![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) |
A term used to refer to distinct conditions caused by a similar sequence of pathologic events-- a temporary or permanent blockage of a coronary artery |
|
|
Adrenergic |
Having the charecteristic of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervious system |
|
|
Afterload |
The pressure or resistance against which the ventricles must pump to eject blood |
|
|
Angina pectoris |
Chest discomfort or other related symptoms of sudden onset that may occur because the increased oxygen demand of the heart temporarily exceeds the blood supply |
|
|
Aortic valve |
SL valve on the left of the heart ; separates the left ventricle from the aorta |
|
|
Apex of the heart |
Lower portion of the heart that is formed by the tip of the left ventricle |
|
|
Arteriosclerosis |
A chronic disease of the arterial system characterized by abnormal thickening and hardening if the vessel walls |
|
|
Atherosclerosis |
A form of anteriosclerosis in which the thickening and hardening of the vessel walls are caused by a buildup of fatty deposits in the inner lining of large and middle sized muscular arteries |
|
|
Atria |
Two upper chambers of the heart (singular, atrium) |
|
|
Atrial kick |
Blood pushed into the ventricles because of atrial contraction |
|
|
Atrioventricular valve |
Valve located between each atrium and ventricle |
|
|
Which valve separates the right atrium form the right ventricle? |
Tricuspid valve |
|
|
Which valve separates the left atrium from the left ventricle? |
Bicuspid valve |
|
|
Atypical presentation |
Uncharacteristic signs and symptoms perceived by some patients experiencing a medical condition; such as ACS |
|
|
Base of the heart |
Posterior surface of the heart |
|
|
Blood pressure |
Force exerted by the blood against the walls of the arteries as the ventricles of the heart contract and relax |
|
|
Cardiac output |
The amount of blood pumped into the aorta each minute by the heart; defined as the stroke volume × heart rate |
|
|
What is stroke volume x heart rate? |
Cardiac output |
|
|
Catecholamines |
Natural chemicals produced by the body that have sympathetic actions ; epinephrine , norepinephrine, dopamine |
|
|
Cholinergic |
Having the characteristics of the parasympathetic division of autonomic nervious system |
|
|
Chords tendineae (tendinitis cords) |
Thin strands of fibrous connective tissue that extend from the AV valves to the papillary muscles that prevent the AV valves from bulging back into the atria during ventricular systolic (contraction) |
|
|
Chronotropy |
A change in (heart rate) |
|
|
Circumflex artery |
Division of the left coronary artery |
|
|
Coronary sinus |
Outlet that drains five coronary veins into the right atrium |
|
|
Diastole |
Phase of the cardiac cycle in which the atria and ventricles relax between contractions and blood enters these chambers |
|
|
Dromotropy |
Refers to the speed of conduction through the AV junction |
|
|
Dysrhythmia |
Any disturbance or abnormality in a normal rhythmic pattern (any cardiac rhythm other than sinus rhythm. |
|
|
Ejection fraction |
The percentage of blood pumped out of a heart chamber with each contraction |
|
|
Endocardium |
Innermost layer of the heart that lines the inside of the myocardium and covers the heart valves |
|
|
Epicardium |
The external layer of the heart wall that covers the heart muscle (also known as visceral pericardium) |
|
|
Great vessels |
Large vessels that carry blood to and from the heart |
|
|
What are examples of great vessles? |
Vena cava, pulmonary veins, aorta, pulmonary trunk |
|
|
Heart failure |
A condition in which the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the metabolic needs of the body. |
|
|
Hypercapnea |
A condition in which there is a elevated concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood |
|
|
Hypovolemia |
Inadequate tissue perfusion caused by inadequate vascular volume |
|
|
Infarction |
Death of tissue because of inadequate blood supply |
|
|
Inotrophy |
Refers to a change in myocardial contractility |
|
|
Ischemia |
Decreased supply of oxygenated blood to a body part or organ |
|
|
Left anterior descending artery |
Division of the left coronary artery |
|
|
Mediastinum |
Middle area of the thoracic cavity |
|
|
What does the mediastinum contain? |
Heart, great vessels, trachea, esophagus |
|
|
Mitrochondria |
The energy producing parts of a cell |
|
|
Myocardium |
Middle and thickest layer of the heart |
|
|
What does the myocardium contain? |
Cardiac fibers, contains the conduction system and blood supply |
|
|
Myofibril |
Slender striated strand of muscle tissue |
|
|
Neurotransmitter |
A chemical released from one nerve that crosses the synaptic cleft to reach a receptor |
|
|
Pericardium |
A double walled sac that encloses the heart and helps protect it from trauma and infection |
|
|
Peripheral resistance |
Resistance to the flow of blood determined by blood vessel diameter and the tone of the vascular musculature. |
|
|
Preload |
Force exerted by the blood on the walls of the ventricles at the end of diastole |
|
|
Proximal |
Location nearer to the midline of the body |
|
|
Pulmonary circulation |
Flow of unoxygenated (venous) blood from the right ventricle to the lungs and oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium |
|
|
Sarcolemma |
Membrane that covers smooth, striated and cardiac muscle fibers |
|
|
Sarcomere |
Smallest functional unit of myofibril |
|
|
Sarcoplasm |
Semifluid cytoplasm of muscle cells |
|
|
Sarcoplasmic reticulum |
Network of tubules and sacs that plays an important role in muscle contraction and relaxation by releasing and storing calcium ions |
|
|
Semilunar valves |
Valves shaped like half moons that separate the ventricles from the aorta and pulmonary ions |
|
|
Septum |
An internal wall of connective tissue |
|
|
Shock |
Inadequate tissue perfusion that results from the failure of the cardiovascular system to deliver sufficient oxygen and nutrients to sustain vital organ function |
|
|
Stroke volume |
The amount of blood ejected from a ventricle with each heartbeat |
|
|
Sulcus |
Groove |
|
|
Syncytium |
Unit of combined cells |
|
|
Systole |
Contraction of the heart during which blood is propelled into the pulmonary artery and aorta |
|
|
Tone |
Referring to the normal state of balanced tension in body tissues |
|
|
Venous return |
Amount of blood flowing to the right atrium each minute from the systemic circulation |
|
|
Ventricle |
Either of the 2 lower chambers of the heart |
|
|
How does blood flow through the heart? |
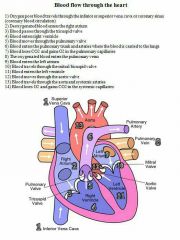
|

