parietal pleura 2. Intercostal space 3. Posterior body wall c. -> 1. Upper -> thoracic duct 2. Lower -> descending intercostal trunk -> cisterna chyli |
|
|
Superior phrenic\Supradiaphragmatic nn
a. Group b. <- c. -> |
a. Thoracic nn
b. <- 1. Liver (bare space) 2. Diaphragm 3. Intercostal 4. Subphrenic space (the recesses in the peritoneal cavity between the anterior part of the liver and the diaphragm, separated into right and left by the falciform ligament) c. -> 1. Parasternal nn 2. Posterior mediastinal nn (3 groups - anterior, middle, posterior) |
|
|
Superior tracheobronchial lymph nodes
a. Group b. <- c. -> |
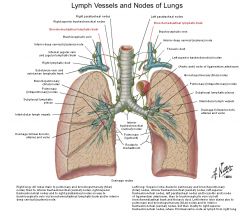
a. Thoracic nn in posterior mediastinum
b. <- 1. Inferior tracheobronchial nn 2. Bronchopulmonary nn 3. Thymus 4. Trachea (5. Thyroid isthmus) c. -> Paratrachael nn (Several large, superior to carina of trachea) |
|
|
Inferior tracheobronchial lymph nodes
a. Group b. <- c. -> |
a. Thoracic nn
b. <- 1. Bronchopulmonary nodes (lungs and visceral pleura, extrapulmonary bronchi) 2. Heart c. -> Superior tracheobronchial & trachael nn (Several large, inferior to carina of trachea) |
|
|
Prevertebral nn
a. Group b. <- c. -> |
a. Thoracic nn
b. <- 1. Esophagus 2. Diaphragm 3. Liver 4. Pericardium c. -> 1. Thoracic duct 2. Bronchomediastinal lymphatic trunk (Along thoracic aorta) |
|
|
Anterior mediastinal group (of nn) \ Brachiocephalic nn include
|
1. Parasternal
2. Prepericardial (Their efferent vessels join those of the tracheal nodes to form the bronchomediastinal trunks) |
|
|
Posterior medastinal group (of nn) - include
|
1. Juxtaesophageal (esophagus, lungs)
2. Prevertebral (extensive) |
|
|
Deep inguinal nn
a. Group b. Divisions c. <- d. -> |
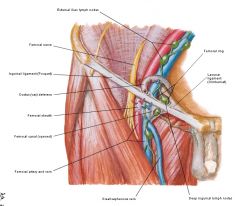
a. Lower limb nn
b. Proximal (Cloquet, Rosenmuller), intermediate, distal c. <- 1. Deep structures of lower limb 2. Glans penis\clitoris 3. Superficial inguinal nn d. -> external iliac nn (several small, deep to fascia lata) |
|
|
Superficial inguinal nn
a. divisions b. <- c. -> |
a. 3 groups
1. Inferior\vertical (inf. to saphenous opening) 2. Superolateral\lateral horizontal (lateral to saphenous opening) 3. Superomedial\Medial horizontal) b. <- 1. Skin and subcutaneous tissue of lower abdominal wall (superolateral\lateral horizontal) 2. Buttock (Superolateral\lateral horizontal) 3. Perineum (Superomedial\medial horizontal) 4. External genitalia (except glans penis\clitoris) (superomedial\medial horizontal) 5. Lower limb (except posterior leg & sole of foot & knee -> popliteal) (inferior\vertical) c. -> great saphenous vein -> saphenous opening -> Cloquet\Rosenmuller) (12-20) |

