![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Anatomy |
The study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts and their relationship to one another |
|
|
Physiology |
The study of how the body and its parts work or function |
|
|
Integumentary system |
The external covering of the body; the skin. - Protects deeper tissue from injury - Helps regulate body temperature - Location of cutaneous nerve receptors |
|
|
Skeletal system |
Consists of bones, cartilages, ligaments, and joints - Protects and supports organs - Provides muscle attachment for movement - Site of blood cell formation - Stores minerals |
|
|
Muscular system |
- Produces movement - Maintains posture - Produces heat |
|
|
Nervous system |
The body's fast-acting control system - Responds to internal and external change - Activates muscles and glands |
|
|
Endocrine system |
- Secretes regulatory hormones (growth, reproduction, metabolism) - The slow-acting control system |
|
|
Cardiovascular system |
Carries oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and other substances via blood pumped by the heart |
|
|
Lymphatic system |
- Returns fluid to blood vessels - Cleanses the blood - Involved in immunity |
|
|
Respiratory system |
Keeps the body constantly supplied with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide |
|
|
Digestive system |
- Breaks down food - Allows for nutrient absorption into blood - Eliminates indigestible material |
|
|
Urinary system |
- Eliminates nitrogenous wastes - Maintains acid-base balance - Regulates water and electrolytes |
|
|
Homeostasis |
The body's ability to maintain relatively stable internal conditions even though the outside world is continuously changing |
|
|
Homeostatic Imbalance |
A disturbance in homeostasis resulting in disease |
|
|
Sagittal section |
Divides the body or organ into left and right parts |
|
|
Median/midsagittal section |
Divides the body or organ into equal left and right parts |
|
|
Frontal section |
Divides the body or organ into anterior and posterior parts |
|
|
Transverse/coronal section |
Divides the body/organ into superior and inferior parts |
|
|
Dorsal body cavity |
- Cranial cavity houses the brain - Spinal cavity houses the spinal cord |
|
|
Ventral body cavity |
- Thoracic cavity houses the heart, lungs, and others -Abdominopelvic cavity houses digestive system and stomach, liver, intestines, reproductive organs, bladder |
|
|
Metabolism |
Refers to all chemical reactions that occur within body cells - Produces energy - Makes body structures |
|
|
Excretion |
eliminates wastes from metabolic reactions; the process of removing excreta from the body |
|
|
Nine body regions |
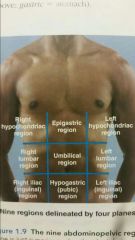
Nine regions. |
|
|
The four abdominopelvic quadrants |
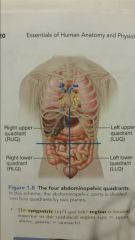
. |
|
|
Atoms |
tiny building blocks of matter that combine to form molecules |
|
|
Tissues |
consist of groups of similar cells that have a common function (epithelial, connective, muscular, and neural) |
|
|
Organ |
a structure composed of two or more tissue types that performs a specific function for the body |
|
|
Organism |
represents the highest level of structural organization |
|
|
Metabolism |
a broad term that refers to all chemical reactions that occur within body cells |
|
|
Excretion |
the process of removing wastes from the body |
|
|
Nutrients |
taken in by the body through food, contain the chemicals used for energy and cell-building |
|
|
Medistinum |
separates the lungs into right and left cavities |

