![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
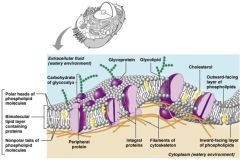
Label and recgonize fluid mosaic model
|
|
|
|
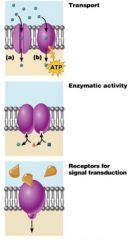
Functions for membrane proteins
|
|
|
|
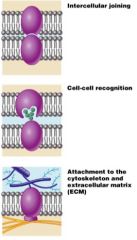
Function of membrane proteins 2
|
|
|
|
Name this membrane junction
|
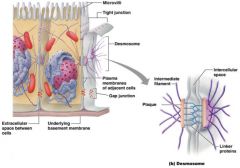
Desmosome
|
|
|
Name this membrane junction
|
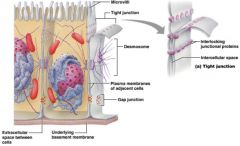
Tight Junction
|
|
|
Name this membrane junction
|
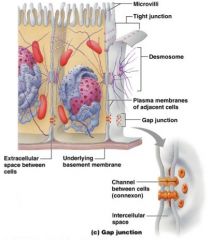
Gap Junction
|
|
|
Plasma membrane seperates __________ from _________
|
intracellular, extracellular
|
|
|
Fluid Mosaic
|
double bilayer of lipids with imbeded, dispersed protiens
|
|
|
Functions of Membrane Proteins
|
1) Transport
2) Enzymatic Activity 3) Receptors 4) Intracellular Adhesion 5) Cell-Cell Recognition 6) Attachment to extracellular Matrix |
|
|
________ are formed only in the __________ surface
|
Glycolipids, Cholesterol
|
|
|
_______% of all membrane lipids is ______
|
20, Cholesterol
|
|
|
Tight Junction
|
Impermeable junction that enters the cell
|
|
|
What junction contains the spot wield
|
Desmosome
|
|
|
Junction that allows chemical substance to pass
|
Gap Junction
|
|
|
Simple Diffusion
|
nonpolar and lipid solution substances
|
|
|
Simple Diffuses _______ through the _______ bilayer
|
Directly, Lipid
|
|
|
Diffusion known as Taxi Cab diffusion
|
Facilitated
|
|
|
Facilitated diffusion transports
|
glucose, amino acids, and ions
|
|
|
Facilitated diffusion binds _______ _______ or passes through ______ ________
|
carrier protons, protein channels
|
|
|
Draw diffusion through the plasma membrane
|
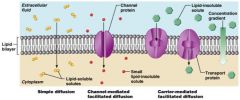
|
|
|
Osmosis occurs when _________ of a solution is different on _______ sides of the __________
|
concentration, opposite, membrane
|
|
|
Osmosis is the _______ of _______ across a semipermeable membrane
|
diffusion, water
|
|
|
Osmolarity
|
Total concentration of solute particles
|
|
|
________ is the process of water and solutes through a membrane by ________ _________
|
Filtration, Hydrostatic, Pressure
|
|
|
Solutions with the same solute concentration
|
Isotonic
|
|
|
Hypertonic solutions have _______ solute concentration
|
Greater
|
|
|
Hypotonic
|
Solutions having lesser solute then that of the cystol
|
|
|
Active Transport
|
Uses ATP to move solutes across a membran in the same direction
|
|
|
Hydrolysis of ATP phospohoylas to transport protiens
|
Primary Active Transport
|
|
|
Secondary Active Transport uses an exchange pump _________ to drive the transport of ______ _________
|
Indirectly, Other, Solutions
|

