![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
198 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Hip/coxal bones |
• Ilium • Ischium • Pubis |
|
|
|
How many vertebrae? |
33 |
|
|
|
How many are moveable? |
26 |
|
|
|
How many intervertebral discs |
23 |
|
|
|
Transmits weight of body from vertebral column to pelvis |
Sacroiliac joint |
|
|
|
Strongest joint of the pelvis |
Interosseous |
|
|
|
Disruption of the symphysis pubis Slight opening of the sacroiliac joints |
Open book fracture |
|
|
|
Fracture of both superior and inferior pubic rami
Genitourinary injury are likely |
Straddle fracture |
|
|
|
The pelvic inlet and brim divides the pelvis into |
False/greater True /lesser pelvis |
|
|
|
Boundaries of the pelvic inlet and brim |
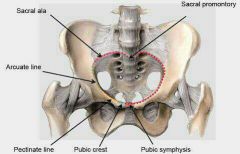
Sacral promontory
Iliopectineal line [arcuate line of the ilium] and pectineal line (pecten pubis)]
Symphisis pubis |
|
|
|
Boundaries of pelvic outlet |
Coccyx Sacrotuberous ligaments Ischial tuberosities Ischiopubic rami Pubic symphysis |
5 boundaries |
|
|
Clinically measurable in pelvic inlet |
Diagonal conjugate |
|
|
|
Shortest conjugate |
Obstetrical conjugate |
Usually 10cm or more |
|
|
Diagonal conjugate minus 1.5 or 2cm |
Obstetrical conjugate |
Usually 10cm or more |
|
|
Smallest pelvic diameter in the midpelvis |
Interspinous diameter |
10cm or slightly greater |
|
|
Smallest diameter of the pelvic outlet |
Intertuberous diameter |
|
|
|
Typical female pelvis |
Gynecoid pelvis |
41% |
|
|
Male shaped |
Android |
33% |
|
|
Long, narrow and oval shaped |
Anthropoid |
24% |
|
|
Wide pelvis flattened at brim |
Platypelloid |
2% |
|
|
Fetal position that is predisposed in anthropoid pelvis |
Occiput posterior position |
|
|
|
Fetal position predisposed position in platypelloid pelvis |
Occiput transverse position |
|
|
|
Walls of the pelvic cavity |
lateral - Obturator internus Posterior - Piriformis Floor - Pelvic diaphragm |
|
|
|
Heart shaped inlet |
Android |
|
|
|
Shallow pelvic cavity |
Platypelloid |
|
|
|
Roomier pelvic cavity |
Gynecoid |
|
|
|
Cylindrical pelvic cavity |
Female pelvis |
|
|
|
Funnel shaped pelvic cavity |
Male pelvis |
|
|
|
Larger outlet |
Female pelvis |
|
|
|
Everted ischial tuberosities |
Female pelvis |
|
|
|
More rounded and wider pubic arch |
Female pelvis |
|
|
|
Muscles of the levator ani |
1. Ani Puborectalis (Maintain anorectal flexure) 2. Iliococcygeous 3. Pubococcygeous |
|
|
|
What's inside of the obturator canal |
Obturator vessels Obturator nerve |
|
|
|
Crossed superiorly by the vas deferens |
Ureter |
|
|
|
Crossed superiorly by the uterine artery |
Ureter |
|
|
|
Maximum capacity of the urinary bladder |
500ml |
|
|
|
Volume to desire to micturate |
300ml |
|
|
|
Useful landmark for ureteral identification |
InterUreteric ridge (Mercier bar) |
|
|
|
Blood supply of the urinary bladder |
Superior vesical artery
Inferior vesical artery (males) Vaginal artery (females) |
|
|
|
Origin of superior vesical artery |
Umbilical artery |
|
|
|
Origin of inferior vesical artery |
Internal iliac artery |
|
|
|
Origin of the vaginal artery |
Internal iliac artery |
|
|
|
Epithelium of the urinary bladder |
Transitional Epithelium |
|
|
|
Muscle layer of the urinary bladder |
Detrussor muscle |
|
|
|
Sphincter that is Involuntary and controlled by the Autonomic nervous system |
Internal urethral sphincter
Sphincter vesicae |
|
|
|
Sphincter that is voluntary and controlled by the somatic nervous system.
Pudendal nerve |
External urethral sphincter
Sphincter urethrae |
|
|
|
Most common type of bladder cancer |
Transitional cell carcinoma |
Painless hematuria Smoking Aniline dyes |
|
|
Level of sigmoid colon |
At the pelvic brim S3 |
|
|
|
Blood supply of sigmoid colon |
Sigmoidal arteries from Inferior mesenteric artery |
|
|
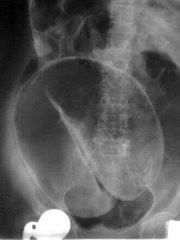
Coffee bean sign |
Volvulus (sigmoid) |
|
|
|
Most common site of volvulus |
Sigmoid volvulus |
|
|
|
Hartman technique |
1.Resection of sigmoid colon 2.Closure of rectal stump 3.Formation of end colostomy |
|
|
|
Number of transverse rectal folds (of Houston) left and right |
Left : two Right : one |
|
|
|
The rectum lacks |
taenia coli haustra epiploic appendices |
|
|
|
Indication for Lower anterior resection |
Upper and mid rectal lesions |
|
|
|
Is the Sphincter mechanism presevered in Lower anterior resection |
Yes |
|
|
|
Qulaity of life in lower anterior resection |
Good |
|
|
|
Indication for abdominopelvic resection |
Lower rectal lesions |
|
|
|
Is the Sphincter mechanism preserved in Abdomino perineal resection (APR)? |
No |
|
|
|
Quality of life in abdominopelvic resection |
Bad |
|
|
|
Level of sigmoidoscopy is at 1.5 inches |
Rectal ampulla |
Inserted in the direction of the umbilicus |
|
|
Level of sigmoidoscopy at 6.5 inches |
Sigmoid colon |
|
|
|
Colorectal cancer screening |
Fecal occult blood testing Flexible Sigmoidoscopy Colonoscopy |
begin at age 50 |
|
|
Dilated inferior part of the rectum |
Rectal ampulla |
|
|
|
Length of the rectum |
5 inches |
|
|
|
Blood supply of the rectum |
Superior rectal artery Middle rectal artery Inferior rectal artery |
|
|
|
Origin of the superior rectal artery |
inferior mesenteric artery |
|
|
|
Origin of the middle rectal artery |
Internal iliac artery |
|
|
|
Origin of inferior rectal artery |
internal pudendal artery |
|
|
|
Venous drainage of rectum |
Superior rectal vein Middle rectal vein Inferior rectal vein |
|
|
|
Drainage and circulation of superior rectal vein |
Drainage: Inferior mesenteric vein
Circulation: Portal circulation |
|
|
|
Drainage and circulation of middle rectal vein |
Drainage: Internal iliac vein
Circulation: Systemic |
|
|
|
Drainage and circulation of inferior rectal vein |
Drainage: Internal pudendal vein
Circulation: Systemic |
|
|
|
Outer fibrous capsule of the testis |
Tunica albuginea |
|
|
|
Coiled tube about 6ft |
Epididymis |
|
|
|
Blood supply of the testis |
Testicular artery |
|
|
|
Venous drainage of the testis |
pampiniform plexus from testicular vein |
|
|
|
Expanded portion of the vas deferens |
Ampulla |
|
|
|
Lining epithelium of the vas deferens |
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium with sterocilia |
|
|
|
Joins the vas deferens to form the ejaculatory duct |
Seminal vesicle |
|
|
|
Lining epithelium of the seminal vesicle |
Simple or pseudostratified columnar epithelium |
|
|
|
Seminal fluid contains |
1. Prostaglandins 2. Ascorbic acid 3. Fructose 4. Amino acids |
|
|
|
Vas deferens + seminal vesicle |
Ejaculatory duct |
|
|
|
Lining epithelium of the ejaculatory duct |
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium |
|
|
|
Deep perineal pouch and opens into the penile urethra |
Bulbourethral (cowpers) gland |
|
|
|
Anatomical division of the prostate gland |
Anterior lobe
Median/middle lobe : central + transitional zones
Posterior lobe : peripheral zone
Lateral lobes (2)
|
|
|
|
Homologue of uterus and proximal vagina |
Prostatic utricle |
|
|
|
Openings of the prostatic ducts |
Prostatic sinus |
|
|
|
Blood supply of the prostate gland |
Inferior vesical artery Middle rectal artery |
|
|
|
Venous drainage of the prostate |
Prostatic venous plexus from internal iliac vein |
|
|
|
% of semen content ejaculated by the seminal vesicle |
60% |
|
|
|
% of semen content ejaculated by the prostate |
30% |
|
|
|
% of semen content ejaculated by vas deferens |
10% |
|
|
|
Life span of semen |
1-2 days |
|
|
|
Normal volume of semen |
3.5ml |
|
|
|
Normal number of sperm needed for fertility |
>20million sperm / ml |
|
|
|
Median lobe of the prostate enlarges hence obstructs the internal urethral orifice |
Benign prostatic hyperplasia |
|
|
|
Most common site for colon cancer?? Prostate? |
posterior lobe |
|
|
|
Hard and irregular mass on digital rectal exam and often asymptomatic |
Prostate cancer |
|
|
|
Lining epithelium and length of the prostatic urethra |
Transitional epithelium
1.25 inches |
|
|
|
Lining epithelium and length of the membranous urethra |
Stratified columnar and pseudostratified epithelium
.5 inches |
|
|
|
Lining epithelium and length of the penile (spongy) urethra |
Stratified columnar and pseudostratified epithelium
6 in |
|
|
|
Lining epithelium of the fossa navicularis |
Stratified squamous epithelium |
|
|
|
Widest and most dilatable male urethra |
Prostatic urethra |
|
|
|
least dilatable male urethra |
Intermediate urethra |
|
|
|
receive openings of the bulbourethral glands |
Bulbar(bulbous) urethera |
|
|
|
narrowest in male urethra |
External meatus |
|
|
|
Covered by germinal epithelium (of Waldeyer ); beneath is the tunica albuginea |
Ovary |
|
|
|
Inside the Suspensory (infundibulopelvic) ligament |
Ovarian vessels Ovarian nerve plexus Lymphatic vessels |
|
|
|
Remains of the upper part of the gubernaculum |
Round ligament of the ovary / ovarian ligament |
|
|
|
Blood supply of ovary |
Ovarian artery , ovarian branches of uterine artery |
|
|
|
Venous drainage of ovary |
Right ovarian vein Left ovarian vein |
|
|
|
Longest and widest segment Most common site of fertilization of the fallopian tube |
Ampulla |
|
|
|
narrowest part of the fallopian tube |
Interstirial part |
|
|
|
folic acid antagonist (against rapidly proliferating trophoblast) |
Methotrexate |
|
|
|
Mass less than 3.5 cm Embryo is dead Beta HCG < 15,000 mIU/mL |
Ectopic pregnancy |
|
|
|
Left unsutured intention to heal by secondary
Indications Less than 2 cm in length Located distal to the fallopian tube |
Salphingostomy |
|
|
|
Incision closed by delayed absorbable suture |
Salphingotomy |
|
|
|
Removal of the fallopian tube Cornual resection |
Salphingectomy |
|
|
|
Parts of the uterus |
Fundus Body Cervix Isthmus |
|
|
|
Between internal cervical os and endometrial cavity |
Isthmus |
Lower uterine segment in pregnancy |
|
|
Dark bluish or purplish red vagina and cervix
Increased vascularity
8 weeks |
Chadwick / Jacquimier sign |
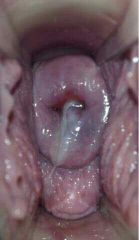
|
|
|
Softening of the isthmus
6 to 8 weeks |
Hegar sign |
|
|
|
Softening of the cervix 6 weeks |
Goodell sign |
|
|
|
Blood supply of the uterus and fallopian tube |
Uterine artery Ovarian artery |
|
|
|
Venous drainage of uterus and fallopian tube |
Uterine vein Ovarian vein |
|
|
|
Long axis of uterus and long axis of the cervix |
Flexion |
Position of the uterus |
|
|
Long axis of uterus and long axis of vagina |
Version |
Position of the uterus |
|
|
Most important ligament supporting uterus and vagina Transmits uterine vessels |
Cardinal ligament (of • Mackenrodt) |
Aka transverse cervical ligament |
|
|
Contents of broad ligament |
uterine tube
round ligaments of the ovary and uterus
uterine and the ovarian blood vessels, lymph vessels, and nerves. |
|
|
|
Ligation of uterine vessels |
Cardinal Ligament |
|
|
|
Ligation of ovarian vessels |
Ligament ??? |
|
|
|
Blood supply of the vagina |
Uterine artery (vaginal branch) Vaginal artery Internal pudendal artery |
|
|
|
hypogastric artery will turn into |
Internal iliac artery |
|
|
|
Posterior division of internal iliac artery |
Ilio Lumbar artery Lateral sacral artery Superior gluteal artery |
|
|
|
Anterior rami of L4-L5 Posterior rami of S1-S4
Lumbosacral trunk — L4 and L5 |
Sacral plexus |
|
|
|
L4-L5, S1-S3 Largest nerve |
Sciatic nerve |
|
|
|
Level of pudendal nerve |
S2-S4 |
|
|
|
Roof of perinium |
Pelvic diaphragm |
|
|
|
Floor of perinium |
skin and fasia |
|
|
|
Divisions of perinium |
Urogenital triangle Anal triangle |
|
|
|
Anal Sphincter that is involuntary and innervated by the autonomic nervous system |
Internal Anal Sphincter |
|
|
|
Sphincter that is voluntary and innervated by the pudendal nerve |
External anal sphincter |
|
|
|
Internal features of the anal traingle |
anal column anal valves anal sinus pectinate (dentate) line |
|
|
|
superior ends of the anal column on the anal canal |
Anorectal junction |
|
|
|
Junction of the upper and lower halves of the anal canal |
Pectinate line |
|
|
|
Epithelium above the pectinate line |
Simple columnar |
|
|
|
Epithelium below the pectinate line |
Stratified squamous |
|
|
|
Innervation above the pectinate line |
Visceral |
|
|
|
Innervation below the pectinate line |
Somatic (inferior rectal nerve) |
|
|
|
Blood supply above the pectinate line |
Superior rectal artery |
|
|
|
Blood supply below the pectinate line |
Inferior rectal artery |
|
|
|
Venous drainage above the pectinate line |
Superior rectal vein to the portal vein |
|
|
|
Venous drainage below the pectinate line |
Middle and Inferior rectal veins to the inferior vena cava |
|
|
|
Lymphatic drainage above the pectinate line |
inferior mesenteric nodes |
|
|
|
Lymphatic drainage below the pectinate line |
Superficial inguinal nodes |
|
|
|
Boundaries of the ischioanal (ischiorectal) fossa |
Medial — (anal canal) Lateral — obturator internus Superior — pelvic diaphragm Inferior — skin |
|
|
|
Contents of pudendal (Alcock’s ) canal |
Pudendal nerve pudendal vessels |
|
|
|
Location of pudendal nerve |
lies against the ischial spine |
|
|
|
Deep transverse perineal muscle Sphincter urethrae |
Urogenital diaphragm |
|
|
|
Boundaries of urogenital triangle |
Superior fascia and Inferior fascia = perineal membrane |
|
|
|
Deep transverse perineal muscles |
Deep perineal pouch |
|
|
|
Membranous urethra |
Deep perineal pouch |
|
|
|
Bulbourethral gland |
Deep perineal pouch |
|
|
|
Portion of the vagina |
Deep perineal pouch |
|
|
|
Internal pudendal vessels |
Deep perineal pouch |
|
|
|
Dorsal nerve of the penis/clitoris |
Deep perineal pouch |
|
|
|
Between the perineal membrane (inferior fascia) and superficial perineal ( fascia |
Superficial perineal pouch |
|
|
|
Bulb and crus of penis (male) |
Superficial perineal pouch |
|
|
|
Bulb of vestibule, crus of clitoris (female) |
Superficial perineal pouch |
|
|
|
Greater vestibular [Bartholin] gland (female) |
Superficial perineal pouch |
|
|
|
Ischiocavernosus |
Superficial perineal pouch |
|
|
|
Bulbocavernosus |
Superficial perineal pouch |
|
|
|
Superficial transverse perineal muscle |
Superficial perineal pouch |
|
|
|
Branches of internal pudendal vessels |
Superficial perineal pouch |
|
|
|
Perineal branches from pudendal nerve |
Superficial perineal pouch |
|
|
|
Correspond to the prostate in males |
Lesser vestibular (Skene) gland |
Aka paraurethral glands |
|
|
Inflammation located at 4 and 8 oclock positions of the female external genitalia |
Bartholin gland cyst/abcess |
|
|
|
Treatment for bartholin gland cyst or abcess |
For small cyst: sitz bath
For symptomatic cyst or abscess: Word catheter placement marsupialization |
|
|
|
Degree of laceration that involves the vaginal mucosa and skin |
1st degree laceration |
|
|
|
Degree of laceration that involves the fascia and muscles of the perineal body |
2nd degree laceration |
|
|
|
Degree of laceration that involves the External anal sphincter |
3rd degree |
|
|
|
Degree of laceration up to the rectal mucosa |
Fourth degree |
|
|
|
Restricted use of episiotomy |
Shoulder dystocia and breech delivery forceps or vacuum extractor deliveries occiput posterior positions instances in which failure to perform an episiotomy will result in perineal rupture |
|
|
|
Support, protection, and nutrition of the developing spermatogeniccells Blood-testis barrier |
Sustentacular(Sertoli) cells |
|
|
|
Secretions of sertoli cells |
Mullerian-inhibiting factor (MIF) Inhibin due to the absence of FSH Androgen-binding protein |
|
|
|
Cells that Contain testosterone in the testis |
Interstitial (Leydig) cells |
|
|
|
Mild indentation of the endometrium at the uterine fundus
Failure of resorption of the midline uterine septum
Least commonly associated with reproductive failure |
Arcuate uterus |
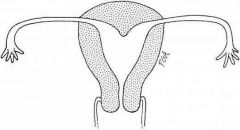
Most common type of abnormal uterus |
|
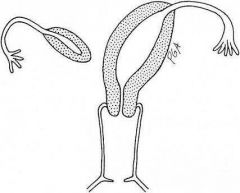
One of the paramesonephric ducts fails/incompletely develops
Associated with second trimester pregnancy loss, malpresentation preterm labor and delivery |
Unicornuate uterus |
|
|
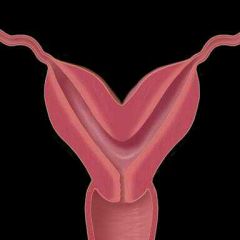
Partial failure of fusion of the mullerianducts
Cleft in the outer contour of the fundus
Associated with second-trimester pregnancy loss, malpresentation, and preterm labor and delivery |
Bicornuate uterus |
Treatment is surgical unification |
|
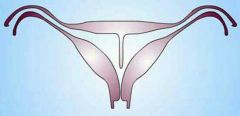
Normal external contour
Septum lacks adequate blood supply
Recurrent first trimester pregnancy loss |
Septate uterus |
Treatment is operative hyseteroscopy |
|
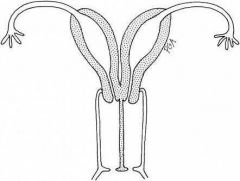
Complete failure of fusion of mullerian ducts
2 uterus 2 cervices
Pregnancy possible |
Uterine didephys |
|
|
|
Mayerduct Rokitansky Kuster Hauser syndrome
(-) uterus (-) cervix
Primary amenorrhea |
mullerian agenesis |
|
|
|
Once used to treat women with threatened abortion Inhibits mullerian differentiation |
Diethylstilbestrol (DES) |
|
|
|
Association with Diethylstilbestrol (DES) |
Clear cell carcinoma of the cervix
Clear cell carcinoma of the vagina
Cervical incompetence
Abnormally shaped uterus |
|
|
|
Most common cause is congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Genotype: 46XX
Phenotype: Masculinization of female external genitalia |
Female pseudohermaphrodism |
|
|
|
Most common cause is 5a reductase deficiency leading to a decrease in DHT
Genotype: 46XY
Phenotype: stunted development of male external genitalia |
Male pseudohermaphrodism |
|
|
|
MC cause is mutation in the androgen receptor (male pseudohermaphrodism )
Genotype: 46XY Phenotype
Normal appearing females Testis may be in the labia majora |
Complete androgen insensitivity syndrome |
|

