![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What does Anatomy stand for? |
(Ana- = up; -tomy = process of cutting) Anatomy is the science structure and the relationship among structures. |
Ex. The parts of the car or parts of the person is the anatomy portion. |
|
|
What does Physiology mean? |
(Physio- = nature; -logy = study of) Physiology is the science of body functions, that is, how the body parts work. |
Ex. How the car runs or person moves/function is the Physiology part. |
|
|
What are the 6 levels of organization of the human body? |
1. Chemical level, 2. The cellular level, 3. The tissue level, 4. The organ level, 5. The system level, 6. The organismal level |
|
|
|
What does the chemical level include? |
The chemical level includes atoms, the smallest unit of matter that participates in chemical reactions, and molecules, two or more atoms joined together. Certain atoms such as carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, and other, are essential for maintaining life. Molecules are found in the body and they are DNA. |
|
|
|
What is the cellular level composed of? |
Cells are the basic structure and functional unit of the organism. Among many types of cells in your body are muscle cells, nerve cells, and blood cells. They're also organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, and lysosomes, that perform special functions. |
|
|
|
What does the tissue level composed of? |
Tissues are groups of cells and the materials surrounding them that work together to perform a particular function the four basic types of tissue in the body are epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscular tissue, and nervous tissue. |
|
|
|
What does the organ level consist of? |
Organs usually have a recognizable shape, are composed of two or more different types of tissues, and has the specific functions. Tissues joined together to form organs. Examples of organs are the stomach, heart, liver, lungs, and brain. The serious membrane is a layer around the outside of the stomach and protects it and reduces friction when the stomach moves and rubs against other organs. The innermost lining of the stomach is an epithelial tissue layer, which country beats fluid and chemicals that aid digestion. |
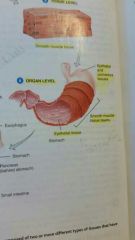
|
|
|
What does the system level consist of? |
A system consist of related organs that have a common function. Organs join together to form systems similar to the way paragraphs are put together to form chapters. They work together to maintain health and protect you from disease. |
|
|
|
What does the organismal level do? |
The organismal level is the largest level of organization. All of the systems of the body combine to make up an organism, that is, one human being. |
|
|
|
What are the 6 important life processes of humans? And what do they do? |
1. Metabolism is the sum of chemical processes that occur in the body includes the breakdown of large complex molecules into smaller ones. 2. Responsiveness is the body ability to detect and respond to change in its environment. 3. Movement includes motion of the whole body, individual organs, single cells, and even tiny organelles inside cells. 4. Growth is an increase in body size. It may be due to an increase in the size of existing cells, the number of cells or the amount of material surrounding cells. 5. Differentiation is the process whereby unspecialized cells become a specialized cells. 6. Reproduction refers to either the formation of new cells for growth repair or replacement or the production of a new individual. |
|
|
|
What is homeostasis? |
The maintenance of the relatedly stable condition is called homeostasis. (Homeo- = sameness; -stasis = standing still) homeostasis ensures that the bodies internal environment remains constant despite changes inside and outside the body. Homeostasis is dynamic; that is, it can change over a narrow range that is compatible with maintaining the cellular life processes. |
|
|
|
What's the percentage of body weight of water? |
60 - 80% |
|
|
|
What is a feedback system? |
Homeostasis is maintained by means of many feedback systems. A feedback system or feedback loop is a cycle of events in which a condition in the body is continually monitored, evaluated, changed, remonitored, and reevaluated. Each monitored condition, such as body temperature, blood pressure, or blood glucose level, is termed a controlled condition. |
|
|
|
What are the three basic components that make up a feedback system? |
1. A receptor is a body structure that monitors change in a controlled condition and Singh information call the input to a control center. 2. A control center is the body for example the brain, set the range of values within which a controlled conditions should be maintained, evaluate the input it receives from the receptors, and generate output commands when they are needed. Output is information common in the form of nerve impulses or chemical signals that is related from the control center to an effector. 3. An effector is a body structure that receives output from the control center and produces a response that changes the control condition. Nearly every organ or tissue in the body can behave as an effector. |
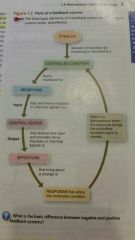
|
|
|
What is a negative feedback system? |
A negative feedback system refers a change in a controlled condition. Blood pressure is the force exerted by blood as it presses against the wall of blood vessels. |
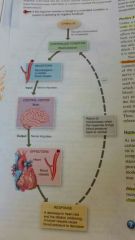
|
|
|
What is a positive feedback system? |
Unlike a negative feedback system, a positive feedback system tends to strengthen or reinforce a change one of the bodies controlled conditions. Normal childbirth provides a good example of a positive feedback system. |
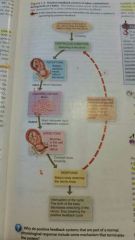
|
|
|
What is the 3D's ? |
Disorder, disease, and death |
|
|
|
What is anatomical position? |
In the anatomical position, the subject stand erect facing the observer, with the head level and eyes facing forward. The lower limbs are parallel in the feet are flat on the floor and directed forward, and the upper limbs are at the sides with the palms facing forward |
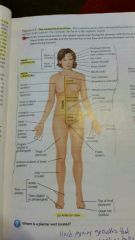
|
|
|
What is the prone and supine position? |
The body is lying face down it is in the prone position. If the body is lying face up, it is in the supine position. |
|
|
|
What does superior mean? |
Toward the head, or the upper part of a structure |
The heart is superior to the liver |
|
|
What does Inferior mean? |
Away from the head, or the lower part of a structure |
The Stomach is inferior to the lungs |
|
|
What does anterior mean? |
Nearer to or at the front of the body |
|
|
|
What does intermediate mean? |
Between two structures |
The Transverse colon is intermediate to the ascending and descending colons |
|
|
What does Ipsilateral mean? |
On the same side of the body as another structure |
The gallbladder and ascending colon are Ipsilateral |
|
|
What does contralateral mean? |
On the opposite side of the body from another structure |
The ascending and descending colon are contralateral |
|
|
What is a parasagittal plane? |
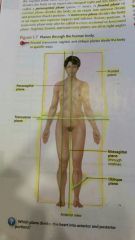
It divides the body or an organ into an equal right and left sides |
(Para- = near) |
|
|
What is an oblique plane? |
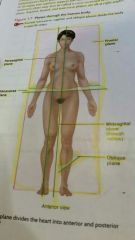
It passes through the body or an organ at an angle between the transverse plane and a sagittal plane or between the transverse plane and the frontal plane |
|
|
|
What's the thoratic cavity? |
Is the chest cavity. It contains the pleural cavity, the pericardial cavity, and the mediastinum. |
|
|
|
What is the abdominopelvic cavity? |
The abdominopelvic cavity stands for the diaphragm to the groin. It contains two cavities. The abdominal cavity which contains the stomach, spleen, liver, gallbladder, small intestine, and most of the large intestine. The other cavity is the pelvic cavity. It contains the urinary bladder, portions of the large intestine, and internal organs of the reproductive system. |
|
|
|
What are the nine abdominal pelvic regions? |
There's the right hypochondriac, epigastric, left hypochondriac, right lumbar, umbilical, left lumbar, right inguinal, hypogastric, left inguinal |
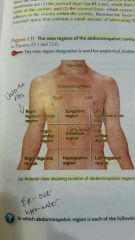
In one method come to horizontal and vertical lines, like a tick-tac-toe grid. |
|
|
What does chemistry mean? |
Chemistry is the science of the structure and interactions of matter, which is anything that occupies space and has mass. |
|
|
|
What is mass? |
Mass is the amount of matter in any living organism or non-living thing. |
|
|
|
What are atoms? |
Atoms are the smallest unit of matter that retains the properties and characteristics of the element. Example of an element is carbon come such as pure coal, contained only carbon atoms, & a tank of helium gas contains only helium atoms. |
|
|
|
What are the major chemical elements in the body? |
Oxygen (O) - 65%, Carbon (C) - 18.5%, Hydrogen (H) - 9.5%, and Nitrogen (N) - 3.2% |
|
|
|
What are molecules? |

A molecule may consist of two or more atoms of the same element or two or more of different elements. |
|
|
|
What is a compound? |
A compound is a substance containing atoms of two or more different elements. |
For example, water is H2O |

