![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
When embryonic connective tissue tissue (mesenchyme) differentiates into bone directly, it is considered ______
This is seen mainly in the _____ |
-Intramembranous ossification
-skull |
|
|
When embryonic connective tissue tissue (mesenchyme) differentiates into a hyaline cartilage model of bone, it is considered ________
Hyaline cartilage model then turns into _______ |
-endochondral ossification
-bone |
|
|
The skeletal and muscular system develop mainly from the (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm) of the embryo
|
mesoderm
|
|
|
During development, the mesoderm differentiates into what three parts on each side of the midline neural tube and notochord (from medial to lateral)
|
-paraxial mesoderm
-intermediate mesoderm -lateral plate mesoderm |
|
|
The _____ is a thickened band of mesoderm on each side of the neural tube. This becomes segmented into paired blocks of _____ which differentiate into spinal
|
-paraxial mesoderm
-somites |
|
|
The somite differentiates into what 4 parts and what do these turn into?
|
1) sclerotome (ventromedial) - contributes to vertebral column
2) epimere (dorsomedial myotome) - intrinsic back muscles 3) hypomere (dorsolateral myotome) - muscle of limbs and body wall 4) dermatome - skin |
|
|
_____ migrate medially to surround the neural tube and notochord to form 2 adjacent vertebrae
|
sclerotome
|
|
|
Describe how sclerotomes form a vertebrae:
Also, how are intervertebral discs formed? |
-caudal half of one sclerotome and cephalic half of sclerotome below form body of vertebra
-intervertebral discs form between these formed halves |
|
|
During development, _____ bridge the intervertebral discs
|
-myotomes
|
|
|
_____ results when half a vertebra is missing, which results in scoliosis
|
hemivertebra
|
|
|
Spina bifida is a defect in the ______
|
vertebral arches of adjacent vertebrae
|
|
|
______ is protrusion and/or defect of the spinal cord
______ is when the defect is not apparent and is covered by hair and/or pigmented skin |
-spina bifida systica
-spina bifida occulta |
|
|
Lateral plate mesoderm is divided into two layers by development of ______
What are these two divisions and what do they contribute to? |
-intraembryonic cavity
1) Somatic/parietal mesoderm - ventral and lateral body walls 2) Splanchnic/visceral mesoderm - gastrointestinal, respiratory, and other systems |
|
|
Somatic mesoderm migrate to form upper and lower _____ at approximately opposite segments of _____ and _____ respectively
|
-limb buds
-C5-T1 and L2-S3 |
|
|
Somatic mesoderm cells form _____ that undergo _______
|
-hyaline cartilage models
-endochonral ossification (give rise to bones of limbs) |
|
|
The ______ is a thickened ectoderm at the distal border of limb bud. This induces adjacent mesoderm to _____ while the more proximal mesoderm ______
|
-apical ectodermal ridge (AER)
-remain undifferentiated and proliferate rapidly *progress zone* -condenses and differentiates into hyaline cartilage models of bone |
|
|
Bone first starts to appear in the embryo at about ____ weeks and primary ossification centers are present by ____ week
|
-8
-12th |
|
|
In 6-week-old embryos, the termal portion of the limb flatten to form _____
|
handplates and footplates
|
|
|
Mesenchyme at handplates and footplates condense to form ______ and between these, the cells undergo ______ to separate fingers and toes from each other
|
-digital rays
-programmed cell death |
|
|
During the ____ week, the upper limbs rotates laterally and lower limbs rotate medially 90 degrees
|
7th
|
|
|
Total absence of one or more extremity is ____ while partial absence is _____
This could be caused by maternal digestion of _____ |
-amelia
-meromelia -thalidomide |
|
|
Extra fingers or toes is _____
|
polydactyly
|
|
|
Abnormal fusion of fingers and toes is _____
This is due to _____ |
-syndactyly
-failer of apoptosis between digital rays |
|
|
The skull is divided into what two parts?
|
-neurocranium - encloses, protects brain
-viscerocranium - forms skeletal face |
|
|
Neural crest cells is unique because:
|
it is ectoderm that gives rise to skeletal and connective tissues that only occurs in anterior portion of head and neck
|
|
|
The anterior portion of the skull develops from _____ and the posterior portion of skull develops from ______
|
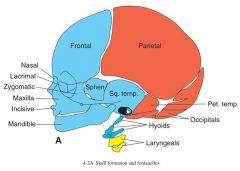
-paraxial mesoderm (red)
-neural crest cells (blue) |
|
|
The skull develops partly by ____ ossification and partly by _____ ossification
|
-intramembranous
-endochondral |
|
|
The flat bones forming the sides and roof of the neurocranium are the _____ which develops ______
The roof (skullcap) is the _____ |
-cranial vault
-intramembranously -calvaria |
|
|
The cranial base of the neurocranium is called the _______ because it develops mainly by _____
|
-chondrocranium
-endochondral ossification |
|
|
The _____ are important sites for growth of the skull, which undergo _____ growth
____ are wider areas where two or more bones meet |
-sutures
-appositional growth -fontanelles |
|
|
The _____ is the soft spot on a baby's head
|
anterior fontanelle
|
|
|
_____ is premature closure of one side of patients coronal and lambdoid sutures
|
plagiocephaly
|
|
|
_____ is premature fusion of the sutures which causes restricted growth and compensatory overgrowth on remaining open sutures
|
craniosynostosis
|
|
|
Most common craniosynostosis is ____, which is narrowing of the skull from premature sagittal suture
|
scaphocephaly
|
|
|
Craniosynostosis can results from ____ such as growth constraint of the fetal head by uterine malformation or triplet pregnancies. This usually results in a ____ forehead
|
-mechanical factors
-wedge shaped |
|
|
Mutations in _____ have been shown to cause syndromes involving craniosynostosis and limb deformities
|
fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs)
|
|
|
_____ is the most common, nonfatal form of dwarfism
This results in what type of features? |
-achondroplasia
-large cranial fault -small midface (due to abnormal chondrocranial growth) -short and bowed extremities -short fingers |
|
|
Skeletal muscle develops from the _____ of the ______
|
somites of the paraxial mesoderm
|
|
|
The hypomere (dorsolateral region of somites) is innervated by the _____ of spinal nerves
|
anterior rami
|
|
|
The epimere (dorsomedial region of somites) is innervated by the ____ of spinal nerves
|
posterior rami
|
|
|
The _____ divisions of the anterior rami innervate the flexor compartments of the upper extremity (musculocutaneous, median, and ulnar nerve)
The _____ divisions of the anterior rami innervate the extensor compartments of the extremities (radial nerve) |
-anterior
-posterior |
|
|
The _____ are innervated by the anterior rami and migrate to the superficial back muscles
|
hypomere
|
|
|
Skeletal muscles are (uninucleated/multinucleated)
|
multinucleated
|
|
|
Skeletal muscle fibers are formed by the fusion of percursor cells called ____
These form long multinucleated _____ and synthesis of contractile proteins |
-myoblasts
-myotubes |
|
|
Skeletal muscle fibers differentiate into different types largely due to:
|
-properties that innervate them
|
|
|
What are the three types of muscle fibers?
|
-slow oxidative (SO) (more numerous in postural muscles)
-fast oxidative glycolytic (FOG) - intermediate -fast glycolytic (FG) |
|
|
Partial or complete absence of the abdominal musculature results in _____
This usually results in urinary tract obstruction, which causes ______ which compresses the lungs resulting in _____ |
-prune belly syndrome
-oligohyramnios -pulmonary hypoplasia |

