![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What percentage of cells must be obscured (by blood, inflammation, etc.) in order to reject a pap-smear as "unsatisfactory"? |
-75%
If 50 to 75%, mention as quality indicator only |
|
|
What is minimal number of endocervical or metaplastic cells you should have in a pap-smear? |
-10 cells (singly or in group)
Quality indicator only, cannot label as unsatisfactory |
|
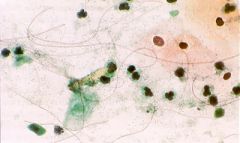
GYN-Pap: If you see these long filamentous stuff, what else should you look for? |
-Trichomonas vaginalis
(filamentous stuff = leptothrix)
Leptothrix are gram (-) organisms and ~80% of cases are associated with trichomonas |
|
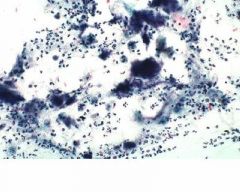
GYN-Pap: What are these findings associated with? |
-IUD use
(actinomyces or "dust bunnies") |
|
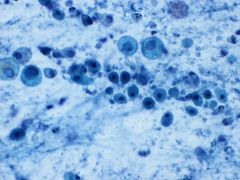
GYN-Pap: Diagnosis? |
-Atrophy |
|
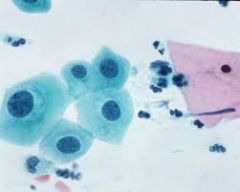
GYN-Pap: Diagnosis? |
-LSIL |
|
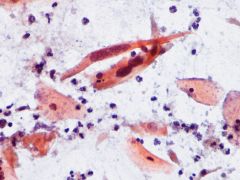
GYN-Pap: Diagnosis? |
-Squamous cell carcinoma
|
|
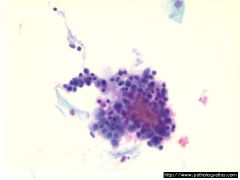
GYN-Pap: What organism is associated with this condition? |
-Chlamydia
(follicular cervicitis) |
|
|
How long should requisitions, slides and reports be retained for cytology? |
-Requisitions: 2 yrs -Slides: 5 years -Reports: 10 years |
|
|
What are the targets of E6 and E7 oncoproteins? |
-E6: p53 -E7: retinoblastoma protein |
|
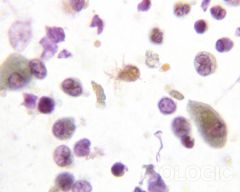
BAL: What is seen here? |
-Ciliocytophthoria
Detached tufts of cilia from bronchial epithelium; associated with viral infections (particularly adenovirus)
Do not confuse with parasite |
|
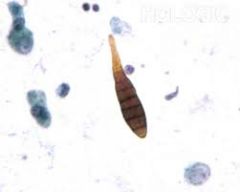
BAL: What is seen here? |
-Alternaria
The macroconidia of Alternaria spp has both longitudinal and septate hyphae.
A contamination. |
|
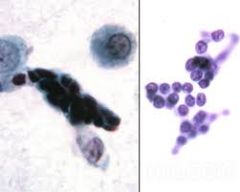
BAL: What's seen here? |
-Reserve cell hyperplasia or "Creola body"
Tight clusters or strips with minimal overlap No salt-pepper chromatin or micronucleoli
DDx: small cell carcinoma |
|
|
Locations of fungi? Cryptococcus Histoplasmosis Blastomycosis Coccidiodomycosis Paracoccidiodomycosis
|
-Cryptococcus: Everywhere -Histoplasmosis: Ohio and Missip River valleys (chickens and bats) -Blastomycosis: Same as histo (but in dogs) -Coccidiodomycosis: Desert regions (San Joiquin desert) -Paracoccidiodomycosis: Central and South America |
|
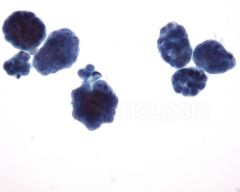
Middle aged woman with these "cannon-balls" in pleural effusion. Diagnosis? |
-Metastatic breast ductal carcinoma
3D cannon ball-like clusters in pleural effusion in women most likely a breast carcinoma met. |
|
|
What type of lung adenocarcinoma can look like PTC with nuclear grooves and inclusions? |
-Bronchioalveolar adenocarcinoma |
|
|
Female Asian Never smoker EGFR mutation* Adenocarcinoma
Are these good or poor prognostic features in NSCLC? |
-Good
Bad: male, caucasian, smoker, sqcc, Kras mutation
*Except in mucinous type of BAC |
|
|
Thymoma Lymphoma Germ cell tumor Thyroid lesions
Which part of mediastinum are these lesions seen? |
-Anterior
Middle: lymphoma, bronchogenic cysts, pericardial cysts
Posterior: neurogenic tumors, GIST, gastroenteric cysts |
|
|
What types of cells are seen in each of these pleuritis?
TB Rheumatoid Trauma/repeated taps SLE |
-TB: lymphocytes, NO mesothelial cells -Rheumatoid: MNGC, necrotic debris -Trauma/repeated taps: eosinophils -SLE: LE cells |
|
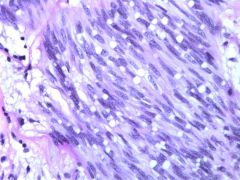
Stomach FNA Diagnosis? |
-GIST |
|
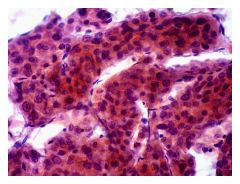
Liver FNA Diagnosis? |
-HCC
Endothelial wrapping Thickened plates Formation of acini Traversing capillaries = diagnostic of HCC |
|
|
What are the characteristics of pancreatic pseudocyst?
Low or high: Amylase Lipase CEA |
- High amylase & lipase - Low CEA
Also hypocellular, "junky" fluid with histiocytes, debris but NO epithelial cells |
|
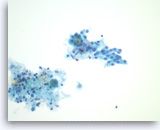
Pancreatic cyst FNA with flat PAS+ epithelial cells.
- Diagnosis? |
- Serous cystadenoma
Characteristic scar on radiology, F>M, tail & body Scant, bland epithelial cells Low amylase, lipase and CEA |
|
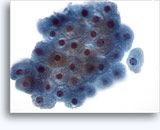
FNA from young woman, cystic lesion from tail of pancreas, with low amylase, lipase, CEA. |
- Solid pseudopapillary tumor
Cells are monomorphic with nuclear grooves; large branching papillary clusters with delicate capillaries |
|
|
What are the differential diagnosis when mucinous epithelium is seen in pancreatic cyst FNA? |
- MCN (low amylase/lipase, HIGH CEA) - IPMN (high amylase/lipase/CEA) - Cystic degeneration of ductal carcinoma - GI contamination |
|
|
Solid pseudopapillary vs NE tumor vs acinar cell carcinoma IHC:
-NE markers -CD10 -Cytokeratin -B-catenin -trypsin/chymotrypsin/lipase |
Add table |
|
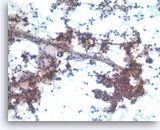
Kidney FNA
Diagnosis? |
- Oncocytoma
DDx: chromophobe RCC (more koilocytic looking with halos; more nuclear atypia) |
|
|
- Affects children & adolescents - Bilateral cervical lymphadenopathy (massive & painless) - Elevated ESR, leukocytosis, polyclonal gammaglobulinemia - Lymph nodes with sinus histiocytosis and emperipolesis
What are these features of? |
- Rosai Dorfman disease |
|
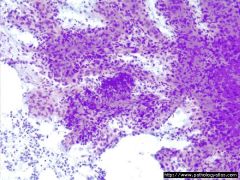
LN FNA Affects children Self-limited process
Diagnosis? |
- Supprative granulomatous lymphadenitis (Cat-scratch disease from Bartonella henselae) |
|
|
Affects Asian men Painless lymphadenopathy of head & neck Polymorphous lymphoid population Significant eosinophils Fragments of collagenous tissue Polykaryocytes
What disease? |
- Kimura disease |
|
|
Positive for: CD19, 20 CD5 CD43 FMC7 Cyclin D1 t(11;14) |
- Mantle cell lymphoma
Also negative for CD23 |
|
|
Positive for: CD19 |
- Follicular lymphoma
Mix of large centroblasts (# determines grading) and smaller centrocytes |
|
|
What is the translocation associated with Burkitt lymphoma? |
- t(8;14)
Also see, t(2;8) and t(8;22) |

