![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cystology |
The study of cells |
|
|
Hystology |
The study of tissues |
|
|
Macroscopic Anatomy |
The study of structures that can be seen without magnification |
|
|
Surface anatomy |
Refers to the superficial anatomical markings |
|
|
Regional anatomy |
Refers to all structures in a specific area of the body, ( head, neck etc.) |
|
|
Systemic anatomy |
The study of the organ systems of the body ( digestive system, cardiovascular system etc.) |
|
|
Developmental anatomy |
Examines structural changes over time. Embryology is the study of early developmental stages |
|
|
Comparative anatomy |
Considers anatomical similarities and differences in different types of animals |
|
|
Clinical anatomy |
Focuses on pathological changes during illness |
|
|
Surgical anatomy |
Studies anatomical landmarks important for surgical procedures |
|
|
Radiographic anatomy |
The study of anatomical structures with the use of x-rays or ultrasound scans on an intact body |
|
|
Cross sectional anatomy |
The use of radiographic techniques (ct MRI and spirals scans) to look at cross sections of the body |
|
|
Levels of organization |
1 Chemical molecular 2 cell 3 tissue 4 organ 5 organ system 6 organism |
|
|
Chemical molecular |
Four of them make up 99% of the body which are hydrogen oxygen carbon and nitrogen |
|
|
Major classes of compounds |
Water carbohydrates proteins and lipids |
|
|
Cell |
The smallest living unit in the body it consists of organelles |
|
|
Tissue |
Many cells and some surrounding material such as epithelial muscular neural and connective tissue |
|
|
Organ |
Combination of tissues for example the heart consist of all the above mentioned tissues |
|
|
Organ system |
Combination of various organs specific system |
|
|
Organ system |
Integumentary system, skeletal system, muscular system, nervous system, endocrine system, cardiovascular system. |
|
|
Integumentary system |
protection from environmental hazards and temperature control |
|
|
Skeletal system |
Support, protection of soft tissues, mineral storage, blood formation. |
|
|
Nervous system |
Directing immediate responses to stimuli, usually by coordinating the activities of other organ systems. |
|
|
Endocrine system |
Directing long-term changes indie activities of other organ systems |
|
|
Cardiovascular system |
Internal transport of cells and dissolved materials, including nutrients, waste, and gases |
|
|
Lymphatic system |
Defense against infection and disease |
|
|
Respiratory system |
Delivery of air to sites where gas exchange can occur between the air and circulating blood |
|
|
Digestive system |
Processing of food and absorption of organic nutrients, minerals, vitamins, and water. |
|
|
Urinary system |
Elimination of excess water, salts, and waste products. control of pH |
|
|
Reproductive system |
Production of sex cells and hormones. |
|
|
Responsiveness |
The ability to respond to changes |
|
|
Adaptability |
The ability to make adjustments to environmental changes |
|
|
Growth |
The increase in size of an organism |
|
|
Differentiation |
Becoming specialized to perform particular functions |
|
|
Reproduction |
The production of new generations of the same organism |
|
|
Movement |
Return of movement is the movement of food or blood, external movement is walking |
|
|
Metabolism |
All the chemical reactions in the body |
|
|
Anabolism |
Does synthesis of complex molecules |
|
|
Catabolism |
The breakdown of complex molecules |
|
|
Absorption |
The process of bringing chemicals into the body |
|
|
Respiration |
The absorption, transport, and use of oxygen by cells |
|
|
Digestion |
The processes of catabolism that make nutrients small enough to be absorbed |
|
|
Excretion |
The removal of waste |
|
|
Supine |
Lying down face up in the anatomical position |
|
|
Prone |
Lying down face down in the anatomical position |
|
|
Anatomical areas |
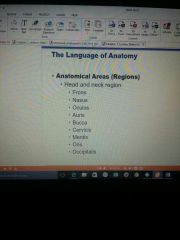
|
|
|
Anatomical areas |
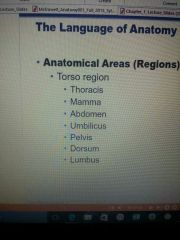
|
|
|
Anatomical areas |
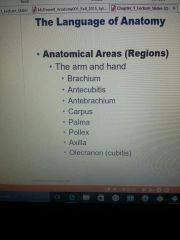
|
|
|
Anatomical areas |
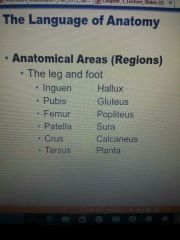
|
|
|
Anatomical regions |
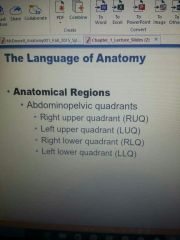
RUQ: most of the liver, gallbladder. LUQ: most of the stomach, spleen RLQ: cecum, appendix, right ureter, right ovary, right spermatic cord. LLQ: left ureter, left ovary, left spermatic cord. |
|
|
anatomical regions |
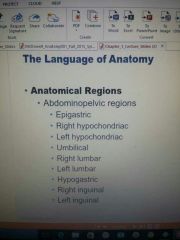
|
|
|
Anatomical directions |
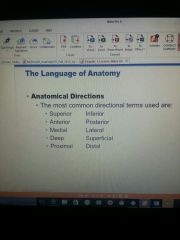
|
|
|
Sectional anatomy |
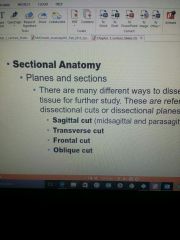
|

