![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
216 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
localization of function |
certain structures are specificaly for prescribed functions
- concept of anatomy and physiology |
|
|
16 days after fertilization the zygote cells belong to one of three germ cells |
endoderm = lining tissues, mucosae of digestive and respiratory systems mesoderm = muscle and ct ectoderm = integumentary and nervous system |
|
|
neuroectoderm |
precursor for the tissue of the nervous system - differentiate into neuroepithelium forming a neural plate (cells that change shape causing tissue to buckle and fold inward) |
|
|
neural groove |
visible line along dorsal surface of embryo |
|
|
neural fold |
ridge edge on either side of the neural groove |
|
|
underlying structure of nerual folds into tube beneath ectoderm |
neural tube |
|
|
cells from neural olds seperate from ectoderm to form cluster of cells - runs lateral to neural tube |
neural crest |
|
|
neural crest migrates away from |
nascent/embryonic cns that forms along neural groove and - develops into parts of pns like enteric nervous tissue |
|
|
tissues that arise from neural crest |
parts of pns like enteric nervous tissue, craniofacial carilage and bone, and melanocytes |
|
|
The neuroectoderm begins to fold inward to form the neural groove. As the two sides of the neural groove converge, they form the |
neural tube, which lies beneath the ectoderm. - The anterior end of the neural tube will develop into the brain, and the - posterior portion will become the spinal cord. -The neural crest develops into peripheral structures |
|
|
- The anterior end of the neural tube will develop into the - beginning at 25 days |
brain |
|
|
posterior portion of neural tube will become the - beginning at 25 days |
spinal cord. |
|
|
-The neural crest develops into |
peripheral structures |
|
|
more complex structures of nervous system develop during |
4th week development |
|
|
3 vesicles form at first stage of anterior neural tube developing into brain |
primary vesicles - prosencephalon = forward most - mesencephalon = midbrain - rhombencephalon = hindbrain |
|
|
3 primary vesicles become 5 secondary vesicles |
- prosencephalon = telencephalon and diencephalon - mesencephalon = not differentiate; remains same; smal portion of brain - rhombencephalon = metencephalon and mylencephalon |
|
|
telencephalon will become |
cerebrum |
|
|
diencephalon will become |
thalamus and hypothalamus - in embryonic diencephalon has eye cup and becomes retina |
|
|
retina example of |
nervous tissue developin as part of cns structures in embryo but becoming a periheral structure in the developed nervous system |
|
|
capillaries filter |
blood plasma making csf |
|
|
metencephalon is same as adult structure known as _____ and gives rise to |
pons , cerebellum |
|
|
10% mass of brain |
cerebellum - significant connection to rest of brain at pons bc both rise from metencephalon vesicle |
|
|
mylencephalon corresponds to adult structure known as |
medulla oblongata |
|
|
structures from mesencephalon and rhombencephalon except for cerebellum are called |
brain stem - pons, midbrain, medulla |
|
|
The embryonic brain develops complexity through enlargements of the neural tube called vesicles; (a) The primary vesicle stage has three regions, and (b) the secondary vesicle stage has five regions. |
ya |
|
|
spinal cord develop from |
posterior neural tube |
|
|
neural tube dorsal surface |
closest to surface - dorsal tissue = sensory funcitons |
|
|
neural tube ventral surface |
deeper side - ventral tissue = motor functions |
|
|
cells making wall of nerual tube proliferate and differentiate into |
neurons and glia of spinal cord |
|
|
neural tube establishes anterior-posterior dimensions of nervous system |
neuraxis - overlays superior-inferior dimensions of body - starts in inferior position at end of spinal cord and ends in anterior postiion at front of cerebellum |
|
|
major curve between brain stem and forebrain called |
cephalic flexure |
|
|
The mammalian nervous system is arranged with the neural tube running |
along an anterior to posterior axis, from nose to tail for a four-legged animal like a dog. Humans, as two-legged animals, have a bend in the neuraxis between the brain stem and the diencephalon, along with a bend in the neck, so that the eyes and the face are oriented forward. |
|
|
telencephalon |
cerebrum, major portion |
|
|
diencephalon |
between cerebrum and rest of nervous system - region through which all projections must pass between cerebrum |
|
|
brain stem includes |
midbrain, pons, medulla (mesenchepalon, metencephalon,myelencephalon |
|
|
retina- |
diencephalon |
|
|
cerebellum originates out of |
metencephalon, and its largest white matter connetion is to pons, also from metencephalon |
|
|
ventricles |
open spaces within cns where cerebrospinal fluid circulates - remenants of hollow center of neural tube of enbryonic brain |
|
|
cerebrum embryonic structures and ventricles |
1= prosencephalon 2= telencephalon ventricle= lateral ventricles |
|
|
diencephalon embryonic structures and ventricles |
1= prosencephalon 2= diencephalon ventricles= third ventricle |
|
|
midbrain embryonic structures and ventricles |
1= mesencephalon 2= mesencephalon ventricle = cerebral aqueduct |
|
|
pons cerebellum embryonic structures and ventricles |
1= rhombencephalon 2= metencephalon ventricle= fourth ventricle |
|
|
medulla embryonic structures and ventricles |
1= rhombencephalon 2= myelencephalon ventricle = fourth ventricle |
|
|
spinal cord nerual tube and ventricle |
posterior neural tube ventricle = central canal |
|
|
spina bifida |
closing of neural tube along posterior region fails to close - occulta,meningocele, and myelomeningocele - spina bifida occult = mildest bc ventral bones do not fully surround spinal cord; hidden - meningocyte = meninges protrude through spinal column and spinal nerves not always affected, cyst - myelomeningocete = meninges protrude through spinal column and spinal nerves always affected, cyst; severe neurological symptoms present - surgery |
|
|
lateral horn mainly |
thoracic bc ribs and interthoracic muscles |
|
|
(a) Spina bifida is a birth defect of the |
spinal cord caused when the neural tube does not completely close, but the rest of development continues. The result is the emergence of meninges and neural tissue through the vertebral column. |
|
|
b) Fetal myelomeningocele is evident in this ultrasound taken at 21 weeks. |
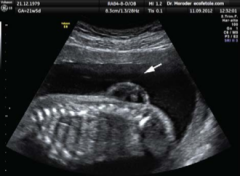
|
|
|
brain 4 main regions |
cerebrum, diencephalon, brain stem, cerebellum |
|
|
portions of cerebrum |
- cerebral cortex = wrinkled - longitudinal fissue = large seperation between 2 sides - cerebral hemisphere = the halves of the longitudinal fissure - corpus collosum = provies path for communication between 2 hemispheres of cerebral cortex |
|
|
cerebral function |
= memory, emotion, consciousness - basal nuclei = responsible for cognitive processing, plan movements - basal forebrain = learning and memory, primary location for acetylcholine production - limbic cortex = part of limbic system, emotion, memory, behavior |
|
|
in mammals the cerebrum is |
outer gray matter (cortex and nuclei) - basal nuclei, basal forebrain |
|
|
- basal nuclei (basal ganglia) = responsible for cognitive processing, plan movements - basal forebrain = learning and memory,primary location for acetylcholine production, loss of this is alzheimers |
ya |
|
|
gyrus |
ridge of wrinkle of cerebral cortex |
|
|
sulcus |
groove between two gyri (ridge of wrinkle in cerebral cortex) |
|
|
cerebral cortex |
- wrinkled gray matter covering cerebrum - 4 regions = - lateral sulcus = separates temporal lobe - parietal lobe and frontal lobe seperated by central sulcus, superior to lateral sulcus - occipital lobe seperated from parietal lobe by parieto-occipital sulcus - no seperation between parietal or temporal lboes on lateral surface |
|
|
ventral side has |
motor connections |
|
|
The cerebral cortex is divided into four lobes. Extensive folding increases the surface area available for cerebral functions |
ya |
|
|
brodmanns areas |
describes anatomical distinctions within cortex - 52 regions - 17 and 18 in occipital lobe are primary visual perception |
|
|
temporal lobe function |
primary auditory sensations - brodmanns areas 41 and 42 in sup temporal lobe - memmory (ultimate location is where sensory perception was processed) |
|
|
sensation of parietal lobe |
somatosensation - general sensations with body |
|
|
posterior to central sulcus is |
postcentral gyrus - parietal lobe - primary somatosensory cortex - bordmanns 1,2,3 - touch, pressure, tickle, pain, itch, vibration, proprioception, and kinesthesia |
|
|
anterior to central sulcus |
- frontal lobe - motor functions - precentral gyrus = primary motor cortex - affector - premotor area = thinking of movement - frontal eye fields = eliciting movements of eye - brocas area = production of language, left side - prefrontal lobe = cognitive, personality, short term memory, consciousness |
|
|
- precentral gyrus = |
primary motor cortex - affector |
|
|
- premotor area = |
thinking of movement |
|
|
prefrontal lobe = |
cognitive, personality, short term memory, consciousness |
|
|
Brodmann mapping of functionally distinct regions of the cortex was based on |
its cytoarchitecture at a microscopic level. |
|
|
beneath cerebral cortex are nuclei |
- subcortical nuclei = augment cortical processes - |
|
|
hippocampus and amygdala |
medial lobe structures, involved in long term memory formation and emotion responses |
|
|
major structures of basal nuclei that control movement are |
- deep in cerebrum - caudate = long nucleus, c shape - putamen = deep in ant regions of frontal and pariatel lobes - globus pallidus = layered nucleus medial to putamen; also called lenticular nuclei ; external and internal |
|
|
caudate + putamen = |
striatum |
|
|
basal nuclei pathways - both from cortex into striatum |
- direct pathway = axons from striatum to globus pallidus internal and substantia nigra pars reticulata, then to thalamus, then back to cortex; causes disinhibition of thalamus ; excites cortex - indirect pathway = axons from straitum to globus pallidus external to subthalamic nucelsu and to globus pallidus internal and substantia nigra pars reticulata; reinforces normal inhibition of thalamus; fails to excite cortex |
|
|
substantia nigra pars compacta |
- swtich between 2 pathways - projects to stratium and releases dopamine (d1 = excitatory, d2= inhibitory) |
|
|
direct pathway is activated by |
dopamine |
|
|
indirect pathway inhibited by |
dopamine |
|
|
left brain vs right brain |
left = language function ; right = spatial and nonverbal reasoning - damage to left side are classified as aphasia = loss of speech function |
|
|
- connectionb etween cerebrum and spinal cord, pns (not olfaction) - output from cerebrum passes through diencephalon - any region with thalamus in name - wall of third ventricle - thalamus and hypothalamus - deithalamus = pineal galnd - subthalamus = subthalamic nucleus, basal nuclei |
diencephalon |
|
|
collection of nuclei that relay info between cerebral cortex and periphery, spinal cord, or brain stem |
thalamus |
|
|
- region of diencephalon - collection of nuclei involved in regulating homeostasis - ans and endocrine system (pituitary gland) - memory and emotion (limbic) |
hypothalamus |
|
|
midbrain and hindbrain (composed of pons and medulla) are referred to as |
brain stem |
|
|
The pons and the medulla regulate several crucial functions, including |
the cardiovascular and respiratory systems and rates. |
|
|
midbrain |
- tectum = 4 colliculi ; inferior colliculus = auditory, project to thalamus; superior colliculus= snesory info about visual space, auditory space, and somatosensory space - tegmentum = continuous with gray matter of brain stem ; send info through cranial nerves - cerebral aqueduct passes through midbrain |
|
|
- ant surface of brain stem - white matter attached to cerebellum - main connection between cerebellum and brain stem - in tergmentum region = has neurons receiving descending input from forebrain to cerebellum |
pons |
|
|
- myelencephalon in embryonic brain - white matter on exterior - process cranial nerve info - reticular formation = gray matter related to sleep and wakefulness |
medulla |
|
|
- little brain - covered in gyri and sulci - compare info from cerebrum with sensory feedback from periphery through spinal cord - 10% mass of brain |
cerebellum |
|
|
Descending input from the cerebellum enters through the |
large white matter structure of the pons. |
|
|
Ascending input from the periphery and spinal cord enters through the |
fibers of the inferior olive. |
|
|
Output goes to the midbrain, which sends a |
descending signal to the spinal cord. |
|
|
Sensory information from the periphery, which enters through spinal or cranial nerves, is copied to a nucleus in the medulla known as the |
inferior olive. |
|
|
axons enter the spinal cord on posterior side through |
dorsal nerve root which marks posterolateral sulcus |
|
|
posterior regions of spinal cord responsible for |
snesory functions |
|
|
anterior regions of spinal cord responsible for |
motor funcitons |
|
|
basal plate |
- close to ventral midline of neural tube - becomes anterior face of spinal cord and gibes rise to motor neurons |
|
|
alar plate |
- on dorsal side of neural tube - gives rise to neurons that receive sensory input from the periphery |
|
|
spinal cord not full length of |
vertebral column bc doesnt grow after 1 or 2 yearold |
|
|
sacral spinal cord is at |
upper lumbar vertebral bones |
|
|
gray horns |
posterior horn = sensory processing anterior horn = sends motor signals to skeletal muscles lateral horn = only in thoracic, upper lumbar, and sacral regions; sympathetic division of autonomic nervous system |
|
|
somatic is |
voluntary |
|
|
visceral |
autonomic |
|
|
name of spinal cord region correspponds to |
level at which spinal nerves pass through intervertebral foramina |
|
|
spinal cord stop growing after |
1st or 2nd year |
|
|
cauda equina |
the spinal cord not meeting vertebral column length and long bundle of nerves results
- sacral spinal cord is at level of upper lumar vertebral bones |
|
|
white columns |
- ascending tracts = carry sensory info to brain - descending tracts = carry commands from brain - posterior columns composed of axons of ascending tracts |
|
|
parkinsons disease |
- disorder of basal nuclei , substantia nigra, neurons dying - neurodegenerative - treat by l dopa amino acid |
|
|
myelination takes place in |
axon |
|
|
this filters blood into cerebrospinal fluid |
cns |
|
|
The major artery carrying recently oxygenated blood away from the heart is the |
aorta. |
|
|
aorta |
- major arter carrying oxygenated blood from heart - first branches off this supply heart with nutrients and oxygen - next branches are common carotid arteries (bases has stretch receptors that immediately respond to drop in blood pressure upon standing) which branch into internal carotid arteris(enters cranium through carotid canal in temporal bone) |
|
|
external carotid arteries supply blood to |
tissues on surface of cranium |
|
|
common carotid arteries |
(bases has stretch receptors that immediately respond to drop in blood pressure upon standing |
|
|
orthostatic reflex |
reaction to change in body position so blood pressure is maintained against increasing effect of gravity - heart reate increases (sympathetic division of ans), and blood pressure raises |
|
|
vertebral arteries |
-protected by transverse foramina of cervical vertebrae - enter cranium through foramen magnum in occipital bone - l and r merge into anterior spinal artery - then merge into basilar artery (which gives rise to branches to brain stem and cerebellum) - l and r internal carotid arteries and branches of basilar artery become circle of willis (arteries that can maintain perfusion of brain even if narrowing or blockage limits flow through one part) |
|
|
after cns blood goes |
- through dural sinuses and veins - superior sagittal sinus = groove of longitudinal fissure, where absorbs csf from meninges, drains to confluence of sinuses with occipital sinuses and straight sinus, to drain into transverse sinuses, these connect to sigmoid sinuses, these connect to jugular veins, then toward heart |
|
|
outer surface membranes of cns |
meninges, protect brain |
|
|
meninges |
- dura mater = thick, fibrous, strong, entire brain and spinal cord, directly attached to inner surface of cranium bones and end of vertebral cavity, foldings that fit into crecasses, midline and surrounds pituitary gland, venous sinuses - arachnoid mater = thin, fibrous, loose sac around cns, under is arachnoid trabeculae - pia mater = thin, fibrous, follows convolutions of gyri and sulci in cerebral cortex and fits into other grooves and indentations |
|
|
dorsal root ganglia part of |
sensory pathway, afferent |
|
|
arachnoid mater |
- middle meninges - sac - trabeculae is at subarachnoid space, filled with csf - emerges into dural sinuses as arachnoid gramulations, where csf filtered back to blood for drainage from ns |
|
|
pia mater |
- outer surface os cns - thin fibrous - continous cells - fluid impermeable membrane - in every convolution in cns, lines inside of sulci in cerebral and cerebellar cortices |
|
|
preganglionic axon is |
myelinated, post is not |
|
|
lumbar puncture |
- bc spinal cord not in lower lumbar region needles can insert through dura and arachnoid layers to withdraw csf - avoids risk of damaging central tissue of spinal cord |
|
|
meningitis |
inflammations of meninges - infections of bacteria or viruses:streptococcus, staphylococcus, or tb, enterovirus - bacteria more severe - fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, light sensitivity, soreness of neck, headache, confusion, memory deficits, hearing loss - lumbar puncture is test |
|
|
csf |
- circulates cns - removes waste from interstital fluids of nervous tissues - in ventricles, produced by choroid plexus |
|
|
ventricles |
open spaces within brain where csf circulates - produces csf through choroid plexus filtering blood |
|
|
4 ventricles from |
central canal |
|
|
ventricles |
- lateral are deep and connected to third ventricle by intervenricular foramina |
|
|
space between let and right sides of diencephalon that opens into cerebral aquedut that passes through the midbrain |
third ventricle - acqueduct opens into fourth ventricle (spacebetween cerebellum and pons and upper medulla) |
|
|
The choroid plexus in the four ventricles produce CSF, which is circulated through the ventricular system and then enters the subarachnoid space through the median and lateral apertures. The CSF is then reabsorbed into the blood at the arachnoid granulations, where the arachnoid membrane emerges into the dural sinuse |
ya |
|
|
The interventricular foramina connect the |
frontal region of the lateral ventricles with the third ventricle |
|
|
third ventricle space bounded by |
medial walls of hypothalamus and halamus |
|
|
two thalami touch at center at |
massa intermedia (surrounded by third ventricle) |
|
|
floor of the fourth centricle is |
dorsal surace of pons and upper medula |
|
|
sinlge median aperture and pair of lateral apertures connect |
to subarachnoid space so that csf flows through ventricles and out of cns |
|
|
production of csf( water, small molecules, electrolytes, o and co3 dissolved into this) |
choroid plexus (membrane) and ependymal cells (glial cell) |
|
|
lfow of csf |
lateral ventricles to third ventricles then to cerebral aqueduct into 4th ventricle then to central canal - 500 ml day |
|
|
csf in subarachnoid space surrounding all of cns functions |
1. picks up metabolic wastes from nervous tissue and moves it out of cns 2. liquid cushion for brain and spinal cord |
|
|
lateral venticles |
located in cerebellum and has choroid plexus |
|
|
third ventricles |
located in diencephalon and has choroid plexus |
|
|
cerebral aqueduct |
located in midbrain |
|
|
fourth ventricle |
located between pons/ upper medulla dn cerebellum and has choroid plexus |
|
|
central canal |
located in spinal cord |
|
|
subarachnoid space |
located external to entire cns and has arachnoid granulations |
|
|
disrpution of blood supply to brain - blockage from clot, fat embolus, or air bubble |
stroke - to lateral medulla is loss of face or extremities - to temporal is memory loss |
|
|
transient ischemic attacks |
- mini strokes
- blockage is temporary cutting off blood and oxygen to region - no cell death |
|
|
fast for sudden loss of neurological function |
F= face muscles issues A= raise arms above head only lift one S= speech changed slurring T= time to call help |
|
|
neural structures that are incorporated into other organs that are features of digestive system |
enteric nervous system (part of pns) |
|
|
anosmia |
loss of sense to smell - olfactory severed - results in loss of enjoyment of food - |
|
|
ganglion |
group of neuron cell bodies in periphery - sensory or autonomic |
|
|
common type of sensory ganglion is |
dorsal (pos) root ganglion - axons that are sensory endings in periphery (skin) and extend into cns through dorsal nerve root - enlargement of nerve root - unipolar cells - small round nuclei of stellite cells surround neuron cell bodies |
|
|
cranial nerve ganglion |
analogous to dorsla root ganglion but CRANIAL nerve instead of spinal nerve - unipolar - associated with satellite cells |
|
|
trigeminal ganglion is |
superficial to temporal bone - nerves attached to mid pons of brain stem |
|
|
autonmoic nervous system divided into |
sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems |
|
|
sympathetic chain ganglia |
row of ganglia along vertebral column that receive central input from lateral horn of thoracic and upper lumbar spinal cord |
|
|
superior to chain ganglia are |
3 paravertebral ganglia in cervical region |
|
|
located outside of sympathetic chain ganglia |
prevertebral ganglia - anterior to verterbral column |
|
|
neurons of autonomic ganglia are |
multipolar in shape - dendrites radiation out around cell body - neurons project to organs in head and neck, thoracic, ab, pelvic cavities to regulate sympathetic aspect of homeostatic mechanisms |
|
|
terminal ganglia |
receive input from cranial nerves or sacral spinal nerves - regulate parasympathetic aspect of homeostatic mechanisms - below head and neck incorporated into wall of target organ as plexus (network of fibers or vessels) |
|
|
enteric plexus |
extensive network of axons and neurons in wall of small and large intestines - ens - gastric plexuses and esophageal plexus - ens receives input from central neurons of ans and doesnt require cns input to function |
|
|
bundles of axons in pns are |
nerves |
|
|
outer surface of nerve is |
fibrous connective tissue called epineurium |
|
|
in nerve axons are bundled into |
fascicles - these are surrounded by perineurium |
|
|
indivudual axons surrounded by |
loose ct called endoneurium |
|
|
cranial nerves |
- attached to brain - responsible for snesory and motor funcitonsof head and neck - thoracic and ab cavitities as part of parasymptathetic nervous system - 12 CNI -CNXII - originate out of sensory ganglia external to cranium or motor nuclei within the brain stem - enter brain synapse in nucleus - 3 composed of sesnory fibers, 5 of motor, 4 mixed nerves |
|
|
oculomotor nerve |
responsible for eye movements by controlling 4 of the extraocular muscles - lifts upper eyelid and pupillary constricution |
|
|
trochlear nerve and abducens nerve |
eye movement by controlling extraocular muscles |
|
|
trigemnial nerve |
cutaneous sensations of face and control mastication muscles |
|
|
facial nerve |
muscles involved in facial expressions and taste and saliva |
|
|
vestibulocochlear nerve |
hearing and balance |
|
|
glossopharyngeal nerve |
controll muscle in oral cavity and upper throat, taste, saliva |
|
|
vagus nerve |
homeostatic control of organs of thoracic and upper abdominal cavities - this targets autonomic ganglia in thoracic and upper ab cavitites - gag reflex |
|
|
spinal accessory nerve |
control muscles of neck, with cervical spinal nerves |
|
|
hypoglossal nerve |
responsible for controlling muscles of lower throat and tongue |
|
|
oculomotor, facial, glossopharyngeal nerves |
contain fibers that contact autonomic ganglia - oculomotor fibers initiate pupillary constriction - other two intitae salivation |
|
|
CNI-CNXII |
CNI = olfactory CNII= optic CNVIII= vestibulocochlear CNIII= oculomotor CNIV= trochlear CNVI= abducens CNXI= spinal acessory CNXII= hypoglossal CNV= trigeminal CNVII= facial CNIX= glossopharyngeal CNX= vagus |
|
|
1st, 2nd and 8th nerves are |
purely sensory |
|
|
three eyemovements nerves are |
all motor - as is spinal accessory and hypoglossal nerves |
|
|
CNI |
-olfactory - smell - olfactory bulb - olfactory epithelium |
|
|
CNII |
- optic - vision - hypothalamus/thalamus/midbrain - retina |
|
|
CNIII |
oculomotor - eye movement - oculomotor nucleus - extraocular muscles, levator palpebrae |
|
|
CNIV |
trochlear - eye movements - trochlear nucleus - superior oblique muscle |
|
|
CNV |
trigeminal - sensory/ motor face - trigeminal nuclei in midbrain, pons, and medulla - trigeminal |
|
|
CNVI |
abducens - eye movements - abducens nucleus - lateral rectus muscle |
|
|
CNVII |
facial - motor , face, taste - facial nucleus, solitary nucleus, sup salivatory nucleus - facial muscles |
|
|
CNVIII |
auditory (vestiubulococholear) - hearing/ balance - cochlear nucleus, vestibular nuclesu/ cerebellum - spiral ganglion, vestibular ganglion |
|
|
CNIX |
glossopharyngeal - motor throat taste - solitary nucleus, inferior salivatory nucleus - pharyngeal muscles |
|
|
CNX |
vagus - motor/sensory- viscera - medulla - terminal ganglia serving thoracic and upper abdominal organs |
|
|
CNXI |
- spinal accessory - motor head and neck - spinal accessory nucleus - neck muscles |
|
|
CNXII |
hypoglossal - motor lower throat - hypoglossal nucleus - muscles of larynx and lower pharynx |
|
|
nerve arrangment of spinal are |
more regular than cranial - and all combined sensory ad motor axons that seperate into two nerve roots - 31 spinal nerves c1-c8 t1-t12 l1-l5 s1-s5 |
|
|
axons from different spinal nerves will come together into |
systemic nerve - 4 places along length of the vertebral column each a nerve plexus - 2 cervical, 1 lumbar, 1 sacral plexus |
|
|
cervical plexus |
axons from spinal nerves c1-c5 - branches into phrenic nerve and neck and head pos - phrenic nerve connects diaphragm at base of thoracic cavity |
|
|
brachial plexus |
cervical level - c4-t1 - nerves of arms - radial nerve and axillary nerve - ulnar nerve and median nerve |
|
|
lumbar plexus |
all lumbar spinal nerves - enervates pelvic region and anterior leg - femoral nerve - saphenous nerve |
|
|
sacral plexus |
lower lumbar nerves l4 and l5 and s1-s4 - sciatic nerve (tibial nerbe and fibular nerve) |
|
|
t2-t11 |
not part of plexuses but give rise to intercostal nerves between ribs |
|
|
lumbar plexus supplies nerves to |
ant leg |
|
|
this supplies nerves to post leg |
sacral plexus l4-s4 |
|
|
13. Aside from the nervous system, which other organ system develops out of the ectoderm? a. digestive b. respiratory c. integumentary d. urinary |
c. integumentary |
|
|
14. Which primary vesicle of the embryonic nervous system does not differentiate into more vesicles at the secondary stage? a. prosencephalon b. mesencephalon c. diencephalon d. rhombencephalon |
b. mesencephalon |
|
|
15. Which adult structure(s) arises from the diencephalon? a. thalamus, hypothalamus, retina b. midbrain, pons, medulla c. pons and cerebellum d. cerebrum |
a. thalamus, hypothalamus, retina |
|
|
16. Which non-nervous tissue develops from the neuroectoderm? a. respiratory mucosa b. vertebral bone c. digestive lining d. craniofacial bone |
d. craniofacial bone |
|
|
17. Which structure is associated with the embryologic development of the peripheral nervous system? a. neural crest b. neuraxis c. rhombencephalon d. neural tube |
a. neural crest |
|
|
18. Which lobe of the cerebral cortex is responsible for generating motor commands? a. temporal b. parietal c. occipital d. frontal |
d. frontal |
|
|
19. What region of the diencephalon coordinates homeostasis? a. thalamus b. epithalamus c. hypothalamus d. subthalamus |
c. hypothalamus |
|
|
20. What level of the brain stem is the major input to the cerebellum? a. midbrain b. pons c. medulla d. spinal cord |
b. pons |
|
|
21. What region of the spinal cord contains motor neurons that direct the movement of skeletal muscles? a. anterior horn b. posterior horn c. lateral horn d. alar plate |
a. anterior horn |
|
|
22. Brodmann’s areas map different regions of the ________ to particular functions. a. cerebellum b. cerebral cortex c. basal forebrain d. corpus callosum |
b. cerebral cortex |
|
|
23. What blood vessel enters the cranium to supply the brain with fresh, oxygenated blood? a. common carotid artery b. jugular vein c. internal carotid artery d. aorta |
c. internal carotid artery |
|
|
24. Which layer of the meninges surrounds and supports the sinuses that form the route through which blood drains from the CNS? a. dura mater b. arachnoid mater c. subarachnoid d. pia mater |
a. dura mater |
|
|
25. What type of glial cell is responsible for filtering blood to produce CSF at the choroid plexus? a. ependymal cell b. astrocyte c. oligodendrocyte d. Schwann cell |
a. ependymal cell |
|
|
26. Which portion of the ventricular system is found within the diencephalon? a. lateral ventricles b. third ventricle c. cerebral aqueduct d. fourth ventricle |
b. third ventricle |
|
|
27. What condition causes a stroke? a. inflammation of meninges b. lumbar puncture c. infection of cerebral spinal fluid d. disruption of blood to the brain |
d. disruption of blood to the brain |
|
|
28. What type of ganglion contains neurons that control homeostatic mechanisms of the body? a. sensory ganglion b. dorsal root ganglion c. autonomic ganglion d. cranial nerve ganglion |
c. autonomic ganglion |
|
|
29. Which ganglion is responsible for cutaneous sensations of the face? a. otic ganglion b. vestibular ganglion c. geniculate ganglion d. trigeminal ganglion |
d. trigeminal ganglion |
|
|
30. What is the name for a bundle of axons within a nerve? a. fascicle b. tract c. nerve root d. epineurium |
a. fascicle |
|
|
31. Which cranial nerve does not control functions in the head and neck? a. olfactory b. trochlear c. glossopharyngeal d. vagus |
d. vagus |
|
|
32. Which of these structures is not under direct control of the peripheral nervous system? a. trigeminal ganglion b. gastric plexus c. sympathetic chain ganglia d. cervical plexus |
b. gastric plexus |

