![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
97 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
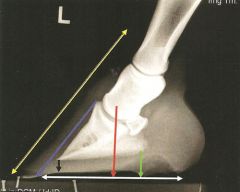
(look at pic..note that point of interest is at the proximal portion of the blue line) explain what clinical problem we might see here
|
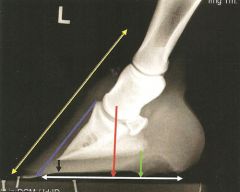
Pyramidal disease: a ringbone condition of the extensor (pyramidal) process of distal phalanx
|
|
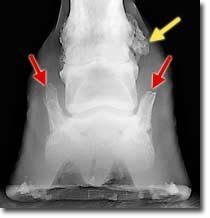
Tell me two clinical problems we see here..yellow arrow is? Red arrow is?
|
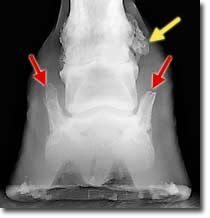
This horse has both high ringbone (yellow arrow) and sidebone (red arrows).
|
|
|
Describe Pyramidal disease
|
:it's a ringbone condition of the extensor (pyramidal) process of the distal phalanx
|
|
|
Tell me three more clinical problems seen with foot
|
-Navicular disease (invol nav bone)
-Sidebone(explain in next notecard) -Quittor (explained in next notecard) |
|
|
Sidebone:
|
-ossified & ridgid cartilages of dist phal (p3)
(attached to palmar process of the phalanx) |
|
|
tell me about the cartilage involved in ringbone
|
normally hyaline cartilages in young but fibrocartilaginous in adults
|
|
|
What is Quittor?
|
a suppurative & degenerative condition of the cartilages
(note suppurative means:to form pus) |
|
|
The hoof is_____?
|
Highly Keratinised
|
|
|
Does the HOOF contain blood vessels or nerves?
|
NO
|
|
|
What is the visible part of the hoof when the the horse is standing..
|
the WALL
|
|
|
What is the junction between the wall and the skin?
|
coronet
|
|
|
What part of the wall of the hoof touches the ground?
|
basal border
|
|
|
Three main topographical regions
(imagine looking at bottom of foot and use "clock face analogy".) |
-toe (11-1)
-quarters (1-5) & (7-11) -heels (5-6) & (6-7) |
|
|
Wall reflected at heels to form____?
|
Bars
|
|
|
wall reflected at heels to form bars, separated from the____by
the______ _______. |
separated from the FROG by the paracuneal grooves (aka Sulcus)
|
|
|
Wall is thickest where?
|
thickest at TOE
thins prgressively heel-ward |
|
|
lateral (OUTER) quarter has....
|
thicker wall than medial (inner) quarter
|
|
|
What is normal angle b/w dorsal surface & ground surface (for the forefoot and the hindfoot)?
|
45-50 degrees =forefoot
50-55 degrees=hindfoot |
|
|
Tell me about the Wall substance
|
-tubules extending proximo-distally & held together by amorphous intertubular horny material.
(note amorphous means:Lacking definite form; shapeless) |
|
|
Three layers of the wall are:
|
-Stratum externum
-Stratum medium -Stratum internum |
|
|
What is the very thin tubular horny covering (two parts)
|
Stratum externum
2 parts: prox part (periople) & the rest is the stratum tectorium |
|
|
so what are the 2 parts of Stratum Externum
|
periople
& Stratum tectorium |
|
|
prox part of Strat Extenum that is SOFT & non pigmented
|
periople
|
|
|
Periople expands where....
|
caudally over the bulbs of the heel.
(similar to the coronet area...fyi) |
|
|
the rest of the Strat Ext that is covering the wall, and is impervious to water, it's smooth and glossy...this is called....?
|
Stratum tectorium
|
|
|
Tell me about the PARALLEL & HORIZONTAL lines involved with the Stratum Tectorium...
|
Parallel: proximo-distal lines=evidence of direction of growth of horny tubules
Horiz:smooth ridges=evidence in variations in growth of hoof |
|
|
very thick
|
Stratum Medium
|
|
|
Where does Stratum Med begin?
|
-Coronary groove proxim
|
|
|
Stratum Med also bears openings that
|
accommodate Papillae of underlying dermis
|
|
|
Has tubules & intertubular horn..
|
Stratum Med
|
|
|
Stratum Med may be pigmented where?
|
outer layers
|
|
|
Non pigmented layer=
|
Stratum Internum
|
|
|
Stratum Internum begins where
|
at the medial part of the coronary groove proximally
|
|
|
like the Strat. Med the Strat. Internum also bears openings accommodating...
|
papillae of underlying dermis
|
|
|
What does the inner surface of Strat Internum carry?
|
Keratinized Primary & Non-keratinized secondary laminae
|
|
|
What do the keratinized primary & non-keratinized secondary laminae of the inner surface of the Strat Internum form?
|
Laminae of the bar...caudally
|
|
|
Condition of a crack in wall of hoof extending proximodistally =
|
sandcrack
|
|
|
Less serious condition, this is a split in the wall extending proximally from basal border
|
Grasscrack
|
|
|
the sole is normally ____ & ____
|
concave & flaky outer surface
|
|
|
Between walls & bars=
|
sole
|
|
|
Is the sole & frog the same composition as the wall?
|
Yes
|
|
|
Well what is it composed of?
|
vertical horn tubules & intertubular horn
|
|
|
Is wedge shaped
|
Frog
|
|
|
Frog is two_____separated by a central_____called_____?
|
2 crura (med/lat) separated by central groove called "sulcus of frog"
(*Remember* the inside of "V"=sulcus of frog.... the outside of "V"=paracuneal groove) |
|
|
two crura meet cranially to form the ____ of frog
|
Apex of frog
|
|
|
The "V" expands palmarly to join____
|
Bulbs (med/lat) of the heels
|
|
|
the frog has softer or harder horn?
|
softer
|
|
|
what is a degenerative condition of the frog?
|
THRUSH (especially when kept on moist or watery ground)
|
|
|
Internal surface of frog=
|
"frog stay"
|
|
|
The "Frog Stay" is bordered by ?
|
grooves which are themselves bound by the "Ridge of the frog"
(frog stay->groove-->ridge of the frog) |
|
|
Frog Stay =
|
Frog Spine
|
|
|
Frog Spine or Frog Stay is embedded where?
|
digital cushion
|
|
|
Frog is ______=softer than wall
|
incompletely keratinized
|
|
|
frog is ____% water content and SOLE is____%?
|
Frog=50%
Sole=33% |
|
|
The internal deep surfaces of the frog have........
|
holes that the papillae of the frog & sole of dermis fit into.
|
|
|
___ is highly vascular & sensitive.
|
The dermis
|
|
|
The dermis attaches.....
|
hoof wall to internal foot structures AND...
(except the laminar dermis) the dermis produces parts of the wall by means of papillae on their surfaces |
|
|
the dermis produces parts of the wall by means of papillae on their surfaces this does not include....
|
except the laminar dermis (so basically the dermis has "papillae of the coronary band" area...and papillae at the basal border area (called "papillae of the sole and frog"..but no papillae in laminar dermal area,
|
|
|
laminar dermis=
|
sensitive laminae
|
|
|
What nourishes wall?
|
Dermis does
|
|
|
Name 5 areas of Dermis
|
1.perioplic dermis
2. coronary dermis 3.laminar dermis 4. sole dermis (rem..sole around frog) 5.frog dermis |
|
|
What dermis is narrow, pale, at coronet below periople?
|
Perioplic dermis
|
|
|
The perioplic dermis broadens out and joins
|
bulbs of the heels
|
|
|
perioplic dermis blends with...
|
frog dermis
|
|
|
Perioplic dermis also have _____
|
Papillae
|
|
|
papillae present in perioplic dermis produce what?
|
produce horn of periople & stratum tectorium
|
|
|
What dermis is thick, and is in the coronary groove DISTAL to perioplic dermis?
|
Coronary dermis
|
|
|
Coronary dermis is _____ in dark hooves.
|
pigmented
|
|
|
Coronary dermis covers
|
-ext tendon &
-cartilages of distal phalanx (via sub Q tissue of the coronary cushion) |
|
|
Does coronary dermis have papillae?
|
yes
|
|
|
tell me about coronary dermis' papillae
|
-numerous
-about 5mm long -on surface -fit into holes in Strat Med & internum of the coronary groove |
|
|
What hole do the papillae of coronary dermis fit into?
|
hole is the Strat Med & Internum of the coronary groove
|
|
|
What produces most of the wall?
|
coronary dermis
|
|
|
the _______ of coronary dermis produces Strat Med of wall
|
Stratum germinativum
|
|
|
The Strat germinativum of coronary dermis produces Strat Med of wall. The cells of ______ produce the _____
|
cells of papillae produce the tubular horn
|
|
|
cells of papillae produce the tubular horn BUT the _____ produce intertubular horn.
|
inter-papillar cells
|
|
|
dermal papillae are directed ____ & ___
|
vertically & downward
|
|
|
the dorsal laminae have papillae where?
|
terminally or where they end
|
|
|
What lies deep in coronary cushion?
|
coronary venous plexus
|
|
|
The coronary venous plexus anastomoses with the _______ through_______.
|
with the palmar/plantar venous plex thru foramina in the cartilages.
|
|
|
What about valves?
|
need to listen to recording to see wht he said
|
|
|
600 primary laminae
|
laminar dermis
|
|
|
each bears several non-keratinized secondary laminae
|
primary laminae of laminar dermis
(so that means there is ALOT of secondary laminae) |
|
|
______are colorless and they interdigitate with laminae of walls & bars
|
Laminar dermis
|
|
|
deep part of laminar dermis blends with _____
|
periosteum of distal phalanx
|
|
|
numerous papillae on distal parts of dermal laminae
|
terminal papillae
|
|
|
what makes up white line
|
terminal papillae & (need to confirm what else)
-only part of the white line is produced by the terminal papillae |
|
|
In the Laminar Dermis the wall laminae are produced by __?
|
distal fringe of coronary papillae
|
|
|
The _____lies deep in the laminar dermis.
|
dorsal plexus
|
|
|
______ is NON sensitive, NON innervated, it's NOT ALIVE, it can't be inflammed.
|
EPIDERMIS*****
|
|
|
Do venous plexuses have valves?
|
NO
|
|
|
what drains venous plexus(s)?
|
Digital veins
|
|
|
Do digital veins have valves?
|
YES
|
|
|
what is the separation of the sensitive and insensitive laminae?
|
Laminitis
|
|
|
Dermis
|
sensitive
|
|
|
Epidermis
|
Insensitive
|
|
|
Laminit causes P3 to ....
|
drop downwards & push ouis
|

