![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
95 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Functions of connective tissue?
|
-support
-exchange of nutrients, waste and metabolites - defence - storage |
|
|
Extracellular matrix of connective tissue composed of?
|
ground substance and fibers
|
|
|
Describe the ground substance of connective tissue.
|
- hydrated
- amourphus |
|
|
Connective tissue ground substance is composed of what?
|
-glycosaminoglycans
-proteoglycans -adhesive glycoproteins |
|
|
What makes up collagen?
|
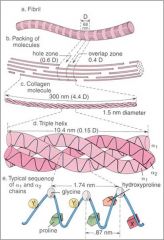
subunits of tropocollagen formed from 3 alpha helices.
|
|
|
describe collagens strength.
|
inflexable with tensile strength
|
|
|
How many types of collagen fibers are there?
How do they vary? |
- about 20
- The amino acid sequence in their alpha structure |
|
|
Where is type I collagen found?
how widespread is it? |
found in CT proper, bone, dentin, cementum
- It is the most widespread |
|
|
Where is type 2 collagen found?
|
Cartilage
|
|
|
Where is type III Collagen found?
|
reticular fibers
|
|
|
Where is type IV collagen found?
|
In basal lamina
|
|
|
What are elastic fibers composed of?
|
elastin and microfibrils
|
|
|
How much can elastic fibers be streched?
|
150%
|
|
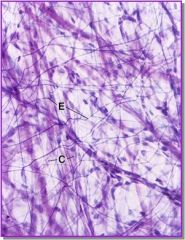
What is this?
|
Elastin
|
|
|
Describe reticular fibers.
|
Very slinder with type III collagen. Very delicate.
|
|
|
Where do you find reticular fibers?
|
around glands and lymphnodes etc...
|
|
|
What is the most abundant connective tissue cell type?
|
Fibroblasts
|
|
|
what are fibroblasts derived from?
|
mesenchyme
|
|
|
The extracellular matrix of connective tissue if formed by what cell?
|
fibroblasts
|
|
|
What is the shape of a fibroblast?
What part of the cell is usually seen in a slide? |
fusiform (spindle)
the nucleus |
|
|
describe fibroblast nuclei.
|
elongated with prominant nucleiolus.
|
|
|
what organelles are prominant in the fibroblast?
|
RER and golgi
|
|
|
describe older fibroblast cells (fibrocytes)
|
smaller with less protein machienary
|
|
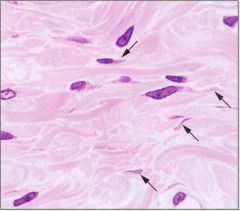
What is this picture showing?
|
fibrocytes
|
|
|
What are myofibroblasts?
|
intermediat between smooth muscle and fibroblasts
|
|
|
Why are myofibroblasts simular to muscle?
Why is it simular to fibroblasts? |
- because it possesses actin and myeosin
- because of its shape |
|
|
Where are myofibroblasts found?
|
- in wound healing and periodontal ligament
|
|
|
What property do myfibroblasts give the periodontal ligament?
|
- elasticity
|
|
|
Periocytes are derived from what?
|
- mesenchyme
|
|
|
Where are pericytes found?
|
partially surrounding the endothelial cells of capillaries and small venules
|
|
|
Pericytes are multipotential which means what?
|
they can develope into other cells
|
|
|
What surround pericytes?
|
a basal lamina - separates it from connective tissue.
|
|
|
pericytes are intermediates of what?
|
endothelial and smooth muscle
|
|
|
What do adipose cells develope from?
|
mesinchymal cells
|
|
|
Do adipose cells divide?
|
no they are post mitotic
|
|
|
What is an adipose cell function?
|
synthesis and storage of triglycerides
|
|
|
What are 2 types of adipose cells?
|
uniocular and multiocular
|
|
|
Describe uniocular adipose cells:
- cell filled with what? - cell shape - size - shape when packed together - location of cytoplasm and nucleus - golgi? - RER, mitochondria and free ribosomes |
- triglycerides
- round - 120 um - polyhedral - periphery - yes - not a lot of RER, or mitochondria. But lots of free ribosomes |
|
|
Descibe multiocular adipocytes.
- size - shape - nucleus - lipid distirbution - amount of RER and SER |
- smaller than unioccular
- polygonal - round and centrally located - small lipid droplets - no RER lots of SER |
|
|
Is unioccular white or brown fat?
|
White
|
|
|
Size of mast cells
|
20-30 um
|
|
|
mast cell shape and location of nucleus?
|
ovoid with central nucleus
|
|
|
mast cells derived from?
|
marrow
|
|
|
mast cell cytoplasm contains what?
|
basophilic granules: heprin, histomine and proteases
|
|
|
how are mast cells activated?
|
by binding of IgE to FC when a forgein antigen is detected.
|
|
|
how big are macrophages?
|
10-30 um
|
|
|
describe macrophage shape
|
irregular sometimes has filopodia
|
|
|
describe macrophage cytoplasm
|
basophilic with vacuoles and granules
|
|
|
describe macrophage nucleus
|
eccentric, heterchromatic and indented
|
|
|
What organelles are prodominant in macrophages?
|
RER, golgi, lysosomes
|
|
|
macrophages are part of what system?
|
the mononuclear phagocyte system (Mps)
|
|
|
macrophages arise from what?
|
marrow
|
|
|
What are macrophages before they mature?
What stimulates macrophages to mature? |
monocytes
macrophage colony stimulating factor (M-CSF) |
|
|
macrophages are called what in the liver?
|
kupffer cells
|
|
|
macrophages are called what in the lungs (2)?
|
dust cells or alveolar cells
|
|
|
macrophages are called what in the skin?
|
Langerhans
|
|
|
macrophages are called what in the blood?
|
monocytes
|
|
|
macrophages are called what in the connective tissue?
|
macrophages
|
|
|
What are other types of MPS cells besides macrophages?
|
osteoclasts and microglial cells
|
|
|
When macrophages fuse they are called what?
|
forgein-body giant cells
|
|
|
What is the role of macrophages?
|
to phagocytise dead/old/damaged cells, clean up cellular debris and eat bacteria.
THEY ARE ANTIGEN PRESENTING CELLS! |
|
|
What are plasma cells?
|
activated B-lymphocytes
|
|
|
What do plasma cells do?
|
produce antibodies
|
|
|
Describe plasma cell shape and nucleus.
|
ovoid with eccentrically placed nuclei. Nucleus is clock face
|
|
|
describe cytoplasm of plasma cells
|
intensily basophilic with lots of RER
|
|
|
What are the 5 types of leukocytes?
|
basophils
neutrophils eosinophils lymphocytes monocytes |
|
|
What is the role of a neutrophil?
|
- to phagocytise bacteria
|
|
|
What is the role of a eosinophil?
|
involved with allergic reactions and paracytes
|
|
|
what is the role of basophils?
How are basophils related to mast cells? |
they are involved in inflamatory responses
Very simular if not the same. |
|
|
What is the role of lymphocytes.
|
Found in sites of chronic inflamation
|
|
|
What is the embrionic connective tissue?
|
mesenchyme
|
|
|
What is mesenchyme composed of?
|
mesenchymal cells and a gel ground substance with reticular fibers
|
|
|
describe mesenchymal cells
- nucleus shape - nucleolus - cytoplasm - mitosis frequency |
- ovoid
- promanent - sparse and light staining - frequent mitosis |
|
|
Where can you find mesenchymal cells in the adult?
|
in the tooth pulp
|
|
|
What cells arise from mesenchymal cells?
|
- osteoblasts
- chondrocytes - fibroblasts - endothelial - mesothelial |
|
|
What is another type of embrionic connective tissue?
|
musus connective tissue
|
|
|
Mucus connective tissue also called what and is found where?
|
Wharton's jelly; found in umbillica cord
|
|
|
Loose connective tissue is found where?
|
-dermis
-mesothelium -adventitia of blood vessels -stroma of glands -lamina propria of digestive -respiratory tracts |
|
|
Loose connective tissue is composed of what types of fibers?
|
Collagen
Reticular Elastic |
|
|
What cells are present in Loose connective tissue?
|
Macrophages
mast cells adipocytes undifferentiated cells |
|
|
Loose connective tissue is primarly what?
|
ground substance and tissue fluid
|
|
|
Loose connective tissue is also called what?
|
areoloar
|
|
|
Dense connective tissue composed of (relative to loose CT)
|
more fibers and less ground substance.
|
|
|
What is the arrangement of dense irregular connective tissue?
|
fibers have multiple orintations
|
|
|
What is the purpose of dense irregular connective tissue?
|
serves to resist stress in all directions
|
|
|
dense irregular connective tissue found where?
|
found in dermis of skin, sheaths of nerves, capsule of spleen, testes, ovaries, kidneys, and lymph nodes
|
|
|
What is the structure of dense regular collagenous tissue?
|
parallel collagen fibers
|
|
|
What is the role of dense regular collagenous tissue?
|
to give tensile strength
|
|
|
Where is dense regular collagenous tissue found?
|
tendons, ligaments, aponeurosis
|
|
|
What is the structure of dense regular elastic tissue?
|
mostly elastic fibers with little collagen
|
|
|
Where is dense regular elastic connective tissue found?
|
found in blood vessels, ligamentum flavum (of vertebral column), suspensory ligament of penis
|
|
|
What is the structure of reticualr connective tissue?
|
a meshwork of type III collagen fibers
|
|
|
What is the role of reticular connective tissue?
|
supports paraychema of:
-liver sinusoids -adipose tissue -bone marrow -lymph nodes and spleen -smooth muscle -islets of Langerhans |
|
|
adipose tissue made of what?
|
adipocytes with connective tissue etc...
|
|
|
What are some specialized connective tissues?
|
blood
lymph bone cartilage |

