![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Muscle Attachments
|
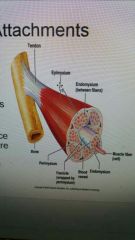
at the ends of each muscle, all of the connective tissue merge to form a tendon which attaches the muscle to a bone.
attached at both ends |
|
|
Tendon
|
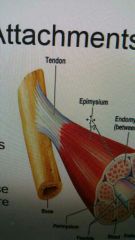
cord-like in appearance
|
|
|
Aponeuroses
|
sometimes flat tendons
|
|
|
Muscle Movement
|
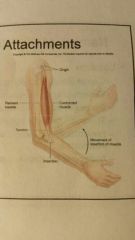
during movement one end of the muscle called the insertion moves towards the other end called the origin
|
|
|
Agonist (prime mover)
|
produces a specific movement when it contracts.
for instance, the biceps brachii is an agonist that causes flexion of the elbow joint |
|
|
Antagonist
|
is a muscle whose action opposes that of an agonist.
the triceps brachii would be an antagonist to the biceps brachii |
|
|
Synergist
|
is a muscle that assist the agonist or prime mover
|
|
|
Fixator
|
prevent movement of bone
|
|
|
Naming Skeletal Muscles
|
qualities include:
1. Appearance 2. Location 3. Function 4. Orientation 5. Unusual Features |
|
|
SIZE
|
|
|
|
Major
|
(large)
i.e. pectoral is major |
|
|
Maximus
|
(largest)
i.e. gluten maximus |
|
|
Minor
|
(small)
i.e. pectoralis minor |
|
|
Minimus
|
(smallest)
i.e. gluteus minimus |
|
|
Longus
|
(long)
i.e. abductor pollicis longus |
|
|
Longissimus
|
(longest)
i.e. longissimus thoracis |
|
|
Brevis
|
(short)
i.e. adductor brevis |
|
|
SHAPE
|
|
|
|
Rhomboideus
|
(rhomboidal)
i.e. rhomboideus major |
|
|
Trapezius
|
(trapezoidal)
i.e. trapezius |
|
|
Teres
|
(round, cylindrical)
i.e. Pronator teres |
|
|
Deltoid
|
(triangular)
i.e. deltoid |
|
|
Quadratus
|
(four-sided)
i.e. pronator quadratus |
|
|
LOCATION
|
|
|
|
Capitis
|
(head)
i.e. splenius capitis |
|
|
Cervicis
|
(neck)
i.e. semispinalis cervicis |
|
|
Pectoralis
|
(chest)
i.e. pectoralis major |
|
|
Thoracis
|
(thorax)
i.e. spinalis thoracis |
|
|
Intercostals
|
(between ribs)
i.e. external intercostals |
|
|
Abdominis
|
(abdomen)
i.e. rectus abdominis |
|
|
Digitorum
|
(fingers or toes)
i.e. flexor digitorum longus |
|
|
Pollicis
|
(thumb)
i.e. oppones policis |
|
|
Indicis
|
(index finger)
i.e. extensor indicis |
|
|
Hallucis
|
(great toe)
i.e. abductor hallucis |
|
|
Superficialis
|
(superficial)
i.e. flexor digitorum superficialialis |
|
|
Profundus
|
(deep)
i.e. flexor digitorum profundus |
|
|
Lumborum
|
(lower back)
i.e. quadratus lumborum |
|
|
Femoris
|
(femur or thigh)
i.e. quadriceps femoris |
|
|
Fibularis
|
(fibula)
i.e. fibularis longus |
|
|
Brachii
|
(arm)
i.e. biceps brachii |
|
|
Carpi
|
(wrist)
i.e. flexor carpi ulnaris |
|
|
Digiti
|
(finger or toes)
extensor digiti minimi |
|
|
ACTION
|
|
|
|
Adductor
|
a muscle that draws a part INWARD the midline or axis of the body
adductor pollicis |
|
|
Abductor
|
a muscle that draws a body part AWAY from the midline or axis of the body
i.e. abductor digiti minimi |
|
|
Flexor
|
a muscle that when CONTRACTED BENDS a joint or limb in the body
i.e. flexor carpi radialis |
|
|
Extensor
|
a muscle that EXTENDS or STRAIGHTENS a limb or body part
i.e. extensor carpi radialis |
|
|
Pronator
|
a muscle that effects or assists in pronation
i.e. pronator teres |
|
|
Supinator
|
cylindrical-shaped muscle in the forearm that normally curves around the upper third of the radius
|
|
|
Levator
|
a muscle that serves to raise a body part
i.e. levator scapulae |
|
|
Depressor
|
a muscle that acts by drawing down a part of the body
i.e. depressor anguli oris |
|
|
NUMBER OF HEADS
|
|
|
|
Biceps
|
(two heads)
i.e. biceps femoris |
|
|
Triceps
|
(three heads)
i.e. triceps brachii |
|
|
Quadriceps
|
(four heads)
i.e. quadriceps femoris |
|
|
ORIENTATION
|
|
|
|
Rectus
|
(straight)
i.e. rectus abdominis |
|
|
Transversus
|
lying across the long axis of the body or of a part
transversus abdominis |
|
|
Oblique
|
(slanted)
i.e. external abdominal oblique |

