![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
260 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
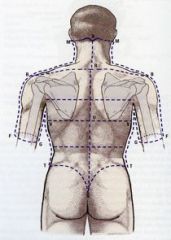
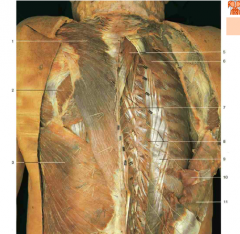
Identify parts of scapula and other key structures |
Occipital protuberance at point X, vertebra prominans (C-7) above point R, acromion process at rounded lateral end of scapula, spine at line separating acromion process, superior and inferior angles at medial corners of scapula, iliac crest at rounded lines above butt |
|
|
Deep Back Muscles |
Semispinalis Capitis, Splenius Capitis, Splenius Cervicis, and Erector Spinae (Spinalis (medial), longissimus, and Ileocostalis (lateral)) |
|
|
Denticulate Ligament |
Separates dorsal and ventral roots, made of pia, has 21 teeth, attaches spinal cord to dura |
|
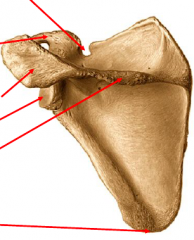
Label each arrow from top to bottom |
Suprascapular notch Coracoid process Acromial process (acromion) Glenoid cavity Spine Posterior angle |
|
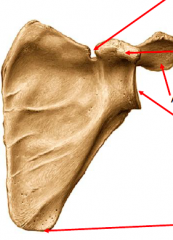
Label each arrow from top to bottom |
Suprascapular notch Coracoid process Acromial process (acromion) Glenoid cavity Anterior angle |
|

Posterior view of left humerus: label top to bottom |
Greater tuberosity Anatomic neck Surgical neck |
|
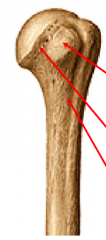
Anterior view of left humerus: label top to bottom |
Lesser tuberosity Anatomic neck Surgical neck |
|
|
Deltoid Actions |
Main action: Abduction of arm (humerus) after first 15 degrees.
Other actions: Flexion and medial rotation by anterior fibers and extension and lateral rotation by posterior fibers |
|
|
Deltoid Innervation |
Axillary nerve |
|
|
Deltoid Attachments |
Proximal attachments: Spine of scapula, acromion of scapula, and lateral one-third of clavicle
Distal Attachment: Deltoid tuberosity of humerus |
|
|
Teres Major Actions |
Medially rotates and adducts the arm Stabilizes shoulder joint |
|
|
Teres Major Innervation |
Lower subscapular nerve |
|
|
Teres Major Attachments |
Medial attachment: Inferior angle of scapula Lateral attachment: Humerus |
|
|
Teres Minor Actions |
Laterally rotates the arm and stabilizes the shoulder joint |
|
|
Teres Minor Innervation |
Axillary nerve |
|
|
Teres Minor Attachments |
Medial: scapula Lateral: Humerus |
|
|
Supraspinatus Action |
First 15 degrees of abduction of arm |
|
|
Supraspinatus Innervation |
Suprascapular nerve |
|
|
Supraspinatus Attachments |
Medial attachment: Scapula Lateral attachment: Humerus |
|
|
Infraspinatus Actions |
Lateral rotation of arm and stabilization of shoulder joint |
|
|
Infraspinatus Innervation |
Suprascapular nerve |
|
|
Infraspinatus Attachments |
Medial: scapula Lateral: Humerus |
|
|
Subscapularis Actions |
Adducts and medially rotates arm |
|
|
Subscapularis Innervation |
Upper and lower subscapular nerves |
|
|
Subscapularis Attachments |
Medial attachment: Scapula Lateral: Humerus |
|
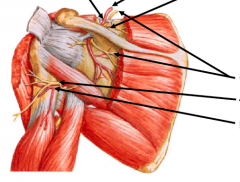
Bottom two arrows |
Axillary nerve Posterior circumflex humeral artery
This is the quadrangular space |
|
|
Muscles that elevate shoulder (scapula) |
Trapezius (upper) Levator scapulae Rhomboids |
|
|
Muscles that depress shoulder (scapula) |
Trapezius (lower) Pectoralis minor Subclavius |
|
|
Muscles that protract the shoulder (pull shoulders away from spine, like giving yourself a hug) |
Serratus anterior Pectoralis minor |
|
|
Muscles that retract the shoulder (pull shoulders back toward the spine) |
Trapezius Rhomboids Levator scapulae |
|
|
Muscles that flex the shoulder/arm (bring arm straight out in front of you and up like Hitler wave) |
Deltoid (anterior) Coracobrachialis Pectoralis major (clavicular) |
|
|
Muscles that extend the shoulder/arm (bring arm straight back behind you and up) |
Deltoid (posterior) Latissimus dorsi Teres major Pectoralis major (sternal) Subscapularis Teres minor Infraspinatus |
|
|
Muscles that internally (medially) rotate shoulder/arm |
Subscapularis Deltoid (anterior) Teres major Latissimus dorsi Pectoralis major |
|
|
Muscles that externally (laterally) rotate shoulder/arm |
Infraspinatus Teres minor Deltoid (posterior) |
|
|
Muscles that adduct (pull down) arm |
Pectoralis major (sternal) Latissimus dorsi Teres major Subscapularis Coracobrachialis |
|
|
Coracobrachialis Attachments |
Medial: Coracoid process of scapula Lateral: Humerus |
|
|
Coracobrachialis Innervation |
Musculocutaneous nerve |
|
|
Coracobrachialis Actions |
Flexes, medially rotates, and adducts shoulder/arm Stabilizes shoulder joint |
|
|
Muscles that abduct shoulder/arm |
First 15 degrees: Supraspinatus Next 75: Deltoid After 90: Trapezius, Serratus anterior |
|
|
Rotator Cuff Tear: Symptoms |
Can be complete or partial Pain and weakness of shoulder Clicking sounds on motion No pain at rest, but maybe during sleep depending on arm position |
|
|
Rotator Cuff Muscles |
Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres Minor Subscapularis
These are not the only muscles that rotate humerus; they hold humerus in glenoid fossa while they and other muscles perform rotation |
|
|
Acromioclavicular Joint |
AC Separation is common clinical problem
Joint made of acromioclavicular ligament, coracoacromial ligament, and coracoclavicular ligament |
|
|
Nipple dermatome |
T4 |
|
|
Basic Anatomy of Breast |
Modified sweat gland consisting of glandular tissue (15-20 lobules) and supporting fibrous tissue imbedded in a fatty matrix
Attached to dermis of skin by suspensory ligaments (of Cooper)
Goes from ribs 2 through 6, overlies 2/3 of pec major and 1/3 of serratus anterior
Axillary tail (of Spence) can seem like lump but is normal |
|
|
Lymphedema (CA) in breast |
Causes ligaments of Cooper to contract, causing peau d'orange sign on surface of skin |
|
|
Breast Innervation |
4th-6th intercostal nerves (sensory fibers to skin and sympathetic fibers to blood vessels and smooth muscle in skin and nipple) |
|
|
Breast Blood Supply |
Anterior and posterior intercostal arteries, lateral thoracic artery, and thoracoacromial trunk |
|
|
Lymphatic Drainage of Breast |
>75% from lateral breast quadrants drain into pectoral nodes Most remaining lymph drains to parasternal nodes or to opposite breast (but some from inferior quadrants can drain onto subdiaphragmatic inferior phrenic nodes) |
|
|
Sentinel Node |
First node that cancer cells invade from a primary tumor. Can be more than one sentinel node
Nodes can be detected using a radioactive marker, blue dye, or both to locate node/s for biopsy and staging |
|
|
Pectoralis Major Innervation |
Medial and lateral pectoral nerves (brachial plexus) |
|
|
Pectoralis Major Actions |
Flexes, adducts, and medially rotates humerus (arm) |
|
|
Pectoralis Major Attachments |
Clavicular head, sternocostal head, and humerus |
|
|
Pectoralis Minor Actions |
Pulls shoulder down and forward |
|
|
Pectoralis Minor Innervation |
Medial (and lateral) pectoral nerves (brachial plexus) |
|
|
Pectoralis Minor Attachments |
Superior: Coracoid process of scapula Inferior: Ribs 3 to 5 |
|
|
Clavipectoral Fascia |
Costocoracoid membrane of the clavipectoral fascia is pierced by lateral pectoral nerve |
|
|
Muscles that adduct and medially rotate the humerus ("chest thumping" muscles) |
Pectoralis major Subscapularis Teres major Latissimus dorsi (also extends) |
|
|
Serratus Anterior Actions |
Laterally rotates scapula and assists in raising arm above horizontal position |
|
|
Serratus Anterior Innervation |
Long thoracic nerve (brachial plexus) |
|
|
Serratus Anterior Attachments |
Anterior: Upper 8th or 9th ribs (covers lateral surface of thoracic wall) Posterior: Anterior surface of scapula along entire length of its medial border |
|
|
Result of injury to long thoracic nerve |
Winged scapula |
|
|
Brachial Plexus Functions |
Motor innervation to upper limb muscles Sensory innervation to skin & joints |
|
|
Brachial Plexus Definition |
Large network of nerves that originates in posterior triangle of neck by union of anterior (ventral) primary rami of C5-T1 spinal nerves (maybe also small contributions from T2 intercostal and/or C4) |
|
|
Dorsal scapular nerve |
m. Rhomboids and levator scapulae |
|
|
Long thoracic nerve |
m. Serratus anterior |
|
|
Nerve to subclavius |
m. Subclavius |
|
|
Suprascapular nerve |
m. Supraspinatus and infraspinatus |
|
|
Lateral pectoral nerve |
m. Pectoralis major (minor) |
|
|
Upper subscapular nerve |
m. Subscapularis |
|
|
Lower subscapular nerve |
m. Subscapularis and Teres major |
|
|
Thoracodorsal nerve |
m. Latissimus dorsi |
|
|
Medial pectoral nerve |
m. Pectoralis major and minor |
|
|
Medial brachial cutaneous nerve |
s. Skin medial arm |
|
|
Medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve |
s. Skin medial forearm |
|
|
Axillary nerve |
Innervated by C5 and C6
Terminal branch of posterior cord
Passes to posterior arm through quadrangular space, then winds around surgical neck of humerus; injuries here in dislocation of shoulder produce loss of abduction at the shoulder
m. Deltoid and Teres minor s. Upper lateral arm skin |
|
|
Radial nerve |
Innervated by C5-C8, T1
Descends posterior to axillary artery, enters arm between long and medial head of triceps in radial groove
m. Extensors (posterior part) of the arm and forearm s. Posterior arm, forearm, and hand skin |
|
|
musculocutaneous nerve |
Innervated by C5, C6, and C7
Continuation of lateral cord, pierces coracobrachialis then descends between Biceps brachii and Brachialis
m. Flexors of the arm (BBC: Biceps brachii muscle, Brachialis muscle, and Coracobrachialis muscle) s. Lateral forearm skin |
|
|
Median nerve |
Innervated by C5, C6, C7, C8, and T1
Formed by union of contributions from lateral and medial cords: Lateral root (C5, C6, C7) is branch of lateral cord and Medial root (C8, T1) is branch of medial cord; join to form median nerve
Located lateral to axillary artery in brachium
m. All but 1 1/2 flexors of forearm and 4 1/2 intrinsic muscles of hand (Laborer's nerve) s. Lateral palm and 3 1/2 digits skin
No innervation in shoulder or arm! |
|
|
Ulnar nerve |
Innervated by C7, C8, T1
Goes down medial side of arm then goes posterior to Medial Epicondyle of humerus to enter forearm
m. 1 1/2 flexors forearm and all but 4 1/2 intrinsic muscles of hand (Musician's nerve) s. Medial palm and 1 1/2 digits skin
No innervation in shoulder and axilla |
|
|
Lateral cord (brachial plexus) |
Formed by union of anterior divisions of upper (C5 and C6) and middle (C7) trunk |
|
|
Medial cord (brachial plexus) |
Formed by anterior division of lower trunk (C8 and T1) |
|
|
Posterior cord (brachial plexus) |
Formed by union of posterior divisions of all three trunks |
|
|
Supraclavicular part of brachial plexus |
Roots (rami) of C5, C6, C7, C8, and T1 emerge from vertebral column between Scalenus Anterior and Scalenus Medius to form upper, middle, and lower trunks of plexus
Trunks C5 and C6 = upper C7 = middle C8 and T1 = lower
|
|
|
Clavicular part of brachial plexus |
Crossing under clavicle along with subclavian artery and over the first rib, each trunk splits into 3 anterior divisions and 3 posterior divisions |
|
|
Infraclavicular part |
Divisions reassemble to form 3 cords (lateral, medial, and posterior) |
|
|
The more distal the upper limb musculature, the more ___________ is the segmental supply |
inferior.
Ex: Intrinsic muscles in hand primarily innervated by T1 |
|
|
Erb-Duchenne Paralysis: Damage to upper trunk of brachial plexus (C5, C6) |
Causes: Excessive stretch of neck of newborn during birth, which can tear upper trunk at its root (rami) OR in adult, blow to or fall on shoulder disrupts suprascapular nerve, nerve to subclavius, and most of axillary and musculocutaneous nerves
Effect: Patient loses shoulder movement and sensation to lateral aspect of arm |
|
|
Waiter's Tip position: upper trunk lesion: Arm just droops and hangs by side. medially rotated elbow extended shoulder adducted forearm pronated What's the damage? |
Loss of lateral rotation of shoulder = paralysis of teres minor and infraspinatus
Loss of flexion at elbow = paralysis of biceps brachii, brachialis, and brachioradialis
Loss of shoulder abduction = paralysis of deltoid and supraspinatus
Loss of flexion of shoulder = paralysis of coracobrachialis and biceps brachii (weak flexor)
Loss of depression of clavicle: paralysis of subclavius |
|
|
Chronic microtrauma of upper trunk: Backpacker's Palsy |
Carrying a heavy backpack for an extended time period can cause motor spasms and sensory deficits in distribution of musculocutaneous and radial nerves. |
|
|
Chronic microtrauma of upper trunk: Brachial plexus neuropathy |
sudden onset, usually at night, of severe pain around shoulder followed by muscle weakness/atrophy. If etiology is a neuritis (inflammation) it may be precipitated by upper respiratory infections, vaccinations, non-specific trauma |
|
|
Klumpke's Paralysis: Damage to Lower Trunk (C8 and T1): Mechanisms of injury/disfunction |
1) Traction injuries caused by excessive abduction of arm (like person falling from a height and grabbing something to save themselves)
T1 is damaged, which affects ulnar and median nerves, which affect small muscles of hand, producing hand that has clawed appearance
2) Can be caused by presence of cervical rib compressing lower trunk or compression caused by malignant metastasis from lungs via deep cervical lymph nodes
Loss of part of median and most of ulnar nerve supplying hand. Also will produce anesthesia on medial side of arm, forearm, and in hand on medial two fingers |
|
|
Injuries to Radial Nerve |
At axilla: Crutch paralysis where nerve is compressed, producing "Saturday Night" palsy
At radial groove: Fracture of shaft/Compression of nerve
Effects: Paralysis of triceps = loss of extension at elbow Paralysis of extensors of wrist = WRIST-DROP Paralysis of supinator and brachioradialis, but biceps compensate to allow supination Sensory loss over small area on lateral part of dorsum of hand
|
|
|
Dural Sac |
encases dura mater and everything within (arachnoid mater, subarachnoid space, pia mater, and spinal cord). Ends at S2 |
|
|
epidural (extradural) space |
space outside of dural sac (between spinal cord and vertebral column) |
|
|
Erector Spinae Action |
Stablize vertebral column |
|
|
Erector Spinae Attachments |
3 parts, attached to transverse and spinous processes. Most lateral to most medial: Iliocostalis (also attached to ileum), longissiumus (also attached to mastoid process of temporal bone), spinalis (I love sex) |
|
|
Intermediate Back Muscles |
Serratus Posterior (Superior and Inferior) |
|
|
Vertebral Ligaments |
From posterior to anterior of spinal cord:
1) Supraspinous ligament runs along edge of spinous processes. 2) Interspinous ligament runs between spinous processes 3) We hit lamina, transverse processes, and pedicles 4) Ligamenta flavum along posterior edge of foramena 5) Posterior longitudinal ligament along anterior edge of foramena 6) Vertebral bodies 7) Anterior longitudinal ligament |
|
|
Latissimus Dorsi Action |
Action: twisting, rotation; extends, adducts (pulls back) & medially rotates the arm |
|
|
Latissimus Dorsi Attachments |
Medial attachments: Spines of vertebrae T7 to T12, iliac crest, and ribs 9 to 12 Lateral attachment: Humerus |
|
|
Latissimus Dorsi Blood Supply |
Thoracodorsal artery |
|
|
Latissimus Dorsi Innervation |
Thoracodorsal nerve |
|
|
Levator Scapulae Action |
Pulls scapula medially and upward. Allows you to pull shoulders back, like rhomboids |
|
|
Levator Scapulae Attachments |
Superior: Transverse processes of upper four cervical vertebrae Inferior: Superior angle of scapula |
|
|
Levator Scapulae Blood Supply |
Dorsal scapular artery |
|
|
Levator Scapulae Innervation |
C3, C4, and C5 (dorsal scapular nerve) |
|
|
ligamenta flava |
connect the laminae of adjacent vertebrae on the posterior side of the spinal cord, anterior to spinal processes |
|
|
Parts of Intervertebral Disc |
1) Nucleus pulposus (center of disc) 2) Annulus Fibrosus (outer area of disc) |
|
|
pia mater |
directly encases spinal cord |
|
|
Rhomboid Major and Minor Actions |
Pulls scapula medially and upward. Allows you to pull shoulders back |
|
|
Rhomboid Major and Minor Blood Supply |
Dorsal scapular artery |
|
|
Rhomboid Major and Minor Innervation |
C5 (dorsal scapular nerve) |
|
|
Rhomboid Major Attachments |
Medial: Spinous processes of vertebrae T2 to T5 Lateral: Medial border of scapula inferior to scapular spine |
|
|
Rhomboid Minor Attachments |
Medial: Nuchal ligament and spinous processes of vertebrae C7 and T1 Lateral: medial border of scapula at level of scapular spine |
|
|
Semispinalis Action |
Stabilizes and extends spinal column |
|
|
Semispinalis Innervation |
spinal nerves - dorsal primary rami of intercostal nerves |
|
|
Serratus Posterior (Superior and Inferior) Action |
Thin, ineffective muscles involved in rib elevation (superior -- causes inspiration) and depression (inferior -- causes expiration) |
|
|
Serratus Posterior Inferior Attachments |
Medial: Spinous processes of T11 to L2 Lateral: Inferior borders of ribs 9 to 12, lateral to their angles |
|
|
Serratus Posterior Innervation (Superior and Inferior) |
Spinal nerves - dorsal primary rami (intercostal nerves) |
|
|
Serratus Posterior Superior Attachments |
Medial: Nuchal ligament and spinous processes of C7 to T3 Lateral: Superior borders of ribs 2 to 5, lateral to their angles |
|
|
spinal meninges |
membranes of the spinal cord |
|
|
Splenius Action |
Stabilizes and extends spinal column |
|
|
Splenius Attachments |
Splenius capitis: attached to mastoid process of temporal bone and superior nuchal line of occipital bone Splenius cervicis: attached to transverse processes of vertebrae C1 to C4 |
|
|
Splenius Innervation |
Spinal nerves - dorsal primary rami of intercostal nerves |
|
|
subarachnoid space |
space between arachnoid mater and pia mater |
|
|
Superficial Back Muscles |
Latissimus Dorsi, Trapezius, Rhomboid Major, Rhomboid Minor, Levator Scapulae |
|
|
Transverospinal group of muscles |
Located deep to erector spinae, attached to transverse and spinous processes, cause rotational and lateral motion of adjacent vertebrae |
|
|
Trapezius Action |
Suspends the shoulder girdle and moves scapula medially (can retract scapula), up, and down |
|
|
Trapezius Attachments |
Medial attachments: External occipital protuberance, nuchal ligament, and spinous processes of vertebrae C7 to T12 Lateral attachments: Clavicle and scapula |
|
|
Trapezius Blood Supply |
Transverse cervical artery |
|
|
Trapezius Innervation |
Accessory nerve (XI) |
|
|
Types of Intervertebral Joints |
1) Cartilaginous (intervertebral discs) - no synovial fluid in these 2) Synovial (facet joints) |
|
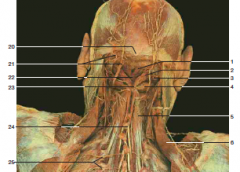
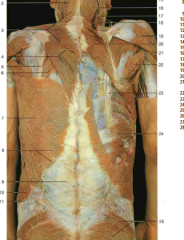
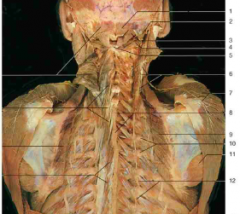
#20 |
External occipital protuberance |
|
#14
|
Greater occipital nerve |
|
#3 |
Trapezius |
|
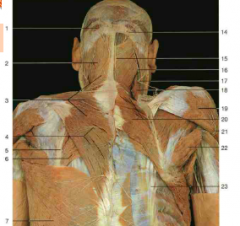
White patch below #6 |
Triangle of auscultation |
|
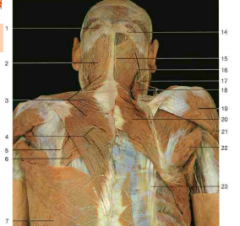
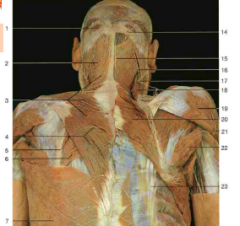
#18 |
Levator Scapulae |
|
#2 |
Splenius capitis |
|
#24 |
Serratus Posterior Inferior (Superior looks same but is higher up near neck; still an intermediate muscle) |
|
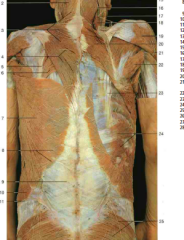
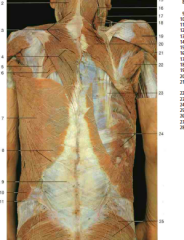
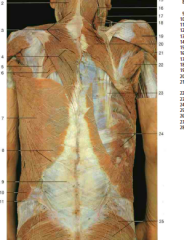
#6, #20 |
Rhomboid major muscle, rhomboid major and minor muscles |
|
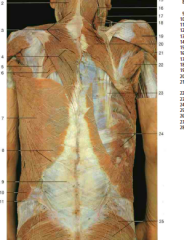
#7 |
Latissimus Dorsi |
|
#5 |
Splenius Cervicis |
|
#10 |
Longissimus (from Erector Spinae) |
|
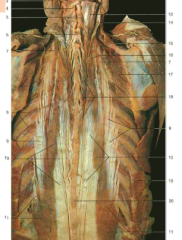
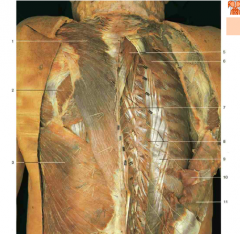
#18 |
Spinalis (from Erector Spinae) |
|
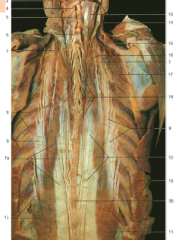
#5 |
Semispinalis (underneath the splenius capitis, which would wrap diagonally over it) |
|
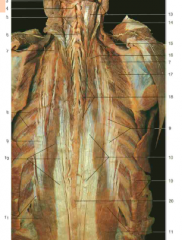
#9 |
Iliocostalis (from Erector Spinae) |
|
#7 |
Accessory nerve (CN XI) (under trapezius) |
|
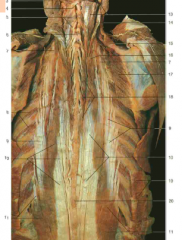
#7, #8 |
Dorsal rami of thoracic spinal nerves |
|
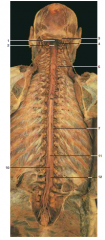
#10 |
Filum terminale |
|
#11 |
Conus medullaris |
|
#12 |
Cauda equina |
|
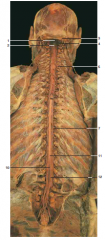
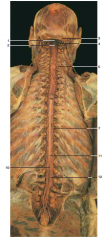
#4 |
Greater occipital nerve |
|
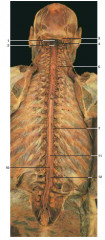
#5 |
Dorsal primary ramus |
|

#6 |
Dorsal roots |
|

#7 |
Dorsal root ganglion |
|

#8 |
Spinal dura mater |
|

#9 |
Spinal arachnoid mater (on underside of dura mater) |
|
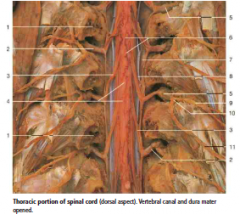
#10 |
Dorsal ramus of spinal nerve |
|
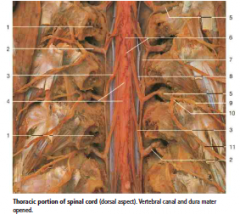
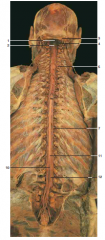
#2 |
Dorsal roots of spinal nerves |
|
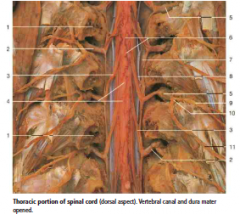
#6 |
Pia mater |
|
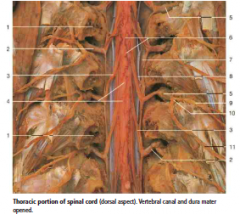
#7 |
Dura mater (opened) |
|
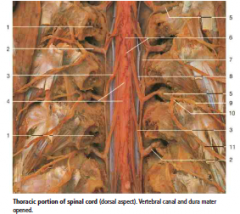
#8 |
Denticulate Ligament |
|
|
What nerve could be damaged if the surgical neck of the humerus is injured? |
Axillary nerve b/c it curves around the surgical neck
|
|
|
What is found in the quadrangular space? What are its borders? |
Axillary nerve and posterior circumflex humeral artery. Teres minor and biceps brachii |
|
|
What is found in the triangular space? What are its borders? |
Circumflex scapular artery. Teres major, long head of triceps |
|
|
What is found in the triangular interval? What are its borders? |
Deep brachial artery (profunda brachii artery) and radial nerve. Long and lateral heads of triceps |
|
|
What ligament passes through the suprascapular notch? What nerve and artery pass over/under this ligament? |
Superior transverse scapular ligament. Suprascapular artery goes over it, suprascapular nerve goes under it. |
|
|
Branches of axillary artery |
She Tastes Like Sweet Apple Pie, 123
1st division: superior thoracic 2nd division: thoracoacromial, lateral thoracic 3rd division: subscapular, anterior circumflex humeral, and posterior circumflex humeral artery |
|
|
Thoracoacromial trunk: arterial branches |
Cadavers Are Dead People
Clavicular branch Acromial branch Deltoid branch Pectoral branch |
|
|
Anterior arm flexors: names and innervation |
Coracobrachialis, biceps brachii (short head and long head), brachialis Musculocutaneous nerve |
|
|
Anterior forearm flexors: names and innervation |
Median nerve
Superficial: (FPFP) Flexor carpii ulnaris (exception: ulnar nerve) Palmaris longus Flexor carpii radialis Pronator teres
Intermediate: Flexor digitorum superficiales
Deep: (FPFDP) Flexor pollicis longus Flexor digitorum profundus (exception: half ulnar nerve, half median nerve) Pronator quadratus |
|
|
Brachioradialis: Attachments, actions, and innervation |
4 Brs:
1- Attaches to Base of Radial styloid process 2- Beer Raising muscle (pronates, supinates, flexes arm) 3- Breaks the Rules (flexor innervated by radial nerve) 4- Below it is the Radial nerve |
|
|
Cubital Fossa contents |
Ron Beats Bad Man
Radial nerve Biceps tendon Brachial artery Median nerve |
|
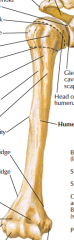
Label this anterior view:
Upper indentation Lower right (medial) indentation Vertical line closest to arm First dashed line Second dashed line 4th and 5th lines from top 10th line down Outermost edges of bottom Big hole/groove at end |
Bicipital groove Spinal groove Head of humerus Anatomical neck Surgical neck Greater tubercle Lesser tubercle Deltoid tuberosity Lateral epicondyle and medial epicondyle (supracondylar ridges are edges of bone going briefly up from these) Coronoid fossa |
|
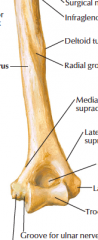
Hole at bottom |
Olecranon fossa |
|
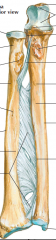
Label:
Top right 3rd down on right Bottom right Just above bottom right Bottom left Top left 3rd down on left Tissue between bones |
Olecranon Coronoid process Styloid process of ulna Head of ulna Styloid process of radius Head of radius Radial tuberosity Interosseus membrane
|
|
|
Compartments |
One or two long bones, surrounded by fascia Can have 2 compartments Compartments act in unified manner Compression affects all compartment contents (muscles, nerves, arteries, veins, etc.) Fascial intermuscular septa attached to bone |
|
|
Compartment Syndrome |
Increased pressure from bleeding, swelling; can follow injury (fracture, bruising) or plaster cast
Affects: -Muscle function/action = paralysis -Nerve function/activity = pain, parasthesia -Vascular function = palor |
|
|
Cephalic vein |
Radial side vein; joins axillary vein at deltopectoral groove |
|
|
Basilic vein |
Ulnar side vein; joins brachial vein to form axillary vein |
|
|
Median cubital vein |
Transverse vein at elbow connecting cephalic and basilic veins |
|
|
Branches of brachial cutaneous nerve |
Lateral, medial, and posterior cutaneous nerves of arm; upper and lower branches off lateral |
|
|
Branches of antebrachial cutaneous nerve |
Lateral, medial, and posterior cutaneous nerves of arm |
|
|
Anterior Arm Compartment Contents |
Muscles: Brachialis Biceps brachii Coracobrachialis
Vessels: Brachial artery Profunda brachii artery Ulnar collateral arteries
Nerves: Musculocutaneous nerve Median nerve Ulnar nerve |
|
|
Biceps brachii attachments |
Glenoid tubercle and coracoid --> radial tuberosity and bicipital aponeurosis |
|
|
Biceps brachii actions |
Flexes at elbow joint Supinates forearm Abducts, adducts and medially rotates arm at shoulder joint |
|
|
Biceps brachii innervation |
Musculocutaneous nerve |
|
|
Coracobrachialis attachments |
Coracoid --> humerus |
|
|
Coracobrachialis actions |
Flexes arm at shoulder joint |
|
|
Coracobrachialis innervation |
Musculocutaneous nerve |
|
|
Brachialis attachments |
Anterior humerus --> ulnar tuberosity |
|
|
Brachialis actions |
Flexes at elbow joint |
|
|
Brachialis innervation |
Musculocutaneous nerve |
|
|
Biceps tendonopathy |
Pain and impaired function of biceps tendon (long head) that may be accompanied by inflammation; tendon is at risk of rupture--if occurs, muscle strength decreases by 25% |
|
|
Anterior forearm compartment contents |
Muscles: Superficial, intermediate, and deep groups of flexors
Vessels: Radial artery Ulnar artery Anterior interosseus artery
Nerves: Median nerve Ulnar nerve |
|
|
Superficial forearm flexors |
Flexor carpi ulnaris, palmaris longus, flexor carpi radialis, pronator teres |
|
|
Intermediate forearm flexors |
Flexor digitorum superficiales |
|
|
Deep forearm flexors |
Pronator quadratus, flexor digitorum profundus, flexor pollicis longus
|
|
|
Forearm flexor attachments |
Superficial and intermediate group muscles attached to medial epicondyle of humerus |
|
|
Forearm flexor innervation |
All muscles supplied by median nerve except flexor carpi ulnaris and part of flexor digitorum profundus
Ulnar nerve runs in superficial layer, next to flexor carpi ulnaris
Median nerve runs anterior to deep layer (between intermediate and deep layers) |
|
|
Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis) |
lateral epicondylar pain upon clenching fist |
|
|
Volksmann's ischemic contracture |
contracture of forearm muscles commonly following fractures of distal humerus or radius/ulna. Results from brachial artery spasm leading to reduced blood supply. Flexors affected more than extensors |
|
|
Fractures of humerus: effects |
Upper humerus: fracture of surgical neck could cause damage to axillary nerve
Lower humerus: Supracondylar fracture - risk of damage to median and ulnar nerves
Shaft of humerus: Radial nerve at risk of injury. However, radial nerve frequently gives off branch to long head of triceps before going into radial groove, so damage to radial nerve doesn't necessarily mean loss of function of long head of triceps |
|
|
Posterior arm compartment |
Muscles: Triceps brachii Anconeus
Vessels: Profunda brachii Radial collateral artery
Nerves: Radial nerve Ulnar nerve |
|
|
Triceps brachii attachments |
Has three heads
Infraglenoid tubercle, dorsal humerus, medial intermuscular septum --> olecranon |
|
|
Triceps brachii and anconeus actions and innervation |
Radial nerve
Extends at elbow joint Extends at shoulder joint |
|
|
Posterior forearm compartment contents |
Muscles: Superficial and deep groups of extensors
Vessels: Radial artery Posterior interosseous artery
Nerves: Radial Nerve |
|
|
Superficial muscles of posterior forearm compartment: names, actions, attachments, and innervation |
Brachioradialis, extensor carpi radialis longus, extensor carpi radialis brevis, extensor carpi ulnaris, extensor digitorum, extensor digiti minimi
(last 4 attached to lateral epicondyle of humerus)
Extend wrist and proximal phalanges
Deep branch of radial nerve (posterior interossesous nerve)
|
|
|
Deep muscles of posterior forearm compartment: names, innervation |
Supinator, abductor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis brevis, extensor pollicis longus, extensor indicis
Deep branch of radial nerve (posterior interosseous nerve) |
|
|
"Fist clenchers" |
Radial extensors of carpus (extensor carpi radialis brevis and longus)
Hand must be slightly extended (dorsiflexed) to permit maximal action by flexors |
|
|
Anatomical snuff box |
Made by abductor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis brevis, and extensor pollicis longus; contains radial artery |
|
|
Colles' fracture |
Fracture of lower end of radius with dorsal displacement of fracture fragments ("dinner fork" deformity) |
|
|
Retinaculum |
Regions of strength of deep fascia created by realignment of fibrous tissue
Prevents bow-stringing of long tendons of forearm (flexors and extensors)
Extensor retinaculum Flexor retinaculum |
|
|
Synovial tendon sheaths |
Synovial compartments around tendons that help reduce friction between retinaculum and tendon
Tendon sheaths can become injured, inflamed, or infected |
|
|
Dorsal digital (extensor) expansion |
Hood-like fibrous tissue around distal metacarpal and dorsum of proximal phalanx For holding extensor tendon in midline, and for insertion of lumbrical and interosseous muscles |
|
|
An open arterial anastomosis in the shoulder occurs between the suprascapular artery and which other artery? |
Circumflex scapular artery |
|
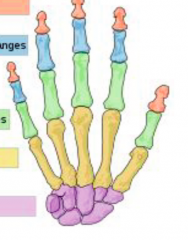
Pink Blue Green Yellow Purple |
Distal phalanges Intermediate phalanges Proximal phalanges Metacarpals Carpals |
|
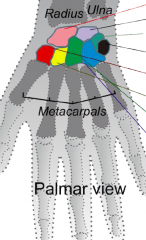
Label colored bones from top to bottom |
Scaphoid Lunate Triquetrium Pisiform Trapezium Trapezoid Capitate Hamate |
|
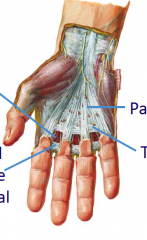
Left top Left bottom Right top Right bottom |
Palmer digital arteries and nerves Superficial transverse metacarpal ligaments Palmer aponeurosis Transverse fasciculi |
|
|
Muscles that flex wrist |
Flexor carpi radialis longus Flexor carpi radialis brevis Palmaris longus |
|
|
Muscles that extend wrist |
Extensor carpi radialis longus Extensor carpi radialis brevis Extensor carpi ulnaris Extensor digitorum |
|
|
Muscles that abduct wrist |
Extensor carpi radialis longus Extensor carpi radialis brevis |
|
|
Muscles that adduct the wrist |
Extensor carpi ulnaris |
|
|
Flexor pollicis brevis: action and innervation |
Flexes MP joint of thumb median nerve |
|
|
Abductor pollicis brevis: action and innervation |
Abducts thumb median nerve |
|
|
Opponens pollicis: action and innervation |
Opposes thumb Median nerve |
|
|
Adductor pollicis |
Adducts thumb Ulnar nerve |
|
|
Abductor digiti minimi: action and innervation |
Abducts 5th finger Ulnar nerve |
|
|
Flexor digiti minimi: action and innervation |
Flexes 5th nerve Ulnar nerve |
|
|
Opponens digiti minimi |
Opposes 5th finger Ulnar nerve |
|
|
Palmaris brevis: action and innervation |
Corrugates (bends/folds inward) hand Ulnar nerve |
|
|
Deep palm muscles |
Palmaris brevis, lumbricals, palmar interossei, dorsal interossei |
|
|
Lumbricals: action and innervation |
Flex MP joints and extend IP joints Ulnar n (medial 2) and median n (lateral 2) |
|
|
Palmar interossei: action and innervation |
Flex MP joints, extend IP joints, and adduct fingers toward center of 3rd finger Ulnar n
PAD |
|
|
Dorsal interossei: action and innervation |
Flex MP joints and extend IP joints, abduct fingers away from center of 3rd finger Ulnar n.
DAB |
|
|
Finger Flexion Muscles DIP PIP MP |
Flexor digitorum profunda Flexor digitorum superficiales Lumbricals |
|
|
Finger extension muscles |
Extensor digitorum Lumbricals Interossei |
|
|
Finger abduction muscles |
Dorsal interossei |
|
|
Finger adduction muscles |
Palmer interossei |
|
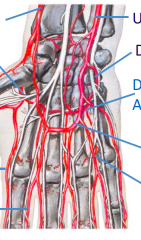
Label from top right going clockwise.
What artery branches off into the thumb? |
Ulnar Deep Palmer Deep Palmer Arch Superficial Palmer Arch Common Digital Proper Digital Radialis Indicis Deep Radial Palmer Radial
Princeps Pollicus |
|
|
Nerves in Palm of Hand |
Ulnar: Palmaris Brevis 3 & 4 Lumbricals Palmer Interossei Dorsal Interossei Adductor Pollicus Abductor Digiti Minimi Flexor Digiti Minimi Opponens Digiti Minimi
Median nerve: 1 & 2 Lumbricals Abductor Pollicus Brevis Flexor Pollicus Brevis Opponens Pollicus |
|
|
Cutaneous Innervation of Hand: Medial wrist Lateral wrist Pinky, half of ring finger, and corresponding palm area, going just past wrist First 2 1/2 fingers, tip and underside of thumb, and rest of palm Top of thumb, going just past wrist Lateral wrist
|
Medial cutaneous Musculocutaneous Ulnar Median Radial |
|
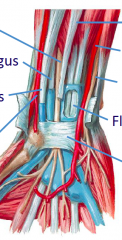
Start at left top, go counterclockwise |
Median nerve Flexor Pollicus Longus Flexor Carpi Radialis Radial artery Transverse carpal ligament Flexor digitorum Ulnar nerve Ulnar artery Palmaris longus |
|
|
Suppurative tenosynovitis (right index finger) |
that finger would be red and swollen |
|
|
Paronychia |
Abscess adjacent to nail involving perinychyial fold |
|
|
Ascending Lymphangitis associated with purulent tenosynovitis |
Super red swollen finger. Artery leading to it is also super red |
|
|
Dupuytren's Contracture (chronic progressive palmar fascitis) |
Ring and pinky finger curl in and can't extend; mostly men |
|
|
Raynaud's Phenomenon |
Pinky and maybe ring finger(s) totally ischemic and white, others super red. mostly young women. can be cured with heat |
|
|
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome |
Swelling of common flexor synovial sheath/ligament Compression of median nerve Pain, weakness, tingling of thumb, index, and middle fingers Weakness of thenar muscles Treated by opening the tunnel
|
|
|
Contents of carpal tunnel |
Radial artery, Palmer carpal ligament, median nerve, ulnar nerve and artery, transverse carpal ligament |
|
|
Number of vertebrae in spinal cord Number of pairs of spinal nerves |
Vertebrae: 7 Cervical 12 Thoracic 5 Lumbar 5 Sacral (fused into one bone) 4 Coccygeal (2-4 fused)
Nerves: 8 Cervical 12 Thoracic 5 Lumbar 5 Sacral 1 Coccygeal
|
|
|
Sacral Foramina |
Anterior Sacral Foramina for Anterior Primary Rami
Posterior Sacral Foramina for Posterior Primary Rami |
|
|
Spinal Cord Blood Supply |
One anterior and two posterior spinal arteries arising from vertebral arteries
Augmented by radicular and medullary branches from descending aorta and remaining primary subclavian artery branches |
|
|
Venous drainage of spinal cord and vertebral column |
Basivertebral vein, Internal (epidural) plexus, and external plexus
Vertebral venous plexuses (internal and external) have thin walls and have incompetent valves or are valveless
Free venous flow can occur between plexuses and skull, neck, thorax, abdomen, and pelvis depending on changing pressure differentials
Increased intra-abdominal pressure forces venous blood into internal plexus and explains how carcinoma of prostate may metastasize to vertebral column and cranial cavity |
|
|
Lumbar puncture |
Used to examine CSF
Insert between L4 and L5 (safe because cord ends at L1) |
|
|
Dermatome: definition and map from neck down through upper limb and chest |
Area of skin supplied by a single spinal nerve, and therefore a single segment of the spinal cord (segmental innervation)
Neck: C3 Clavicle area: C4 Lateral upper arm: C5 Lateral forearm through thumb: C6 Medial arm: T2 Medial forearm: T1 1st and 2nd fingers and corresponding wrist area: C7 Ring and pinky fingers and corresponding wrist area: C8 Below clavicle area down ribs: T1-T12 Nipples: T4
|
|
|
Herniated Disc (HNP) |
HNP = herniated nucleus pulposus
Herniated discs compress the spinal nerve corresponding to the lower vertebra of the pair. For cervical spine, it's because nerve of lower one is in between the two. For rest of spine, it's because nerve for upper vertebra comes out above the herniated disc, so it's not affected.
Examples: Thoracic/lumbar/sacral: L4-5 herniated disc compresses L5 nerve root. L5-S1 HNP compresses S1 nerve root |
|
|
Cervical Subluxation |
Flexion injury (ex: C5 crashing into C6: anterior dislocation of C5 with locked facets; can fix surgically
|
|
|
Hangman's Fracture |
fractures of pedicles and usually also the odontoid process of the axis |
|
|
Common primary sites of cancer for metastatic cancer in spinal cord |
Lung Breast Prostate Kidney Thyroid |

