![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
89 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
2 parts of the cranium
|
Neurocranium (cranial vault)
Viscerocranium (facial skeleton) |
|
|
|
Dome-like roof of neurocranium (a.k.a. skullcap)
|
Calvaria
|
|
|
|
Floor of neurocranium (a.k.a. basicranium)
|
Cranial Base
|
|
|
|
8 bones of the neurocranium:
|
frontal
ethmoidal (only a minor contribution, this is mostly a part of the viscerocranium) sphenoidal occipital temporal (x2) parietal (x2) |
|
|
|
The 3 bones forming the calvaria, the _______, _______, and _______ are primarily _______ bones.
|
frontal
temporal parietal flat |
|
|
|
2 bones that connect via hyaline cartilage (synchondroses) in childhood
|
sphenoid
occipital |
|
|
|
Opening in the cranial base where the spinal cord and brain are continuous
|
Foramen Magnum
|
|
|
|
The viscerocranium consists of 15 _______ bones. Name them.
|
Irregular
Mandible Ethmoid Vomer Maxilla (x2) Inferior nasal concha (x2) Zygomatic (x2) Palatine (x2) Nasal (x2) Lacrimal (x2) |
|
|
|
Bones that house the teeth.
|
Maxillae & Mandible
|
|
|
|
Where the mandible articulates with the cranial base.
|
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
|
|
|
|
4 Pneumatized bones
|
frontal
temporal sphenoid ethmoid |
|
|
|
Smooth, slightly depressed area between superciliary arches
|
Glabella
|
|
|
|
Upper rim of eye socket, just superior to the supraorbital margin, a prominence deep to the eyebrows.
|
Supraciliary arches
|
|
|
|
Intersection of the frontal and nasal bones. Is usually depressed.
|
Nasion
|
|
|
|
"Cheek bones"
|
Zygomatic
|
|
|
|
"bridge of the nose"
|
Nasion
|
|
|
|
Pear-shaped anterior opening in the cranium.
|
Piriform aperture
|
|
|
|
The _______ divides the nasal cavity into right and left spaces. The _______ are curved bony plates on the lateral wall of each cavity.
|
Nasal septum, nasal conchae
|
|
|
|
6 empty spaces of the skull.
|
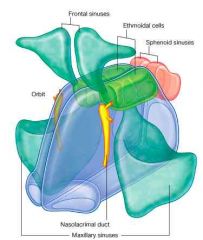
frontal sinuses, ethmoidal cell, sphenoid sinuses, nasolacromial duct, orbit, maxillary sinuses
|
|
|
|
3 suture boundaries.
|
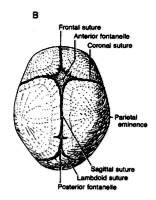
Sagittal (parietal) --> "the archer"
Coronal (frontoparietal) Lambdoid (occipitoparietal) |
|
|
|
Five layers of the scalp
|
Skin
Connective tissue Aponeurosis Loose connective tissue Periosteum of calvaria |
mnemonic "SCALP"
|
|
|
Cranium = Skull - _____________
|
Mandible
|
|
|
|
The scalp has the greatest concentration of hair and ________ glands in the whole body.
|
Sebaceous
|
|
|
|
3 unpaired midline _________ bones make up the base of the neurocranium. Name them.
|
endochondral
1.) ethmoid (anterior) 2.) sphenoid (central) 3.) occipital (posterior) |
|
|
|
Paired lateral dermal (intramembranous) bones form the ________. Name them.
|
Calvarium
1.) Frontal (anterolateral) 2.) Temporal (lateral) 3.) Parietal (superior/posteriolateral) |
|
|
|
Bone, name means "the wall"
|
Parietal bone
|
|
|
|
Bone, name means "Time"
|
Temporal ("timekeeper" --> where white hair grows)
|
|
|
|
4 Diploic vein trunks
|
occipital
posterior temporal anterior temporal frontal |
|
|
|
2 synovial joints of the cranium
|
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
Alanto-occipital joint |
|
|
|
Squamous bones form via ____________
|
Intramembranous ossification
|
|
|
|
6 childhood fontanelles (shape and locations)
|
Anterior (diamond)
Posterior (triangular) Anterolateral (a.k.a. "Sphenoidal") --> located at the pterion. Posterolateral (a.k.a. "Mastoid") |
|
|
|
6 Childhood fontanelles
|
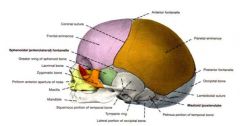
anterior, posterior, sphenoidal (x2), mastoid (x2)
|
|
|
|
Bony plates consist of compact inner and outer ______ separated by cancellous ______.
|
tables, diploe
(think corrugated cardboard) |
|
|
|
Smooth prominence immediately superior to bridge of nose (aka nasion).
|
Glabella
|
|
|
|
Point at which the supraorbital artery and nerve leave the orbit and run onto the forehead.
|
Supraorbital notch (foramen)
|
|
|
|
4 frontal bone landmarks
|
Glabella
Superciliary crest Supraorbital notch Supraorbital margin (& ridge) |
|
|
|
More pronounced in men and monkeys (prevents them from wearing their face off when they chew).
|
Supraorbital margin (& ridge)
|
|
|
|
Lies immediately posterior to the articular tubercle. The two form an articular surface for mandible.
|
Condylar notch
|
|
|
|
Temporal bone landmarks
|
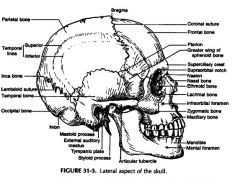
Articular tubercle
Condylar notch Tympanic plate External auditory meatus Mastoid process Supramastoid crest (continuance of zygomatic arch) Styloid process |
|
|
|
The _______, a surgical landmark for the mastoid antrum, is made up of the ______ spine and ______ crest.
|
small suprameatal triangle
suprameatal supramastoid |
|
|
|
The Zygomatic Arch becomes the __________ which continues laterally and superiorly to become the _______, which is the point of origin for the ______ muscle.
|
supramastoid crest
temporal line temporalis |
|
|
|
The _________ is the long, pointy thing that projects from the base of the cranium inferior to the ____________. It is a remnant of the ___________.
|
styloid process
external auditory meatus second branchial arch |
|
|
|
2 Ligaments from the styloid process:
|
stylohyoid
stylomandibular |
|
|
|
Mastoid process is found _________ to the styloid process.
|
posterolateral
|
|
|
|
2 muscles insert into the posterolateral aspect of the mastoid process.
|
splenius capitis
longissimus capitis |
|
|
|
Mastoid air cells communicate with the middle ear cavity through the __________.
|
Mastoid antrum
|
|
|
|
This stout part of the skull is not present at birth.
|
Mastoid process
|
|
|
|
Fills the gap between the squamous portion of temporal bone and frontal bone.
|
Greater wing of sphenoid bone.
|
|
|
|
H-shape suture, junction of sphenoid, parietal, frontal, and temporal.
|
Pterion (remember: where "Hermes" had his wings)
|
|
|
|
The pterion is the location of the ___________ in children.
|
Anterolateral fontanelle
|
|
|
|
_________ processes arise from the inferior surface of the greater wing of the sphenoid bone.
|
Pterygoid
|
|
|
|
The ______ and _______ extend along the posterior sagittal plane to the foramen magnum. The _______ attach to the occipital bone along this line.
|
external occipital protuberance (inion)
external occipital crest ligamentum nuchae |
|
|
|
The superior nuchal line connects the _____ with the ______ and gives origin to the ______ muscle.
|
inion
mastoid process trapezius muscle |
|
|
|
The inferior nuchal line divides the insertions of the ______ muscle from the insertion of the ______ muscle
|
splenius capitis
posterior rectus capitis |
|
|
|
The highest nuchal line provides origin for the ______ muscle.
|
occipital belly of the occipitofrontalis muscle
|
|
|
|
The ______ is the point at which the sagittal and coronal sutures meet. It is the location of the ______ in children.
|
Bregma
Anterior fontanelle |
|
|
|
The ______ is the point at which the sagittal and lamboid sutures meet. It is the location of the _____ in children.
|
Lambda
Posterior fontanelle |
|
|
|
Sutural bones (a.k.a. ______) (tiny bones that form in sutures) are most common in the ______ suture.
|
lamboid, wormian, or Incan bones
lamboid |
|
|
|
The ______ portions of the temporal bones consist of two columns of dense bone that abut the anterolateral edges of the basal part of the occipital bone.
|
Petrous
|
|
|
|
The infratemporal fossa is formed by the ______ and ______. It is bound by the _____ and _________ laterally and the _______ posteriorly.
|
Greater wing of sphenoid bone
Squamous portion of temporal bone Zygomatic arch Mandible Mastoid process |
|
|
|
The infraorbital fissure lies between _______ and _________ and transmits _______.
|
Greater wing of the sphenoid
Maxilla Infraorbital branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V2) & infraorbital vessels |
|
|
|
The ______, which arise from _______ form the lateral boundaries of the nasal choanae.
|
Pterygoid processes
Greater wing of the sphenoid bone |
|
|
|
5 Components of pterygoid process
|
Medial plate
Hamulus Lateral plate Scaphoid fossa Pterygopalatine fossa |
|
|
|
The medial pterygoid plate gives rise to the __________ and terminates in the _______.
|
Superior constrictor of the pharynx
Hamulus |
|
|
|
The hamulus functions as a trochlea for the tendon of the _______ muscle.
|
Tensor veli palatini
|
|
|
|
The lateral pterygoid plate gives rise to ______.
|
Pterygoid muscles (lateral and medial)
|
|
|
|
Arteries and nerves gain access to the nasal cavity, palate, orbit and face via the __________. The _________ opens into this fossa.
|
Pterygopalatine fossa
Pterygomaxillary fissure |
|
|
|
Boundaries of the pterygomaxillary fissure.
|
Maxillary tuberosity (anterior)
Pterygoid process of sphenoid bone (posterior) Infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone (superiorly) Perpendicular plate of palatine bone (medially) |
|
|
|
3 foramina that lie along posterior border of sphenoid bone and their locations.
|
Pterygoid (vidian) canal (base of medial pterygoid plate)
Foramen ovale (anteromedial) Foramen spinosum (posterolateral) |
|
|
|
The pterygoid (vidian) canal lies at the base of the ______ and caries the ____ nerve (which made up of the ______ nerve and _____ nerve conjoined) to the ________.
|
Medial pterygoid plate
Vidian nerve (a.k.a. nerve of the pterygoid canal) greater superficial petrosal deep petrosal pterygopalatine fossa |
|
|
|
5 things that pass through the foramen ovale
|
Mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V3)
Accessory meningeal artery lesser superficial petrosal nerve recurrent meningeal branch of trigeminal nerve emissary vein |
|
|
|
What passes through the foramen spinosum
|
Middle meningeal artery
|
|
|
|
Fracture of skull that passes through foramen spinosum may result in _____ hematoma or ______ hemorrhage due to the severing of ________.
|
epidural
extracranial middle meningeal artery |
|
|
|
Three rows (name them) of foramina can be found **here** in the temporal bone.
|
1.) lateral row, 2.) intermediate row, 3.) medial row.
**petrous portion and adjacent edges of the squamous portion. |
|
|
|
The lateral row of foramina lies along the _____ edge of the ______ portion of the temporal bone. Name the three components.
|
anterior
petrous 1.) middle ear cleft 2.) tympanic plate 3.) mastoid process |
|
|
|
The tympanic plate forms the vertical _____ wall of the _______.
|
anterior
external auditory meatus |
|
|
|
The middle ear cleft continues anteriorly as the ________. The bony portion emerges from the _______.
|
tympanic (auditory, eustachian) tube
tympanic plate |
|
|
|
The mastoid process is groved on its medial side for the _____ muscle and _____ artery.
|
digastric
occipital |
|
|
|
The intermediate row lies ______ in the petrous portion of the temporal bone. Name the three components.
|
central
1.) Petrosquamous (tympanosquamosal) fissure (and its medial portion, the petrotympanic fissure) 2.) Stylomastoid foramen 3.) Styloid process |
|
|
|
The petrosquamous fissure lies between the ______ and _____ portions of the ______ bone. Its medial portion, the ______ fissure transmits the _______ nerve.
|
petrous
squamous temporal petrotympanic chorda tympani |
|
|
|
The stylomastoid foramen lies between the _____ and ____ processes. It is the termination of the _____ and transmits the ____ nerve (CN ___)
|
mastoid
styloid facial canal facial VII |
|
|
|
The shaft of the styloid process gives origin to 3 muscles and 2 ligaments. Name them.
|
Stylohoid muscle
Stylopharyngeus muscle Styloglossus muscle Stylomandibular ligament Stylohoid ligament |
|
|
|
The medial row lies along the ______ edge of the _____ portion of the temporal bone. Name the 3 components.
|
posterior
petrous 1.) foramen lacerum 2.) carotid canal 3.) jugular foramen |
|
|
|
The foramen lacerum results from superior and inferior defects in the _______. It separates the _____ bone from the _____ bone. The ______ is the only thing that passes through it.
|
carotid canal
petrous temporal bone sphenoid bone greater superficial petrosal nerve |
|
|
|
The jugular foramen runs _______ into the cranial cavity. Name the 4 things it transmits.
|
posteriorly
internal jugular vein glossopharyngeus nerve (CN IX) vagus nerve (CN X) spinal accesory (CN XI) nerves |
|
|
|
Name the two parts of the occipital bone.
|
Y-shaped basilar part (basi-occiput)
Squamous part (occipital squama) |
|
|
|
The Y-shaped basilar part of the occipital bone forms the anterior boundary of the _______. Paired occipital condyles articulate with _______.
|
foramen magnum
atlas |
|
|
|
The _______, at the _____ end of each occipital condyle transmits an emissary vein.
|
posterior condylar canal
posterolateral |
|
|
|
The ________ contributes to the posterior boundary of the foramen magnum. The ______, which lies ______ to the mastoid process transmits an emissary vein.
|
occipital squama
mastoid foramen immediatly posterior |
|

