![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
towards the nose or forehead and is higher in reference to the bottom of the brain |
rostral |
|
|
|
toward the tail or the back where the spinal cord is |
caudal |
|
|
|
three principle parts of the brain |
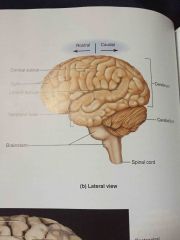
cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem |
80%, 10%, and 10% |
|
|
80% of the brain at the top |
cerebrum |
|
|
|
10% at the base of the brain |
cerebellum |
balance and your name |
|
|
10% at the very bottom of the brain |
brainstem |
base of the brain that sticks out |
|
|
half globes making up the cerebrum |
cerebral hemispheres |
remember hemispheres and globes in terms to a globe map |
|
|
hills or the part that goes up in the brain |
gyri |
|
|
|
the valleys or parts that dip in |
sulci |
|
|
|
separates the cerebrum into different hemispheres up and down |
longitudinal fissures |
long line up and down |
|
|
separate the cerebrum from the cerebellum |
transferred cerebral fissures |
|
|
|
structure that runs thru the middle of the brain to separate left and right fissure |
corpus collosum |
large or colossal |
|
|
area mostly made of neuron soma and dendrites that is outside the brain |
gray matter |
|
|
|
a cluster of gray matter inside the brain |
nuclei |
|
|
|
areas of matter that, when in the brain, are called this |
tracts |
a pathway |
|
|
three meninges in the brain |
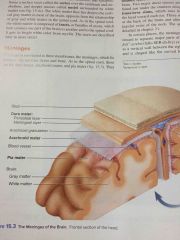
dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater |
same as in spinal cord gentle mater spiderweb consistency pia mater |
|
|
meninges between the brain and the skull |
dura mater |
tough mother |
|
|
meninge that is pushing against the spinal cord |
pia mater |
gentle mother |
|
|
where the dura mater goes inward down into the longitudinal fissure |
falx cerebri |
sickle-shaped |
|
|
where the dura mater goes in between the cerebellum and the rest of the brain |
tentorium cerebelli |
like a tent covering the brain |
|
|
four ventricles of the brain |
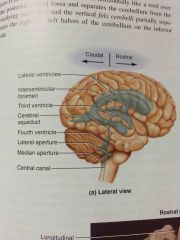
2 lateral ventricles, 3rd ventricle, and the 4th ventricle |
|
|
|
connects the 2 lateral ventricles to the 3rd ventricles |
interventricular foramen |
intertwined in the ventricle |
|
|
connects the third ventricle to the 4th ventricle |
cerebral aqueduct |
water duct between 3 and 4 |
|
|
connects the 4th ventricle to the spinal cord |
central canal |
main pathway |
|
|
filtered from blood from the choroid plexus |
CSF |
fluid in the spinal cord |
|
|
how does CSF flow into the brain? |
the heart beats, pushing the blood into it |
|
|
|
space where the CSF is reabsorbed |
subarachnoid space |
in the arachnoid space |
|
|
the 3 functions of the CSF |
buoyancy, protective insulation, chemical regulation |
star cells |
|
|
The BBB is made of ____. |
astrocytes |
|
|
|
keeps out harmful bacteria in blood from getting into the brain |
BBB |
|
|
|
what chemicals can pass thru the BBB? |
H2O, O2, CO2, alcohol, and nicotine as well as some helpful medicines |
|
|
|
bottom inch of the brain stem |
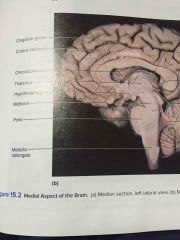
medulla oblongata |
|
|
|
two baseball bat shaped figures on the medulla oblongata |
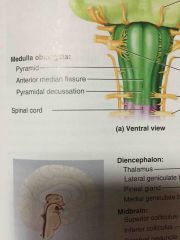
pyramids |
heart control, BP control, breathing, and coughing, sneezing, or puking |
|
|
functions of the medulla oblongata |
cardiac control, vasometer control, respiratory control, and reflexes |
|
|
|
bulges on the medulla oblongata lateral to the pyramids |
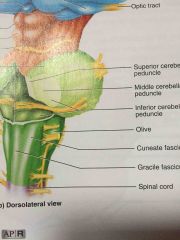
olives |
|
|
|
middle inch of the brainstem |
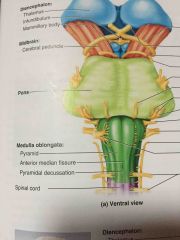
pons |
large, middle, and small |
|
|
three parts of the pons |
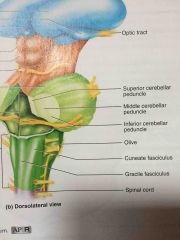
superior, middle, and inferior cerebellar peduncle |
|
|
|
functions of the pons |
sleep, respiration, and bladder control |
middle of the brain |
|
|
last inch of the brainstem |
midbrain |
|
|
|
upper colliculi for visual reflexes |
superior colliculu |
|
|
|
colliculi for auditory reflexes |
inferior colliculi |
4 |
|
|
superior and inferior colliculi both make up the _____ |
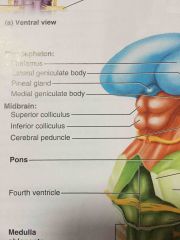
corpora quadrigemina |
substantial niagra falls |
|
|
part of the midbrain that is a dark or gray nucleus that relays inhibitory signals to the thalamus and the basal nuclei |
substantia nigra |
retina forming |
|
|
loose organized network of many nuclei that involves many parts of brain to perform a function |
reticular formation |
|
|
|
function of the reticular formation |
habituation |
habits, or repeating of an action |
|
|
learning to ignore repetitive stimuli, while remaining sensitive to others |
habituation |
|
|
|
two hemispheres diving the cerebellum down the middle |
cerebellar hemispheres |
|
|
|
worm-like structure between two lobes |
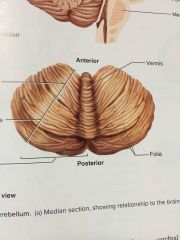
vermis |
tree of life |
|
|
white matter that runs into the brain like a tree |
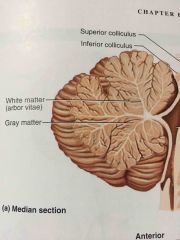
arbor vitae |
great comparator |
|
|
function of the cerebellum |
ensuring muscles are acting as necessary |
|
|
|
dumbbell shaped gateway to the cerebral cortex right in the middle of the brain |
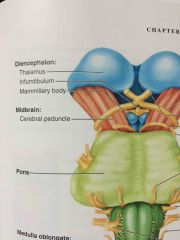
thalamus |
|
|
|
relay station for all messages coming in from the spinal cord to be processed |
thalamus |
|
|
|
emotional brain |
thalamus |
|
|
|
below the thalamus |
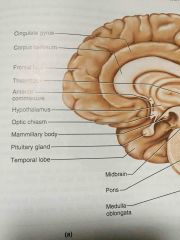
hypothalamus |
PITFO |
|
|
stalk that attaches pituitary gland to the hypothalamus |
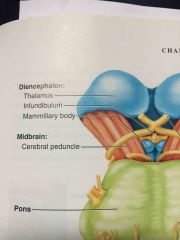
infundibulum |
|
|
|
five lobes of the cerebrum |
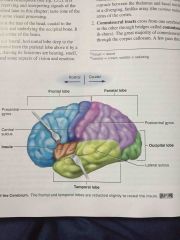
parietal, insula, temporal, frontal, occipital |
|
|
|
three fiber tracts in the white matter of the cerebrum |
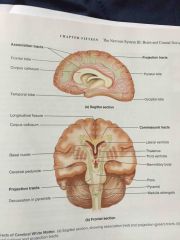
projection, commissural, association |
|
|
|
vertical fiber tract that connects the cerebrum to be lower brain and spinal cord |
projection tract |
|
|
|
horizontal fiber tract that connects the two hemispheres of the cerebrum |
commissural |
|
|
|
fiber tract that runs back and forth within a hemisphere |
association tract |
|
|
|
two types of neurons in the central cortex |
stellate and pyramidal cells |
|
|
|
neurons that carry messages amongst themselves |
stellate cells |
|
|
|
neurons that carry messages from cortex to white matter inside the brain |
pyramidal cells |
|
|
|
the outer layer of the the cerebrum where most of the brain matter is |
cerebral cortex |
emotional brain |
|
|
neocortex has ___ layers |
six |
|
|
|
system where there is clusters of gray matter that perform a function that is scattered around the brain |
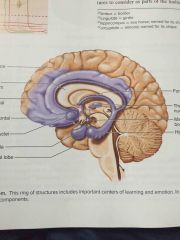
limbic system |
|
|
|
names of the 3 basal nuclei |
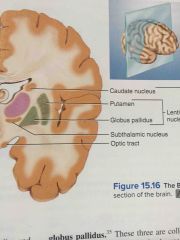
caudate, putamen, and globus pallidus |
large movement |
|
|
located where some of the gray matter is deep inside the brain |
basal nuclei |
main cortex |
|
|
basal nuclei are involved with _____ control |
motor |
|
|
|
areas where cells interpret certain stimuli into senses |
primary cortex |
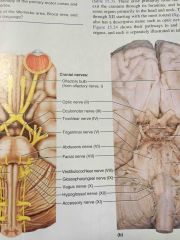
Old Opie Occasionally Tries Trig And Feels Very Gloomy Vague And Hypoactive |
|
|
areas where there is associating of an image being sense in order to interpret the stimuli |
association area |
|
|
|
12 pairs of cranial nerves |
Olfactory Optic Oculomotor Trochlear Tregeminal Abducens Facial Vestibulocochlear Glossopharyngeal Vagus Accessory Hypoglossal |
|

