![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
115 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Amoeba reproduce by |
binary fission |
|
|
Transmission of amoeba is generally by |
ingestion of the cyst phase in contaminated water |
|
|
Stain to visualize and identify amoeba |
trichrome |
|
|
cause of amoebic dysentery |
Entamoeba histolytica |
|
|
a rod shaped structure of condensed RNA inside the cytoplasm of some amoeba cysts |
chromatoid body (or bar) |
|
|
Amoeba's non-motile, usually infective stage, non-feeding. it's wall protects the organism from drying |
cyst |
|
|
a disorder marked by bloody diarrhea and/ or mucus in the feces |
dysentery |
|
|
the small mass of chromatin within the nucleus, comparable with the nucleolus |
endosome or karyosome |
|
|
a cytoplasmic extension that allows the amoeba trophozoite to move and engulf food |
pseudopod |
|
|
the motile, reproducing, feeding stage of the amoeba. generally lives in the lower GI tract |
trophozoite |
|
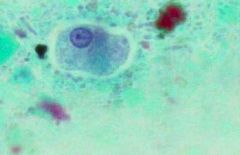
|
Entamoeba histolytica troph |
|
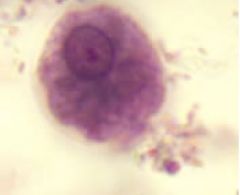
|
Entamoeba histolytica trophozoite |
|
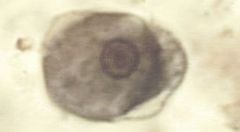
|
Entamoeba histolytica trophozoite |
|
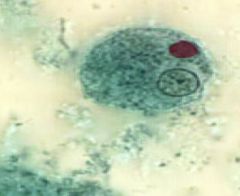
|
Entamoeba histolytica trophozoite |
|

|
Entamoeba histolytica trophozoite |
|
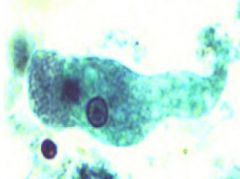
|
Entamoeba histolytica trophozoite |
|
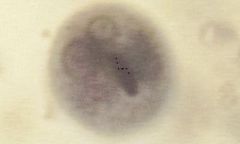
|
Entamoeba histolytica cyst |
|
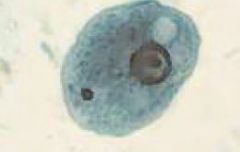
|
Entamoeba coli trophozoite |
|
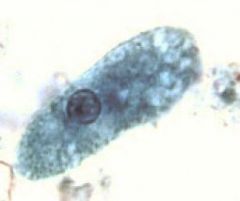
|
Entamoeba coli trophozoite |
|
|
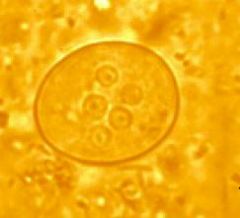
Entamoeba coli cyst |
|
|
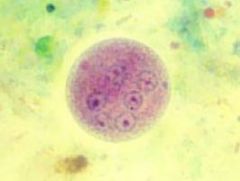
Entamoeba coli cyst |
|
|
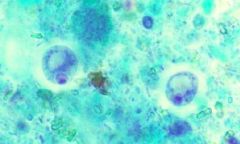
Iodamoeba butschlii |
|

|
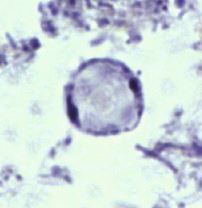
Blastocystis hominis |
|
|
Blastocystis hominis |
|
|
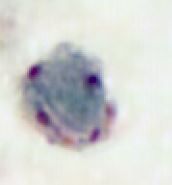
Blastocystis hominis |
|
|
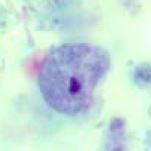
Endolimax nana trophozoite |
|
|
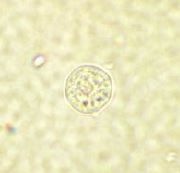
Endolimax nana cyst |
|
|
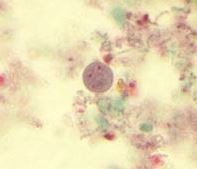
Endolimax nana cyst |
|
|
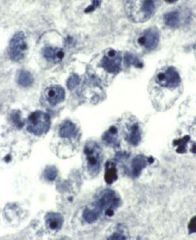
Naegleria fowleri |
|
|
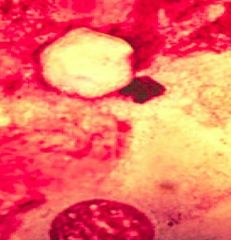
Acanthamoeba in GAE |
|
|
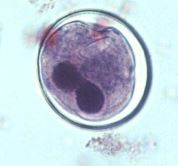
Balantidium coli cyst |
|
|
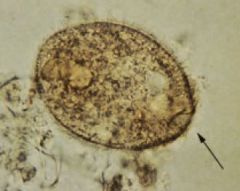
Balantidium coli trophozoite |
|
|
can be sexually transmitted |
E. histolytica |
|
|
a commensal |
E. dispar |
|
|
unless trophozoites are seen with ingested RBCs _____ and _______ are identical |
E. histolytica and E. dispar |
|
|
invades the intestinal wall and multiplies in the mucosal tissue |
E. histolytica |
|
|
trophozoites can invade the intestinal wall and cause ulceration of other tissues after spreading through the blood stream |
E histolytica, E. dispar |
|
|
similar to E. histolytica but small |
E. hartmani |
|
|
anaerobic parasite; doesn't seem to cause disease- but must be considered if seen in large numbers |
Blastocystis hominis |
|
|
humans become infected after swimming in infected ponds and lakes |
Naegleria fowleri |
|
|
amoeba more motile at 35 C, warming media will increase motility |
N. fowleri |
|
|
disease is rapid and fatal within a week |
Primary Amoebic Microencephalitis- Naegleria fowleri |
|
|
enters through nasal passages, travels along olfactory nerves to the brain |
Naegleria fowleri |
|
|
lesions in brain tissue may contain cysts and trophs |
granulomatous amebic encephalitis |
|
|
infection caused by inhalation of dust and aerosols |
GAE |
|
|
cause of GAE |
Acanthamoeba spp. |
|
|
traced to using contaminated saline cleaning solutions with contact lenses, or swimming in contaminated water while wearing contacts |
Acanthamoeba keratitis |
|
|
Largest parasitic protozoan |
Balantidium coli |
|
|
Has a well developed oral cytostome (rudimentary mouth) |
Balantidium coli |
|
|
Multiply asexually and by conjugation with exchange of micronuclei |
Balantidium coli |
|
|
Invades tissues producing lesions along the intestinal submucosa |
Balantidium coli |
|
|
Intracellular portion of the flagella |
axoneme |
|
|
The axial rod that supports the flagella |
axostyle |
|
|
A thin firm rod like structure that supports the undulating membrane |
costa |
|
|
A membrane with a flagellar rim that extends out from the body of the flagellate. |
undulating membrane |
|
|
which flagellate has no cyst |
Trichomonas hominis |
|
|
needed to diagnose Giardia lamblia |
trophs or cysts in the feces |
|
|
falling leaf motility |
Giardia lamblia |
|
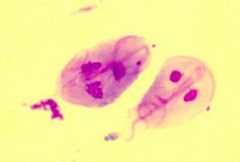
|
Giardia lamblia |
|
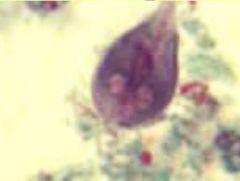
|
Giardia lamblia |
|
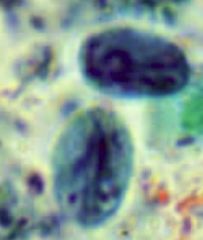
|
Giardia lamblia cyst |
|
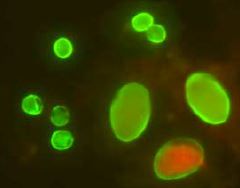
|
Giardia lamblia cyst |
|
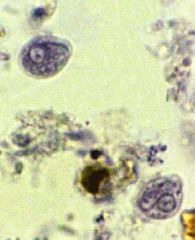
|
Chilomastix mesnili |
|
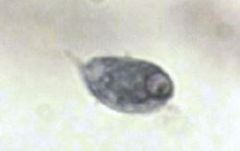
|
Chilomastix mesnili |
|
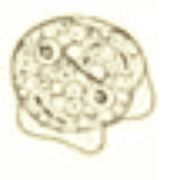
|
Dientamoeba fragilis |
|
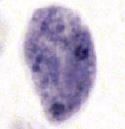
|
Dientamoeba fragilis |
|
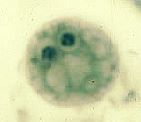
|
Dientamoeba fragilis |
|
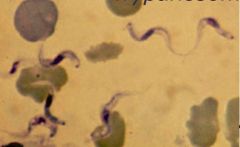
|
Trypanosoma brucei |
|
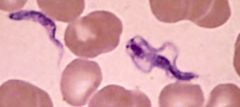
|
Trypanosoma brucei |
|
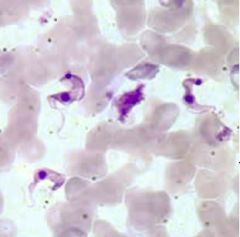
|
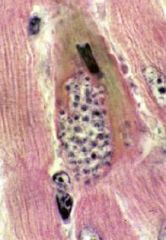
Trypanosoma cruzi |
|
|
Trypanosoma cruzi |
|
|
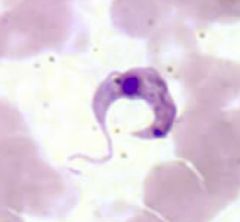
Trypanosoma cruzi |
|
|
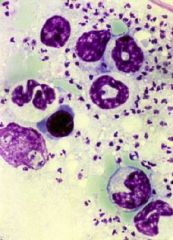
leishmania. amastigote in macrophages are diagnostic |
|
|
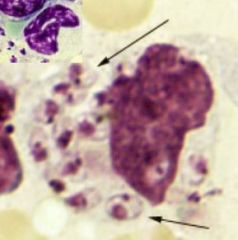
leishmania. amastigote in macrophages are diagnostic |
|
|
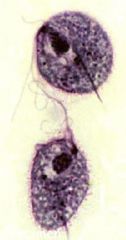
Trichomonas vaginalis |
|
|
Trypanosome diagnostic stage |
trypomastigote |
|
|
trypanosome intermediate host |
arthropod |
|
|
arthropod vector of Trypanosoma brucei/ gambiense and Trypanosoma brucei rhodiense |
Tsetse fly |
|
|
Trypanosoma brucei/ gambiense and Trypanosoma brucei rhodiense cause the disease |
West and East Africa Sleeping Sickness |
|
|
central nervous system involvement in disease is faster with which? Trypanosoma brucei/ gambiense or Trypanosoma brucei rhodiense |
T. brucei rhodiense |
|
|
Trypanosoma cruzi Trypomastigote |
tend to be C or S shaped |
|
|
Trypanosoma cruzi: trypanomastigotes are found in |
heart, muscle, liver, or CNS in macrophages |
|
|
arthropod intermediate host of Trypanosoma cruzi |
reduviid bug |
|
|
trypanomastigotes of T.cruzi are deposited __________ after it takes a blood meal |
in the feces from the bug |
|
|
T. cruzi is found in which geographical locations |
Found primarily in Mexico, Central America and South America, cases have been reported in Texas and California |
|
|
how can T. cruzi be transmitted |
trans placentally |
|
|
method to identify T. cruzi |
xenodiagnosis |
|
|
T. cruzi causes |
Chagas disease, Romana;s sign- swollen eye |
|
|
Kissing Bug |
Chagas Disease. Trypanosoma cruzi |
|
|
New World Leishmaniasis |
Leishmania brasiliensis |
|
|
Old World Leishmaniasis, Oriental, Baghdad and Delhi Boil |
Leishmania tropica |
|
|
diagnostic stage of Leishmania |
amastigote in macrophages aspirated from lesion site |
|
|
Leishmania intermediate host |
sandfly |
|
|
zoonotic infection |
leishmania |
|
|
diseases of Leishmania donovani |
Visceral Leishmaniasis, Kala-azar, Dumdum fever |
|
|
how soon will you die from Leishmania donovani if not treated? |
2 years |
|
|
Leishmania donovani infects |
macrophages throughout organs throughout the body |
|
|
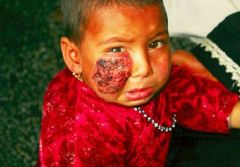
cutaneous Leishmaniasis |
|
|
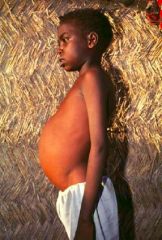
Visceral Leishmaniasis |
|
|
how is Trichomonas vaginalis identified? |
motile trophs must be identified in fresh urethral discharge or urine sample. can also be identified on PAP smear |
|
|
Trichomonas vaginalis motility is described as |
jerky or rippling |
|
|
Trichomonas vaginalis symptoms in men are |
non-symptomatic |
|
|
Thrichomonas vaginalis cyst |
has none |
|
|
Intestinal amoeba |
Entamoeba histolytica, Entamoeba dispar, Entamoeba hartmani, Entamoeba coli, Endolimax nana, Iodamoeba buschlii, Blastocystis hominis |
|
|
Intestinal flagellate |
Giardia lamblia, Chilomastix mesnili, Dientamoeba fragilis, Balantidium coli |
|
|
Intestinal sporozoan |
Cryptosporidium parvum, Isopora belli, Sarcocystis sp., Cyclospora cayatenensis, Microsporidia |
|
|
Blood flagellate |
Trypanosoma cruzi, Trypanosoma brucei |
|
|
Blood sporozoan |
Plasmodium vivax, Plasmodium ovale, Plasmodium malariae, Plasmodium falciparum, Babesia microti |
|
|
Urinary/ Vaginal flagellate |
Trichomonas vaginalis |
|
|
cutaneous flagellate |
Leishmania (tropica and mexicana complex) |
|
|
mucocutaneous flagellate |
Leishmania brazilliensis complex |
|
|
Internal organs flagellate |
Leishmania donovani complex |
|
|
Internal organ sporozoan |
Toxoplasma gondii |
|
|
Lungs sporozoans |
Pneumocystis carnii (fungus) |
|
|
Free living/ Central Nervous amoeba |
Naegleria fowleri, Acanthamoeba |

