![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 3 muscle types? |
1. Skeletal 2. Cardiac 3. Smooth |
|
|
What is the function of Skeletal muscle? |
Skeletal muscle moves the bones under conscious nervous control. Skeletal muscle is voluntary. |
|
|
What is the function of Cardiac muscle? |
Makes up the heart and requires no conscious nervous control. Cardiac muscle is involuntary. |
|
|
What is the function of Smooth muscle? |
Moves along objects inside the body, such as food through the digestive tract or urine in the bladder. Smooth muscle is involuntary. |
|
|
What is Homeostasis? |
An equilibrium that must be kept to maintain life. Like air conditioning and heating keeping a room a certain temperature. |
|
|
What are the 3 types of chemical bonds? |
1. Covalent bonds 2. Ionic bonds 3. Hydrogen bonds |
|
|
How is a Covalent bond formed? |
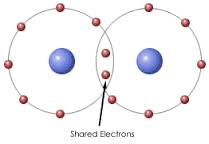
A Covalent bonds is formed when atoms share electrons. |
|
|
How is a Ionic bond formed? |
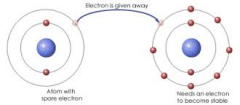
An Ionic bond is formed when electrons are transferred from one atom to another |
|
|
How is a Hydrogen bond formed? |
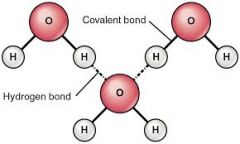
A Hydrogen bond is formed between hydrogen atoms of already formed covalent bonds |
|
|
Which of the 3 Chemical Bonds is the weakest? |
The Hydrogen Bond |
|
|
How is a Polar Molecule formed? |
A polar molecule is formed when electrons spend more time at one end of the molecule than the other, resulting in the molecule end with more electrons having a slight positive charge and the end with fewer electrons a slight negative charge. |
|
|
What is a Polar Molecule? |
A molecule with slightly charged ends |
|
|
What is a cation? |
A positively charged ion |
|
|
What is an anion? |
A negatively charged ion |
|
|
What are the 3 types of chemical reactions? |
1. Synthesis 2. Decomposition 3. Exchange |
|
|
How does a Synthesis Reaction work? |
A new, complex chemical is created from multiple simple chemicals, ie A+B=AB |
|
|
How does a Decomposition reaction work? |
A single, complex chemical is broken down into multiple, simple chemicals; ie AB=(A) (B) |
|
|
How does an Exchange reaction work? |
Certain atoms are exchanged between molecules, ie AC< >DB=AB><DC |
|
|
Contrast Solutes, Solution, Solvent |
Solutes: Chemicals added to water Solution: Result of chemical plus water Solvent: a substance into which other substances are dissolved |
|
|
What are the 4 special properties of water? |
1. Ideal transport medium 2. Has a high heat capacity 3. Has a high heat of vaporization 4. Good lubricator |
|
|
What are salts in their ionic form called? |
Electrolytes |
|
|
What is the simplest form of a carbohydrate? |
A simple sugar (monosaccharide) |
|
|
What is another name for neutral fats? |
Triglycerides |
|
|
Define Fatty Acid |
A chain of carbon atoms with 1 or hydrogen atoms attached by double or single bonds |
|
|
Define Saturated Fatty Acid |
A chain of carbon atoms where all bonds in the hydrocarbon chain are single and attached to the carbon |
|
|
Define Unsaturated Fatty Acids |
A chain of carbon atoms where some double bonds between the carbon and hydrogen atoms exist |
|
|
What do Lipoproteins do? |
Transport fats within the body |
|
|
What do Phosolipids do? |
Make up the lipid bilayer of cells |
|
|
What do Steroids do? |
Aid in the production of hormones |
|
|
What do Eicosanoids do? |
Mediate complex chemical processes |

