![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
142 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Anatomy is the study of the ____________ of body parts and their relationship to one another. |
structure |
|
|
Physiology- function; study of how body parts ___________ and carry out activities. |
work |
|
|
Gross anatomy (macroscopic) |
study of large structures visible with the naked eye, such as the heart, kidneys, bones, and the liver. |
|
|
______________ anatomy focuses on the anatomy of one particular area. For example, if we were studying the arm, we would study the bones, muscles, nerves, and blood vessels in that area. |
Regional |
|
|
Study of individual organ systems. For example, when we study the nervous system, we'll learn about the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. |
Systemic Anatomy |
|
|
_______________ anatomy- study of general form and superficial markings. |
Surface |
|
|
Study of structures that cannot be seen with the naked eye |
Microscopic anatomy |
|
|
Cytology |
Study of cells |
|
|
Histology |
study of tissues, such as connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue |
|
|
Developmental anatomy |
covers changes that occur over time; main division is embryology |
|
|
Medical/____________________ Anatomy |
Pathological anatomy- changes in the body during illness |
|
|
_____________ Anatomy- study of internal structures using x-ray, CT scans, and MRIs |
Radiographic |
|
|
Systemic and Special Physiology |
Study of the function of a particular organ or organ system (kidneys, neurophysiology, cardiophysilogy , respiratory physiology) |
|
|
Cell physiology |
study of the functions of cells |
|
|
Pathological Physiology |
study of the effects of disease on the body |
|
|
Structure and function are _______________. A fork, given it's form, is meant for stabbing, while a knife with a single edge is for cutting. |
interdependent |
|
|
Complementarity of structure and function |
what a structure can do depends on its form |
|
|
Chemical (______________) level- atoms join together to form molecules, such as water, proteins, and sugars |
Molecular (molecules join together to form organelles) |
|
|
Cellular Level- __________________ join together to corm cells |
Organelles |
|
|
___________ Level- Groups of cells that have a common function join together to form epithelium, muscle _________ , connective __________, and nervous _____________ |
Tissue |
|
|
__________________ Level- different types of tissues work together to form an ____________. |
Organ |
|
|
Organ Systems |
Groups of organs that work together (the heart and blood vessels work together to move blood throughout the body) |
|
|
Organism Level |
All the organ systems work together to maintain the organism |
|
|
Maintaining ___________________- internal and external boundaries are separated |
Boundaries |
|
|
What structure provides the boundary for the entire body? |
Skin |
|
|
____________________________- Motion of the whole body or part of the body, ____________ of substances through the body, and _____________________ of cells and organs. |
Movement |
|
|
Responsiveness (________________________ or excitability)- ability of the body to detect and respond to changes in the environment (stimuli' stimulus is singular) |
Irritability |
|
|
Digestion– breaking down of food into ___________________ ________________________
examples: carbs being broken down into sugar |
useable nutrients |
|
|
________________________ – sum of all chemicalprocesses in the body
|
Metabolism |
|
|
Catabolism – breaking something down from _________________to simple (ex: breakdown of proteins into amino acids)
|
complex |
|
|
_______________________ – building up from simple tocomplex
1. Joiningof amino acids to form proteins |
Anabolism |
|
|
Cellular Respiration |
using nutrients and oxygen to produce energy |
|
|
Excretion |
removal of waste from the body (urination, defecation, vomiting, sneezing, breathing) |
|
|
Reproduction |
formation of new cells or production of a new individual |
|
|
Growth |
increase in size of body or organism |
|
|
Nutrients |
Taken in by diet and include carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals |
|
|
Oxygen |
Many chemical reactions in the body require oxygen and water |
|
|
We are __ to ___ % water |
60% to 80% (provides environment for chemical reactions and provides fluid base for excretions) |
|
|
Normal body temperature is ______ |
98.6 degrees Fahrenheit or 37 degrees Celcius |
|
|
Atmospheric Pressure |
Force that air puts on the body (helps with breathing and gas exchange on the blood) |
|
|
Homeostasis |
Defined as the existence and maintenance of a stable internal environment in an ever changing external environment |
|
|
Receptor |
sensor that detects changes in the environment |
|
|
Control Center (brain) |
Receives and processes information, makes a "decision", then sends out commands |
|
|
Effector |
carries out the commands sent out by the control center |
|
|
Mechanisms |
negative and positive feedback loops |
|
|
_______________ Feedback- action of the effector shuts off the original stimulus when normal conditions return |
Negative |
|
|
_____________ Feedback- action of the effector increases the intensity of the original stimulus |
Positive |
|
|
Equilibrium |
opposing forces are in balance |
|
|
Body temp |
amount of heat generated is equal to the amount of heat lost |
|
|
Disorder |
any abnormality of structure of function |
|
|
Disease |
more specific term for illness characterized by signs and symptoms |
|
|
Symptoms |
Subjective changes in body functions ; not observable (headache, nausea, anxiety) |
|
|
Signs |
objective, measurable changes (high BP, fever, swelling) |
|
|
Humans have ______ different types of cells |
250 |
|
|
Humans have up to 100 ______ cells |
trillion |
|
|
Cells are the basic _______________ and functional unit of a living organism |
structural |
|
|
Activity of cells depends on their ____________ |
structure |
|
|
Continuity of life depends on cellular _________________ |
reproduction |
|
|
All cells have 3 basic components |
cell membrane, nucleus, and cytoplasm |
|
|
Cell (or plasma membrane) membrane |
outside wall of the cell |
|
|
The cell membranes 4 functions |
1. Separates cell's internal from external environment 2. Regulates flow of materials in and out of the cell 3. Maintains appropriate internal environment 4. Plays important role in communication both with other cells and with the external environment |
|
|
The cell membrane is made of _________________ |
a lipid bilayer/ double layer of fats |
|
|
Membrane proteins |
proteins embedded ion the membrane |
|
|
Membrane protein function A |
Form pores or holes for ions and transports molecules in or out of the cell |
|
|
Membrane protein function B |
Act as receptors so molecules can bind to the cell |
|
|
Membrane protein function C |
Provide support within a cell |
|
|
Membrane protein function D |
Help start or speed up reactions (enzymes) |
|
|
Membrane Protein Function E |
Join cells together |
|
|
Cell Identity |
Help cells recognize one another |
|
|
Cytoplasm |
consists of all contents of a cell between plasma membrane and nucleus |
|
|
Cytosol (intracellular fluid) |
fluid portion of cytoplasm (made of water, has dissolved and suspended components, site of chemical reactions) |
|
|
Organelles |
Specialized structures within a cell that perform specific functions |
|
|
Mitochondria |
the power plant of the cell |
|
|
Ribosomes |
make proteins |
|
|
Inclusions |
chemical substances that vary according to the cell type (lipid droplets in fat cells, pigment in skin cells, and glycogen in the liver and muscles) |
|
|
Nucleus |
control center for cell functions |
|
|
Epithelial Tissue |
Covers body surfaces, lines hollow organs, body cavities, ducts, and forms glands (skin, inside of kidneys) |
|
|
Connective tissue |
protects and supports the body, binds organs together, and stores energy |
|
|
Muscle tissue |
generates force to move the body structures (skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle that forms the walls of hollow organs- esophagus, intestines) |
|
|
Nervous Tissue |
carries messages from one part of the body to another (brain, spinal corn, nerves) |
|
|
Epithelia |
layer or layers of cells that cover or line something |
|
|
Glands |
structures that produce fluid secretions (sweat glands) |
|
|
Epithelial tissues have ___ characteristics |
5 |
|
|
Polarity |
2 distinct surfaces |
|
|
Exposed surface that faces the exterior of the body or an internal surface (inside of the stomach) |
Apical surface |
|
|
Base- attached to the tissue underneath |
called the Basal Surface |
|
|
Basal lamina and reticular lamina |
make up the basement membrane |
|
|
Cellularity |
composed of cells that are bound tightly together; other tissues often have a lot of space between cells |
|
|
Attachment |
bound to the basement membrane which holds it to the connective tissue underneath that provides support |
|
|
Avascularity |
lack blood vessels, but is innervated |
|
|
Avascular tissue receives oxygen by ____________ or absorption from surrounding tissue |
diffusion |
|
|
Epithelial functions |
1. physical protections 2. absorption 3. filtration 4. excretion 5. provide sensation gland cells produce secretions |
|
|
Epithelial cells have _____________________ |
microvilli- fingerlike projections that increase surface-area (digestive and urinary tracts) |
|
|
Intracellular connections |
cells of epithelium are firmly attached to each other and the basal lamina |
|
|
Tight Junction |
Two cell membranes are held together by interlocking membrane proteins (impermeable) |
|
|
Gap junction |
Two cells are held together by connexons (channel proteins, allow movement between cells) |
|
|
Desmosome |
Two cells are connected by cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) that form a zipper |
|
|
Simple epithelium |
composed of a single layer |
|
|
stratified epithelium |
consists of two or more layers, usually stacked on top of one another |
|
|
Squamous cells |
Are very flat |
|
|
Cuboidal cells |
Are box shaped |
|
|
Columnar cells are |
Tall and slender |
|
|
Simple squamous epithelium |
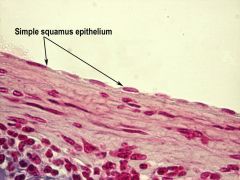
Very thin and delicate (includes pericardium, pluera, and peritoneum) |
|
|
Stratified Squamous Epithelium (high stress, mouth, skin, esophagus) |
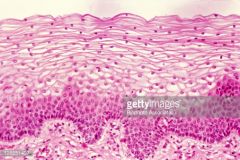
|
|
|
Simple Cuboidal |
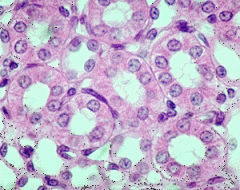
|
|
|
Stratified cuboidal (found in the sweat glands) |
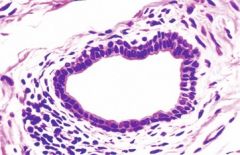
|
|
|
Transitional epithelium (stretches; bladder, urethra) |
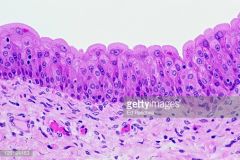
|
|
|
Simple columnar epithelium |
Found in the stomach, intestines, and gallbladder (secretions protect the stomach and intestines from chemicals) |
|
|
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium (appears to have several layers/different levels of nuclei; secretes mucus to trap foreign particles) |
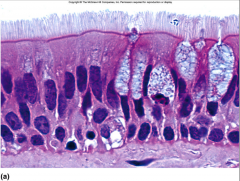
|
|
|
stratified columnar epithelium (found in the pharynx, salivary glands, and epiglottis) |
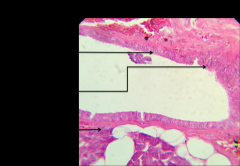
|
|
|
Glandular epithelium |
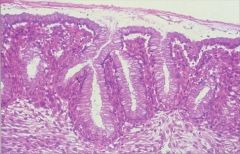
|
|
|
Endocrine Glands |
Release secretions into the interstitial space between cells (secrete hormones) |
|
|
Exocrine Glands |
(release secretions onto a surface through a duct (sweat glands, tear glands, mammary glands) (mucous, sweat, oil, saliva, bile (liver) and digestive enzymes (pancreas) |
|
|
Unicellular Glands |
Single cells that secrete mucous |
|
|
Goblet cells |
Trachea, intestines |
|
|
Connective Tissue |
Binds/Supports- bone & cartilage Protects Organs- Bone & Cartilage Insulates- Fat Stores Energy- Fat |
|
|
Loose connective tissue |
fibers are loosely intertwined, many cells present |
|
|
Dense Connective tissue |
more fibers and fewer cells than loose |
|
|
Cartilage |
Dense network of collagen fibers and elastic fibers embedded in ground substance |
|
|
Bone |
Osteocytes and extracellular matrix |
|
|
Fibroblasts |
Always present. Secrete proteins that help hold epithelial cells together and form extracellular fibers |
|
|
Chrondoblasts |
Found in cartilage |
|
|
Osteoblasts |
Found in bone |
|
|
Mast cells |
Produce histamine as part of inflammatory response |
|
|
Macrophages |
"Big Eater". Part of the immune system that engulf pathogens and damaged cells |
|
|
Collagen Fibers |
Long and straight. Protein fibers that wrap around each other like rope. Flexible, and strong |
|
|
Tendons |
Connect muscle to bone |
|
|
Ligaments |
Connect bone to bone |
|
|
Reticular Fibers (network) |
Intertwining framework that resist force and stabilize blood vessels in organs |
|
|
Elastic fibers |
Can stretch and recoil to their original length |
|
|
Ground substance |
fills the spaces between cells and surround connective tissue fibers (clear and viscous) |
|
|
Loose Connective Tissue |
fill spaces, provide cushioning for organs, support blood vessels, nerves, and epithelial tissue |
|
|
Areolar Tissue |
Very open structure and viscous ground substance (shock absorber, layer under skin, gives oxygen and nutrients to epithelial tissue) |
|
|
Adipose |
Shock absorption, stores energy |
|
|
Reticular Tissue |
Provides support for spleen, lymph nodes, and bone marrow, filters/removes old red blood cells |
|
|
Dense regular connective Tissue |
collagen fibers are lined up parallel to each other and packed tightly together (tendons and ligaments) |
|
|
Dense irregular connective tissue |
Fibers are close together, but aren't arranged in a pattern (form a sheath around bone and cartilage (periosteum, pericardium) (encloses kidneys, liver, and spleen) |
|
|
Chondrocytes occupy |
Lacunae |
|
|
Cartilage is separated from other tissue by |
Perichondrium |
|
|
Hyaline cartilage |
Most common. Found at junctions between ribs and sternum, trachea, ends of bones that form joints. |
|
|
Elastic cartilage |
Has a lot of elastic fibers. (forms ear, larynx, epiglottis) |
|
|
Fibrocartilage |
Very little ground substance. Found in intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, menisci of the knee) |

