![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
macroscopic (gross) anatomy
|
structures seen with th naked eye
|
|
|
systemic anatomy
|
the study of the 11 specific body systems
|
|
|
regional anatomy
|
specific region including their tissues
|
|
|
microscopic anatomy
|
structures that cannot be seen with the naked eye
|
|
|
cytology
|
study of cells
|
|
|
histology
|
study of tissues
|
|
|
medical/ radiological
|
characteristic changing in anatomy during disease. visible with radiographic technology
|
|
|
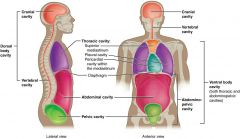
body can be divided in 3 main divisions
|
body wall, body cavities, organs
|
|
|
integumentary system
|
forms the outermost part of the body (skin) protect from the environment and temperature control
|
|
|
skeletal system
|
consists of bones, ligaments, cartilage, tissue. supports, protects, blood formation, mineral storage
|
|
|
muscular system
|
consists skeletal muscles and tendons. supports, heat production and mobility
|
|
|
nervous system
|
central(brain,spinal cord) peripheral(motor,sensory nerve) controls body systems, identify internal& external environments
|
|
|
endocrine system
|
glandular tissue in body. coordinates and controls body systems with hormones
|
|
|
cardiovascular system
|
heart and blood vessels, internal transport of dissolved material: nutrients, gases,waste
|
|
|
lymphatic system
|
structures throughout the body, consists lymph vessels, nodes, organs. internal defense & blood volume maintenance
|
|
|
respiratory system
|
exchange of gases with the body and environment
|
|
|
digestive system
|
primarily within abdominal cavity, processing of food &absorption of nutrients,minerals, vitamins, water. eliminates waste
|
|
|
urinary system
|
pelvic cavity, consists kidney, ureter, bladder,urethra. regulation of blood chemistry by the elimination of excess water,salts,n waste
|
|
|
reproductive system
|
pelvic cavity. contains sex organs. production n support of sex cells and hormone production
|
|
|
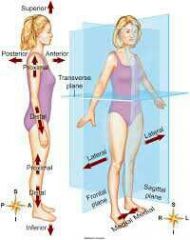
standard anatomical position
|
stand straight
arms to side lower limbs together palms away n thumbs away from body |
|
|
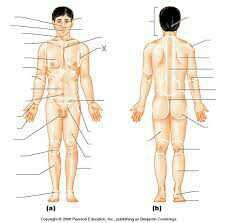
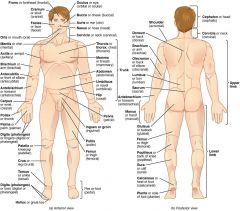
anatomical name and region for armpit
|
axilla
axillary |
|
|
cavities
|
|
|
planes and directional terms
|
|
|
cavities
|
|
|
|
|
|
anatomical name and region for knee
|
patella
patellar |
|
|
anatomical name and region for calf
|
sura
sural |
|
|
anatomical name and region for front of elbow
|
antecubitis
antecubital |
|
|
anatomical name and term for forearm
|
antebrachium
antebrachial |
|
|
anatomical name and region for upper arm
|
brachium
brachial |
|
|
anatomical name and region for shoulder
|
acromium
acromial |
|
|
anatomical name and region for back of the leg
|
sura
sural |
|
|
midsagittal plane
|
midline separates left and right
|
|
|
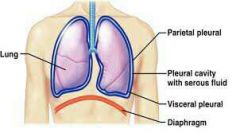
serous membrane
|
tissue that lines internal cavities
|
|
|
mediastinum
|
a membranous partition between 2 body cavities or parts of an organ ex lungs
|
|
|
lines the heart
|
parietal pericardium
|
|
|
lines the pleural cavity, lungs
|
parietal pleura
|
|
|
embryology
|
study of developmental changes of the body before birth
|
|
|
principal of complementarity
|
function depends on structure
form follows structure |
|
|
pathologist
|
studies tissue and how disease changes them
|
|
|
hierarchy levels of structural organization
|
chemical
cellular tissue organ organ system organismal |
|
|
necessary life functions
|
maintaining boundaries
movement responsiveness digestion metabolism excretion reproduction growth |
|
|
increase in size of a body part (increase in cell number or size of cell)
|
growth
|
|
|
all the chemical reactions that occur in body cells
|
metabolism
|
|
|
catabolism
|
break down substances to smaller ones, releasing energy
|
|
|
add small molecules to make larger ones
|
anabolism
|
|
|
5 survival needs
|
nutrients
oxygen water normal body temperature atmospheric pressure |
|
|
stimulus, receptor,control center, effector,
|
negative feedback
|
|
|
axial region
|
head neck trunk
|
|
|
appendicular region
|
all limbs
|
|
|
visceral
|
covers internal organs
|

