![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
151 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Angiogram |
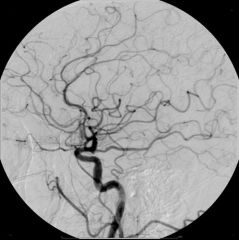
imaging of the blood vessels/vascular system
'vessel picture' |
|
|
Adenocarcinoma |
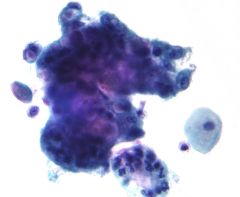
Cancerous tissue/tumor
'glandular crab swelling/tumor' |
|
|
Anthropomorphic |

'human shaped' |
|
|
Epiphyseal plate |
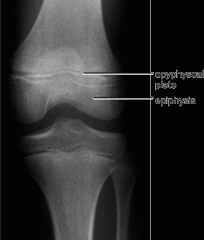
bone structure responsible for bone lengthening/growth. |
|
|
Periosteum |
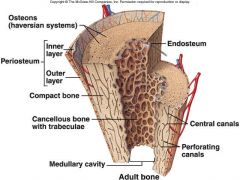
membrane surrounding the bone |
|
|
Cancellous Bone |
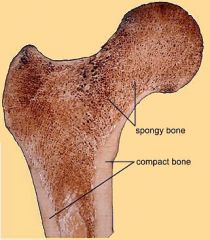
Trabecular/Spongy bone |
|
|
Cortical Bone |
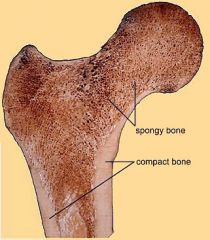
Compact bone structure |
|
|
Anterior-Posterior (AP) Projection |
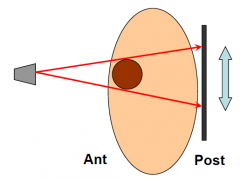
X-ray source anterior to subject, film flat against posterior surface. |
|
|
Posterior-Anterior (PA) Projection |
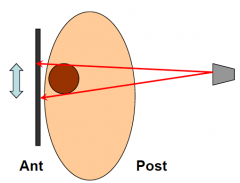
X-ray source posterior to subject, film flat against anterior surface. |
|
|
Computed Tomography Limitations |
-Back projection = computationally intensive
-Resolution limited by a) size of detectors b) thickness (collimation) of x-ray beam
-Noise determined by sensitivity of detectors, rotational speed. Fewer photons = more noise |
|
|
Chest/Abdominal radiograph orientation |
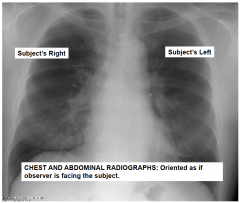
Facing patient |
|
|
LUT |
Lookup table - contrast range for image formation |
|
|
Hounsfield Number |
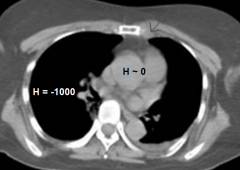
(CT numbers) = linear mapping of tissue density |
|
|
'Windowing' CT images |
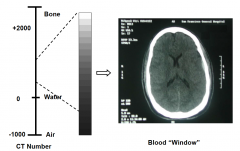
|
|
|
Major planes used in sectional anatomy |
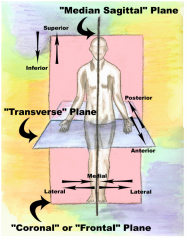
|
|
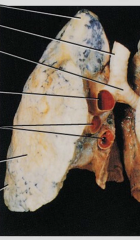
|
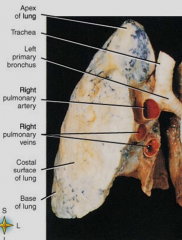
|
|
|
Echocardiography |
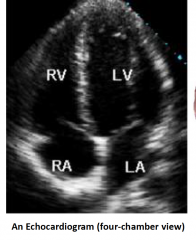
Ultrasound image of the heart |
|
|
Subpleural |
under the membrane of the lungs |
|
|
Pneumothorax |
collapsed lung (air leaks into space between chest and lungs) |
|
|
Intercostal |
space between the ribs |
|
|
Nephrolithiasis |
kidney stones |
|
|
Uterolithiasis |
kidney stone in ureter |
|
|
Gonads |
male-testicles
female-ovaries |
|
|
Crohn's disease |
fistula (abnormal passage between organs) of the colon/bowels |
|
|
Cranio-caudal |
head to tail |
|
|
Lithotripsy |

ultrasound procedure that breaks up kidney stones |
|
|
Erythema |
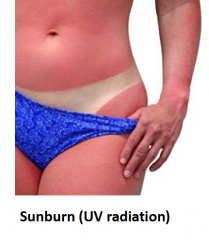
red skin |
|
|
Epilation |
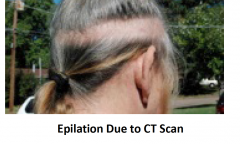
hair falling out |
|
|
Stenosis |
Narrowing of something (blood vessels, lumbar, aortic valve etc) |
|
|
Renal |
kidneys |
|
|
Lumen |
refers to inside of a cylinder` |
|
|
Hemodynamics |
motion of the blood |
|
|
Renal artery stenosis |
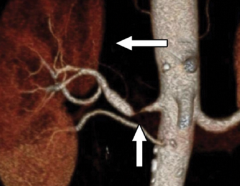
|
|
|
micturating cystourethrography |
imaging of urethra/bladder while urinating |
|
|
Conceptus |
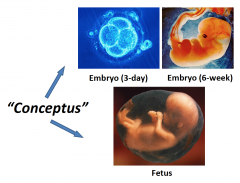
refers to any stage of pregnancy |
|
|
Extravasation |
leaking of fluid out of its container... i.e. bad IV placement |
|
|
Papillary thyroid carcinoma |
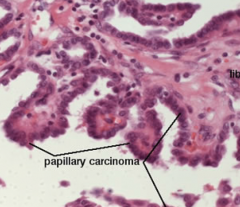
|
|
|
Anaplastic carcinoma |
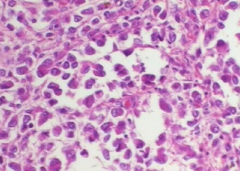
fast, out of control growth |
|
|
Cineangiography |
flouroscopic images of contrast through blood vessels by motion picture techniques. |
|
|
Desquamation |
skin peeling |
|
|
Electrocardiogram |
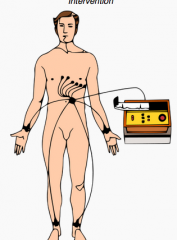
recording of the electrical activity of the heart |
|
|
Epidemiology |
study of patterns/causes of health and disease conditions in defined populations. |
|
|
Intraperitoneal |
injection of substance into abdominal area |
|
|
Intrathecal |
introducing/occurring in the space under the arachnoid membrane of the brain/spinal cord |
|
|
Lymphangiography |
contrast induced imaging of lymphatic system |
|
|
Metastasis |
spreading of cancer from one organ to another |
|
|
Myelosuppressive |
side effect of some cancer treatments (bone marrow activity is decreased) |
|
|
Neutropenia |
abnormally low count of neutrophilis
(white blood cells that help fight off infections) |
|
|
Pancytopenia |
medical condition in which there is a reduction in the number of red and white blood cells & platelets. |
|
|
Parenchyma |
the functional tissue or cells of an organ or gland
as distinguished from supporting or connective tissue |
|
|
Pharmacokinetics |
what the body does to a drug/ movement |
|
|
Pyrogen |
fever inducing substance |
|
|
Reticuloendothelial |
(system) - also called macrophage system, class of cells that are throughout body and take up particular substances (part of body's defense mechanisms) |
|
|
Sarcoma |
general term for cancers of the bone and soft tissue |
|
|
Scintimmamography |
breast imaging for cancer cells (TC-99) (gamma camera) |
|
|
Thrombocytopenia |
low blood platelet(thrombocyte) count
-blood clotting |
|
|
Thrombolytic |
Therapy- drugs used to break up or dissolve blood clots
(heart attack/stroke) |
|
|
Thryrotoxicosis |
excessive amount of thyroid hormone in the body |
|
|
Tomography |
process of imaging by sections/sectioning |
|
|
Urticaria |
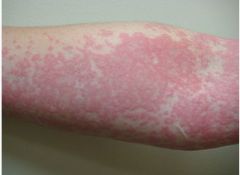
Hives
(pale red, raised, itchy bumps) |
|
|
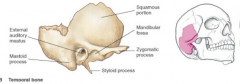
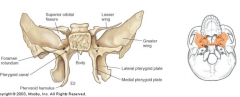
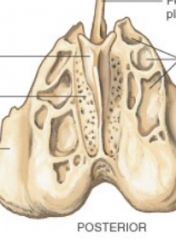
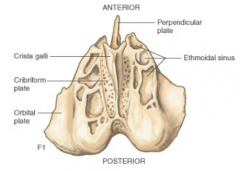
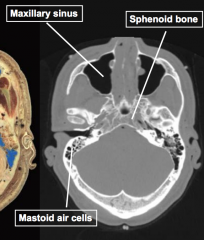
Foramen |

ie. sphenoid bone for neurovascular bundles |
|
|
Fossa, sulcus, & groove |
depressions for various shapes/depths/sizes |
|
|
Process, tubercle, and tuberosity |
bumps of various sizes/shapes |
|
|
Spine |
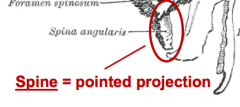
|
|
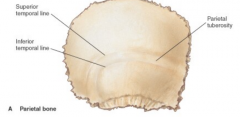
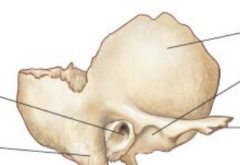
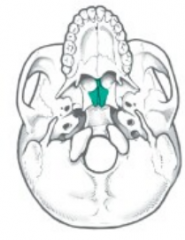
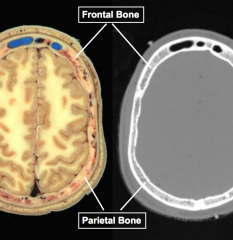
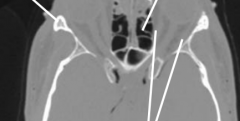
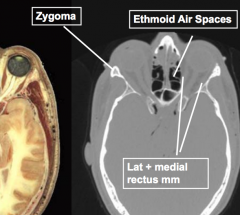
Name the bones |
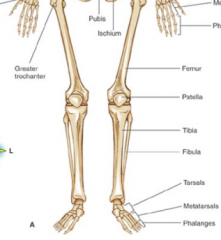
|
|
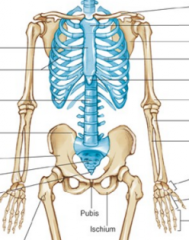
Name the bones |
|
|
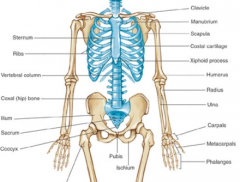
Name the bones |
|
|
|
Axial skeleton vs appendicular skeleton |
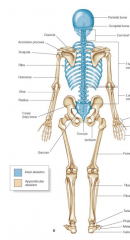
Blue = axial
|
|
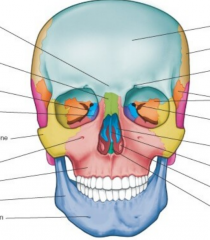
Name the bones |
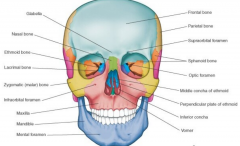
|
|
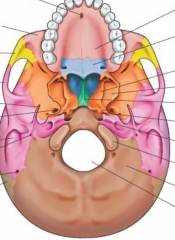
Name the bones |
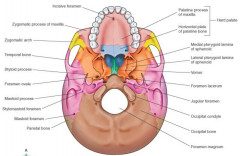
|
|
|
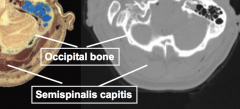
Squamous |
Flat |
|
|
Nuchal |
neck |
|
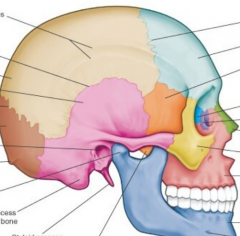
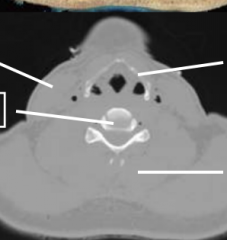
Name the bones |
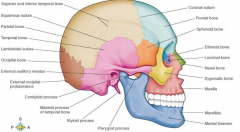
|
|
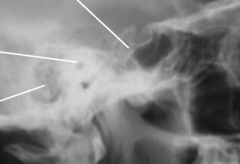
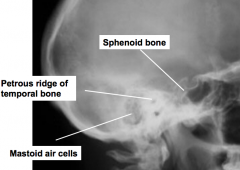
Skull lat proj |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
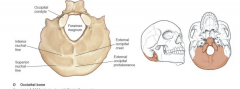
|
|
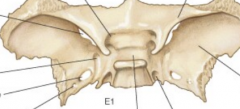
|
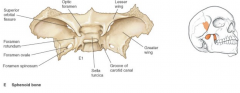
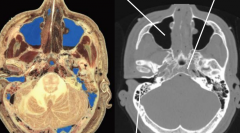
Note : pituitary gland is in the sella turcica |
|
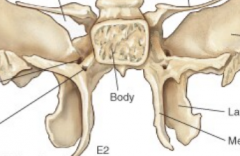
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
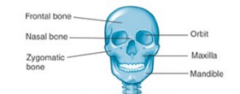
Vomer |
|
|
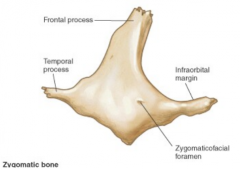
Zygomatic Bone |
|
|
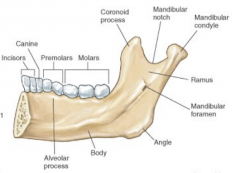
Mandible |
|
|
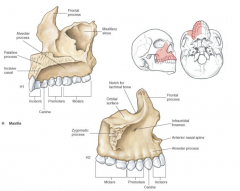
maxilla |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
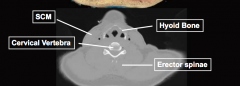
|
|
|
Number of true ribs vs false ribs |
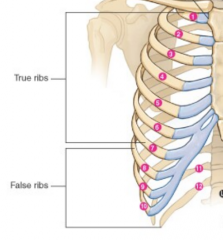
7- true ribs
5- false ribs |
|
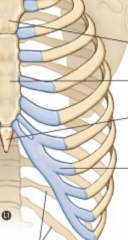
|
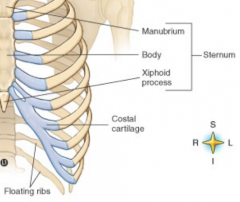
|
|
|
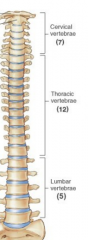
Number of vertebrae in spine and locations/sections |
|
|
|
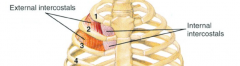
Intercostals |
|
|
|
|
|
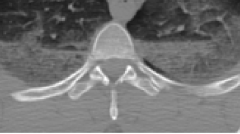
|
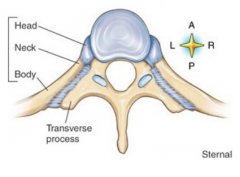
Spinal vertebrae |
|
|
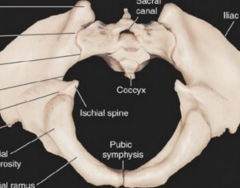
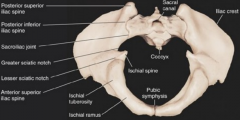
Main difference in the male/female pelvis |
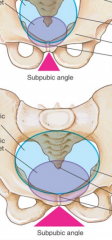
subpubic angle & pelvic aperture |
|
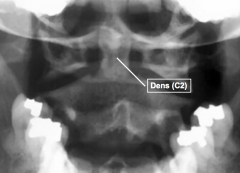
|
the dens provides support/rotation for the skull.
fractured dens = death |
|
|
|
|
|
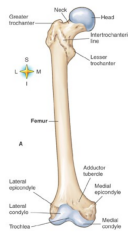
Radius or ulna supports majority of the weight |
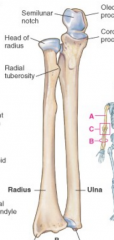
radius |
|
|
Deltoid Tuberosity |
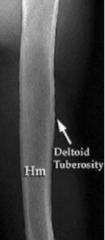
excess bone on the humerus usually seen on body builders/hard working persons |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
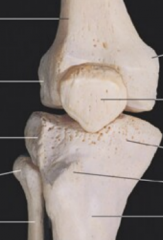
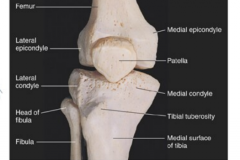
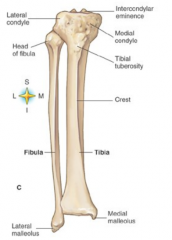
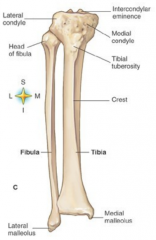
Tibia of Fibula holds majority of the weight |
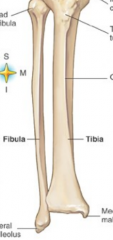
Tibia |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
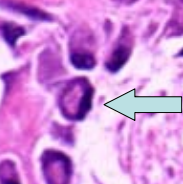
Bone remodeling process |
osteoclasts break bone down and osteoblasts build bone back up.
continuous and cyclical process. 2-4 week resorption phase. 4-6 month formation phase. |
|
|
Osteoblast (builds bone) |
|
|
Osteoclast (breaks bone down) |
|
|
Bone re-construction process |
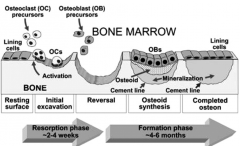
|
|
|
Bone remodeling process is stimulated by what? |
piezoelectric effects secondary to stresses on hydroxyapatite crystals in bone |
|
|
Types of muscle tissue |
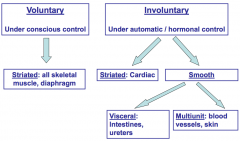
|
|
|
Types of involuntary muscle |
Striated (cardiac) & smooth |
|
|
Types of smooth muscle |
Visceral (intestines, ureters)
Multiunit (blood vessels, skin) |
|
|
Fascia |
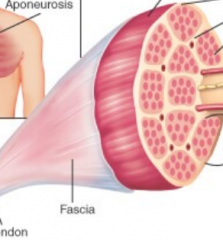
muscle 'skin' |
|
|
muscle stuff. Not crucial to memorize. |
|
|
Structural hierarchy of striated muscle |
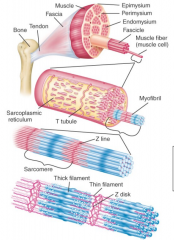
(skeletal = striated)
Muscle, fascicle, muscle fiber cell, myofibril, myofilament |
|
|
Muscle fiber vs cellular anatomical terminology
Muscle fiber = Sarcolemma = Sarcoplasm = Sarcoplasmic Reticulum = T - Tubules (transverse tubules) |

|
|
|
Thin myofilaments components and arrangement with thick myofilaments |
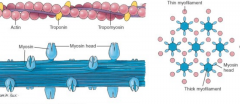
thin myofilaments = actin, troponin, tropomyosin
thick filaments = myosin / myosin heads |
|
|
Sarcoma |
General term for cancer of the bone and soft tissue |
|
|
Reticuloendothelial |
(system) macrophage cells. Defense mechanism |
|
|
Microvilli, Cilia, Flagella |
Microvilli - extensive folding for SA increase (cellular membrane).
Cilia - motile projections that move fluids external to cell.
Flagella - motile projections that permit cell to move. |
|
|
Cell Cycle |
G1, S, G2, Mitosis, Cytokinesis |
|
|
Mitosis
Haploid Gamete |
Before meiosis -Diploid Parent cell (46 pair chromosomes)
Haploid gamete - Product of meiosis 2 (23 chromosomes) |
|
|
Meiosis 1 & 2 |
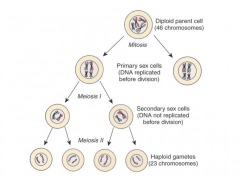
|
|
|
The chemical messengers of the body are called __________. |
hormones |
|
|
The ball and socket joint for humerus. Name and location. |
Name - Glenoid Fossa
Location - Scapula |
|
|
Mark that indicated the superior border of the sternum |
suprasternal notch |
|
|
Locations and function of respiratory epithelial mucosa. |
Located in the paranasal cavities, larynx, trachea, and bronchi.
Function - to moisten the air and trap particulates (cilia) |
|
|
Where are microvilli located |
mainly in small intestines |
|
|
Trachea generations (~total number) |
~ 14 total generations
ie. 1st = trachea 2nd = primary bronchi |
|
|
Atmospheric partial pressures of O2 and CO2 |
O2 ~160 mmHg
CO2 ~ 2 mmHg
Total atm pressure ~ 760 mmHg |
|
|
CO2 Transport percentages and forms |
10% dissolved in blood plasma
20% in RBC as carbaminohemoglobin
70% as bicarbonate dissolved in blood plasma |
|
|
Calcium storage site and critical function |
Calcium
- stored in bones
- critical in muscle contraction |
|
|
Yellow marrow vs red marrow |
yellow - in very center of bone, radiation irrelevant, fat & cells that remove dead RBCs and bacteria from blood
red - in trabeculai of bone, radiation target, cells that create RBCs WBCs and platelets. (sternum, ribs, ends of long bones) |
|
|
Parenchyma |
the functional part of an organ |
|
|
Amino Acids |
used in metabolism but mainly the building blocks of proteins |
|
|
Proteins |
complex organic molecules that consist of amino acids linked via peptide bonds |
|
|
Protein structural levels |
primary - amino acid sequence
secondary - H2 bonding (helices, sheets, chains)
tertiary - H2 bonding & disulfide bridging (folds)
quaternary - combination of tertiary structures |
|
|
Sterols |
cholesterol & steroid hormones
(cholesterol, cortisol, estrogen, testosterone) |
|
|
Example/name of simple sugar |
monosacchrides |
|
|
ATP and flow between food and cellular energy |
adenosine triphosphate -
food converted to ATP to be used by muscles then ADP (adenosine diphosphate) is sent back to where ATP conversion sites to make more ATP |
|
|
DNA structure is stabilized by _________ bonding
DNA constituents and classes. |
Hydrogen
classes - Purines and pyrimidines
purines - adenine & guanine
pyrimidines - cytosine & thymine |
|
|
The main cell structure consists of _________, ___________, and ____________. |
organelles, plasma membrane, and cytoplasm |
|
|
When were x-rays discovered and by whom? |
Wilhem Roentgen in 1895 |
|
|
Problems with radiographs - |
1. overlapping structures
2. geometric distortions
3. reduced contrast |
|
|
Supine |
position of patient when he/she is lying on their back |
|
|
Hematoxycin and Eosin |
Hematoxysin - dye that reacts with negative phosphate groups (DNA) and stain them dark blue.
Eosin - acidic dye that reacts with positively charged chains and stains them red. |
|
|
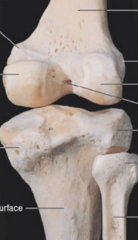
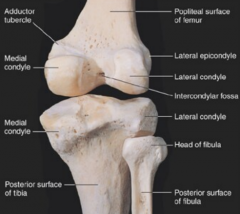
Intercondylar eminence |
top of the tibia |
|
|
Ischemia vs Infarction |
Ischemia - restricted blood supply/flow
Infarction - necrosis (death) of the tissue |

