![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
166 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the two types of active transport? |
Active transport and vesicular transport |
|
|
What are three reasons to use active transport |
Solute too large, solute not lipid soluble, solute moving up concentration gradient |
|
|
What are the three different types of Carrie proteins |
Simple transporters, antiporters, and symporters |
|
|
Simple transporter |
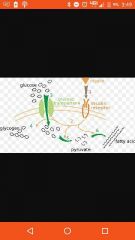
Allows one substance in |
|
|
Antiporter |
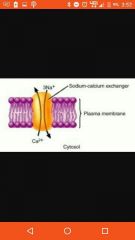
Allows one substance into cell and one cell out |
|
|
Symporter |

Allows 2 different substances to enter in the same direction |
|
|
Transyctosis |
Movement of material into cell (endocytosis) and then out of cell (exocytosis) |
|
|
Genes |
Code for one polypeptide |
|
|
RNA |
Single stranded nucleic acid (copy of DNA) |
|
|
What is the RNA backbone made of? |
Phosphate and ribose or deoxyribose |
|
|
What is the RNA base made of? |
A,C,G,T or U |
|
|
Which RNA translates to proteins |
mRNA |
|
|
Which RNA combines with proteins to make ribosomes |
rRNA |
|
|
tRNA |
Collects proper amino acid and brings it to ribosomes |
|
|
Where's the epidermis not located |
Eyes, mouth, kidneys, etc |
|
|
Dendritic cells |
Protects nucleus and makes sure nothing gets in |
|
|
Tactile cell |
Sensory cell in epidermis that's attached to a nerve |
|
|
What type of tissue is in the epidermis |
Epithelial |
|
|
What type of tissue is in the dermis |
Connective tissue |
|
|
3 types of accessory structure |
Hair nails and glands |
|
|
What do macrophages in the dermis do |
Eat invaders and are wandering cells |
|
|
What makes up the cutaneous layers |
Epidermis and dermis |
|
|
What are the two layers of the dermis |
Papillary and reticular |
|
|
How is the epidermis important to bones |
Vitamin d3 synthesis takes place here |
|
|
What organs are used in vitamin D3 synthesis |
Liver and kidneys |
|
|
Which layer of the epidermis is fastened together by desmosones and is considered "spiney" |
Stratum spinosum |
|
|
Which epidermal layer has granules of keratin and lipids in the cytoplasm |
Stratum granulosum |
|
|
Which epidermal layer has visible nuclei |
Stratum granulosum |
|
|
Which epidermal layer has disintegrating organelles |
Stratum granulosam |
|
|
What are the two types of epidermis |
Thick and thin |
|
|
Where's thick epidermis located |
Palms, soles, lips |
|
|
What type of tissue is found in the papillary later of the dermis |
Areolar |
|
|
Which layer of the dermis contains tactile corpuscles |
Papillary |
|
|
What type of tissue is found in the reticular layer of the dermis |
Dense irregular connective tissue |
|
|
Lines of collagen fibers in reticular later |
Lines of tension |
|
|
Vessels, nerve endings, and accessory structures are located in what dermal layer |
Reticular |
|
|
Melanin protects what structure |
Folic acid |
|
|
Flexure lines |
Permanent wrinkles around joints |
|
|
What are the two types of melanin |
Pheomelanin and eumelanin |
|
|
Pheomelanin |
Reddish yellow melanin |
|
|
Eumelanin |
Brownish black melanin |
|
|
What three things affect skin color |
Melanin carotene and hemoglobin |
|
|
This chemical in your skin is converted to vitamin A |
Carotene |
|
|
Root |
Portion in skin |
|
|
Shaft |
Portion outside skin |
|
|
Medulla (hair) |
Inner, large cells and air spaces |
|
|
Cortex (hair) |
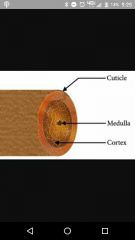
Middle, flattened cells |
|
|
Cuticle (hair) |
Outter later |
|
|
Terminal hair |
Hair on head |
|
|
Vellus hair |
Fine body hair |
|
|
Lanugo |
Hair on infants |
|
|
Enzyme |
Protein (chain of amino acids folded into a specific shape) |
|
|
How do you name an enzyme |
Add "ase" to it's substrate |
|
|
What type of tissue makes glands |
Epidermal tissue |
|
|
Sebaceous gland |
Secretes oil (sebum"lipid mixture) |
|
|
What hormones control sebaceous glands |
Sex hormones |
|
|
Sudoriferous glands |
Sweat glands |
|
|
Eccrine gland |
Sweat glands on palms, soles, and forehead that is mostly water and similar to a sports drink. |
|
|
Apocrine gland |
Armpits and genial seat glands that secrete milky yellowish substance and is stinky |
|
|
Mammory and earwax are what types of glands |
Appocrine |
|
|
Nail plate |

Whole thing |
|
|
Free edge (nail) |
|
|
|
Nail root |
|
|
|
What are the parts of the skeletal system |
Cartilage, bone, and ligaments |
|
|
Ligament |
Connects bone to bone |
|
|
What type of tissue makes up ligaments |
Dense regular connective tissue |
|
|
Hemopoesis |
Make blood. Dinner in bones |
|
|
Functions of cartilage |
Support for soft tissue, gliding joints, template for growth |
|
|
3 types of cartilage |
Hyaline, fibrocartilage, and elastic |
|
|
Hyaline cartilage |
Movement in slidey joints. (Rib cage) can shatter |
|
|
Fibrocartilage |
Shock absorber. Found in disks |
|
|
Elastic cartilage |
In ears and epiglottis |
|
|
3 tissues that make up bones |
Connective, epithelial, and nervous |
|
|
Epithelial tissue in bones? |
Blood vessels |
|
|
Diaphysis |
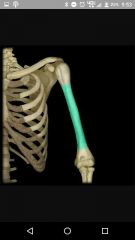
Middle part of bone |
|
|
Epiphysis |
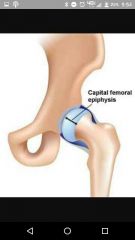
Ends of bone |
|
|
Epiphyseal plate |
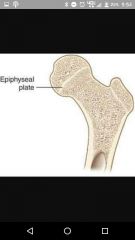
Used to be cartilage |
|
|
Articular cartilage |
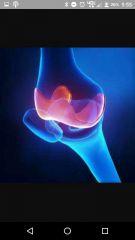
|
|
|
Flat bones |

Look like a bone sandwich |
|
|
Sesamoid bones |
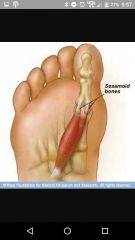
Firm inside tendons (knee cap) |
|
|
Red marrow |
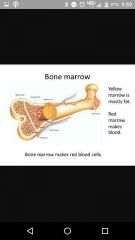
In spongey bone, cite of hematopoiesis |
|
|
Yellow marrow |
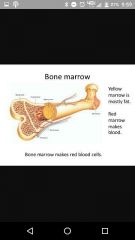
In shaft. Fat storage. As we grow older we go from red to yellow |
|
|
What are the three bone coverings |
Perosteum,, perforating fibers, endosteum |
|
|
Perosteum |
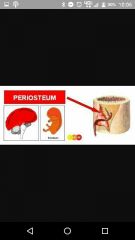
Outside layer of bone (denseirregular CT) and osteogenic layer |
|
|
Osteogenic layer |
Layer of periosteum where bone cell growth is promoted |
|
|
Perforated fibers |
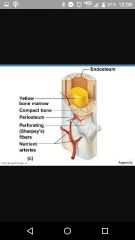
Continuous with ligament and tensions. Contains nerves and blood vessels |
|
|
Endosteum |
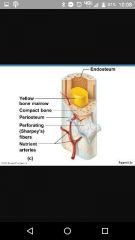
Covers trabeculae and internal surfaces. Contains cells |
|
|
Trabeculae |
Little holes in bone |
|
|
Osteogenic cells |
Bone stem cells |
|
|
Osteoblasts |
Build. Secrete bone matrix that becomes bone |
|
|
Osteoid |
Organic (collagen) part of bones |
|
|
Osteocytes |
Stay. Keep tissue healthy. Stay in lacunae. Respond to pressure |
|
|
Osteoclasts |
Breaks down bone |
|
|
Spongey bone |
Withstand force from all directions. Contains trabeculae |
|
|
Compact bone |
Bends |
|
|
Four parts of compact bone |
Osteons, lamella, lacunae, and canaliculi |
|
|
Lamella |
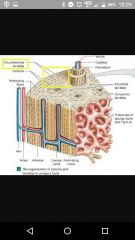
Layers of collagen tissue (circumferential and interstitial) |
|
|
Lacunae |
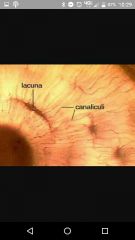
Spaces where osteocytes live |
|
|
Canaliculi |
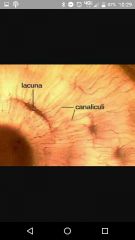
Canals connecting lacunae |
|
|
In utero all one is made from |
Headline cartilage and fibrous membranes |
|
|
These bones are made by intramembranous ossification |
Skull and clavicle |
|
|
Which bones use endochondrial ossification? |
All except clavicle |
|
|
Appositional growth |
Bone added under periosteum while bone is removed inside |
|
|
Where's the parathyroid hormone |
Back of neck |
|
|
This hormone monitors blood calcium |
Parathyroid |
|
|
Wolf's law |
Bone grows thicker where stressed |
|
|
Articulations |
Places where two bones meet |
|
|
4 types of fractures |
Position of bone ends, completeness of fracture, orientation of break, perversion of skin |
|
|
Nondisplaced fracture |
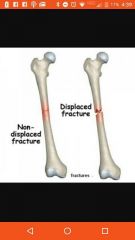
Bone didn't move |
|
|
Displaced fracture |
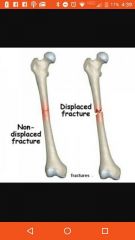
Bone moved |
|
|
Transverse fracture |
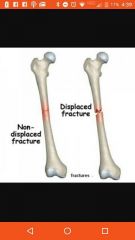
Across bone |
|
|
Compound fracture |

Touches skin |
|
|
Hematoma stage in fracture |
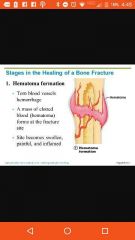
Swelling after few minutes. Some cells die |
|
|
Fibrocartilaginous stage |
Vessels begin to grow back |
|
|
What happens during callus stage of fracture |
Soft callus becomes boney callus |
|
|
Osteomyelitis |
Bone infection |
|
|
Synarthroses |
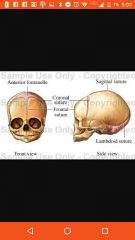
Immovable |
|
|
Ampharthroses |
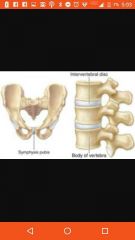
Slightly movable |
|
|
Diarthroses |
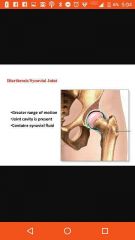
Freely movable |
|
|
2 ways to classify articulations |
Motion and structure |
|
|
3 structures of articulations |
Fibrous, cartilage, synovial(membrane) |
|
|
3 types of fibrous joints |
Sutures, syndesmoses, gomphoses |
|
|
Syndesmoses |
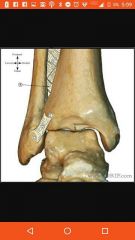
Immovable joint |
|
|
Gomphoses |
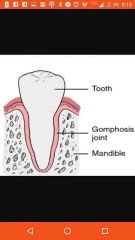
In teeth |
|
|
5 parts of synovial joints |
Articular cartilage, joint cavity, articular capsule,synovial fluid, reinforcing ligaments |
|
|
Articular cartilage |
At ends of bones, prevents crushing of bone ends |
|
|
Joint cavity |
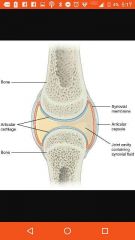
Filled with synovial fluid |
|
|
Articular capsule |
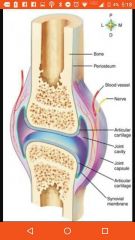
External fibrous layer |
|
|
Bursae |
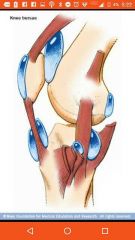
Bags of synovial fluid that act as ball bearings |
|
|
Tendon sheath |
Elongated bursae |
|
|
Luxation |
Dislocation of joint |
|
|
Glenohumeral |
Shoulder joint |
|
|
3 types of muscle |
Skeletal, smooth, cardiac |
|
|
Synctial |
Fusion of many cells |
|
|
Satellite cells |
Muscle repair |
|
|
Endomyseum |
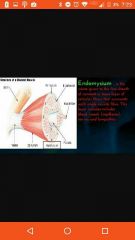
Areolar tissue that covers a muscle cell |
|
|
Perimyseum |
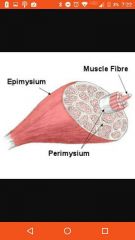
Covers bundles (fasicles) of cells |
|
|
Epimysium |
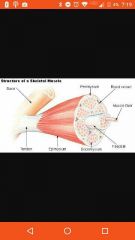
Covers muscle |
|
|
Fascia |
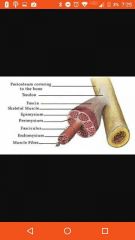
Covers multiple muscles |
|
|
Aponeurosis |
Fibrous white tissue that takes the place of tendons |
|
|
Hinge joint |
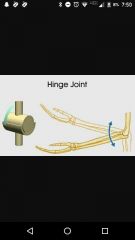
Elbow |
|
|
Pivot joint |
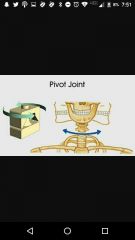
|
|
|
Condyloid joint |
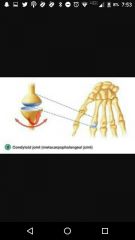
Fingers |
|
|
Sliding joints |
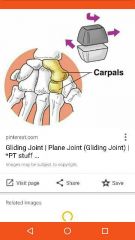
Carpals |
|
|
Ball and socket joint |
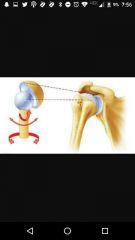
Shoulder |
|
|
Saddle joint |
Thumb |
|
|
Agonist muscle |
Muscle that contracts and does movement |
|
|
Antagonist |
Relaxes |
|
|
Synergist |
Helps agonist |
|
|
Fixator |
Keeps form and joints steady during flexure |
|
|
Muscle cell membrane |
Sarcolema |
|
|
Muscle cell cytoplasm |
Sarcoplasm |
|
|
Muscle cell ER |
Sarcoplasmic reticulum (stores calcium) |
|
|
Transverse tubules |

Deep tunnels of sarcolemna in cell |
|
|
Myoglobin |
Stores oxygen in muscle |
|
|
Myofibrils |
Threadlike organelle made of myofilaments |
|
|
Actin |
Long twisted chains of globular proteins |
|
|
Tropomyosin |
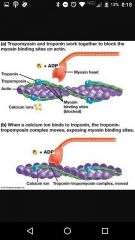
Protein that covers actin |
|
|
Troponin |
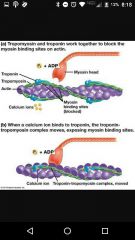
|
|
|
Myosin |
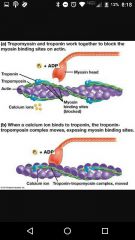
Golf club shaped protein |
|
|
Elastic filaments |
Run through middle of thick filaments |
|
|
Sarcomere |
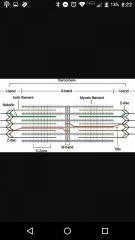
Runs z to z disc |
|
|
A band |
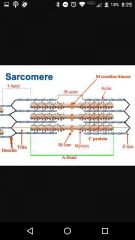
Overlapping myosin and thin filaments |
|
|
I band |
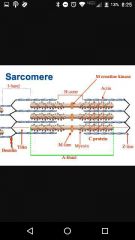
Light part. Only thin filaments |
|
|
Depolarization |
Large influx of NA+ into cell |
|
|
Repolarization |
Potassium out of cell |

